
Which of the following are called food factories of the plants?
(a) Leaves
(b) Stem
(c) Roots
(d) Flowers
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The part of the plant that manufactures food for the plant by the process of photosynthesis. They have a large surface that enables them to be spread over a larger area thus increasing the area where the light falls.
Complete answer:
Leaves are the specialized structures for food production and hence, called food factories of the plants. Leaves are flat green structures which have a large surface area. The large surface area of leaves also provides a larger area for stomata to be spread all over the leaf. The amount of sunlight falling on the leaf is an important factor for many physiological processes of the plant, these include transpiration, photosynthesis, and respiration.
Additional information:
-Stomata is responsible for the exchange of gases in a plant and water loss due to transpiration.
-The leaves get their green color from a photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll.
-Plant cells have chloroplasts, these contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis.
-The interior part of the leaf between the upper and lower layers of epidermis is a parenchyma or chlorenchyma tissue called the mesophyll.
-The outer layer of the cells is covered with a waxy cuticle which is impermeable to liquid water.
-The cuticle performs several functions like protection against water loss by transpiration, regulation of gas exchange, and secretion of metabolic compounds.
So, the correct answer is ‘Leaves’.
Note:
-Most of the gymnosperms have thin needle-like or scale-like leaves that are advantageous in cold climates with frequent snow and frost.
-In C4 plants, Kranz leaf anatomy facilitates carbon fixation in plants.
-The presence of hairs on the leaf surface traps humidity in dry climates and creates a boundary layer reducing water loss.
Complete answer:
Leaves are the specialized structures for food production and hence, called food factories of the plants. Leaves are flat green structures which have a large surface area. The large surface area of leaves also provides a larger area for stomata to be spread all over the leaf. The amount of sunlight falling on the leaf is an important factor for many physiological processes of the plant, these include transpiration, photosynthesis, and respiration.
Additional information:
-Stomata is responsible for the exchange of gases in a plant and water loss due to transpiration.
-The leaves get their green color from a photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll.
-Plant cells have chloroplasts, these contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis.
-The interior part of the leaf between the upper and lower layers of epidermis is a parenchyma or chlorenchyma tissue called the mesophyll.
-The outer layer of the cells is covered with a waxy cuticle which is impermeable to liquid water.
-The cuticle performs several functions like protection against water loss by transpiration, regulation of gas exchange, and secretion of metabolic compounds.
So, the correct answer is ‘Leaves’.
Note:
-Most of the gymnosperms have thin needle-like or scale-like leaves that are advantageous in cold climates with frequent snow and frost.
-In C4 plants, Kranz leaf anatomy facilitates carbon fixation in plants.
-The presence of hairs on the leaf surface traps humidity in dry climates and creates a boundary layer reducing water loss.

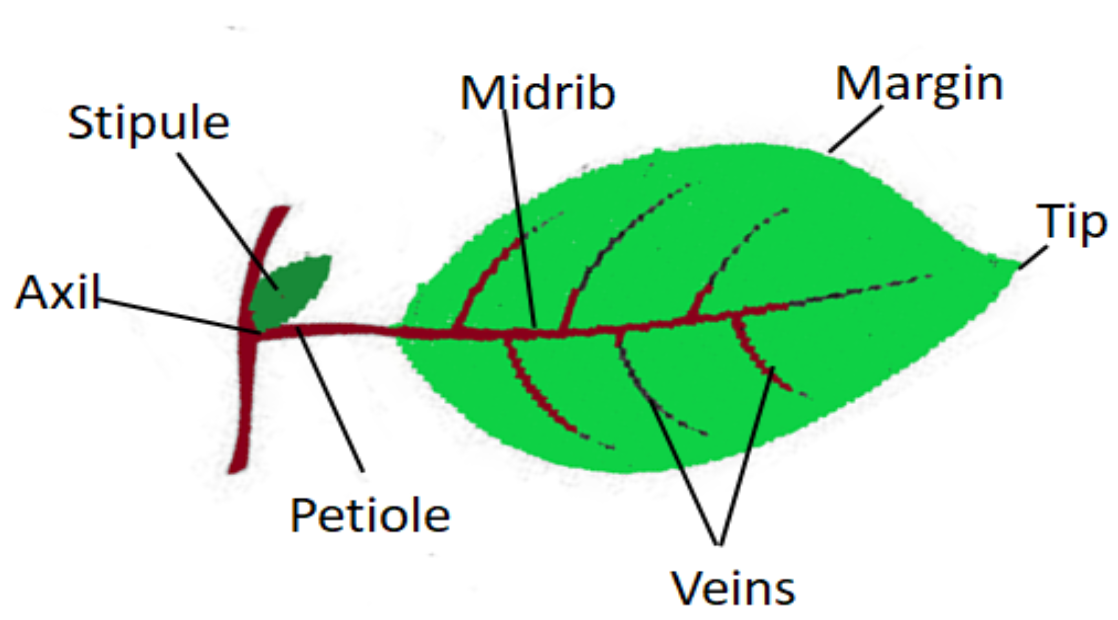
Figure: Structure of leave
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




