
Which of the following acids has the highest $p{K_a}$ value?
A. $C{H_3}CHFCOOH$
B. $FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$
C. $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$
D. $C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The $p{K_a}$ value is the method that is used to determine the strength of an acid. The lower value of $p{K_a}$ for an acid indicates stronger acid and the higher value indicates the weaker acid. It is the negative logarithm of ${K_a}$ or acid dissociation constant. As we know that ${K_a}$ or acid dissociation constant also indicates the strength of an acid. A higher value of ${K_a}$ indicates a stronger acid and a lower value indicates weaker acid. So we can say that a strong acid has a higher ${K_a}$ or acid dissociation constant value and lower $p{K_a}$ value and vice-versa.
Some points to remember:
1.Higher the electronegativity halogen present in the acid molecule, the stronger is the acid and vice-versa.
2.The acidic strength of the acid decreases with an increase in distance of the halogen atom from –COOH group.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we will discuss the given options one by one.
First option is $C{H_3}CHFCOOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 2-Fluoropropanoic acid and the structure of this acid is
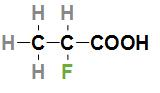
In the above structure, we can see that the fluorine atom is attached to the second carbon which is nearer to –COOH group. As we know fluorine is the most electronegative halogen atom and is attached nearer to the –COOH group so the given acid will have higher ${K_a}$ and lower $p{K_a}$ value.
Second option is $FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 3- Fluoropropanoic acid and the structure of this acid is
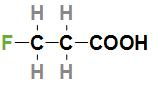
In the above structure, we can see that the fluorine atom is attached to the third carbon which is far from the –COOH group. As we know that fluorine is the most electronegative halogen atom and is attached far from the –COOH group so the given acid will have a $p{K_a}$ value which is more than 2- Fluoropropanoic acid but less than other the two acids which contain bromine.
Third option is $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 3- Bromopropanoic acid and the structure of the acid is
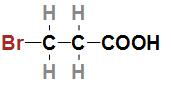
In the given structure we can see that the bromine atom which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached to the third carbon which is far from the –COOH group. As we know that bromine which is less electronegative than fluorine and is attached far from the –COOH group so the given acid will have a lower ${K_a}$ value and higher $p{K_a}$ value.
Fourth option is $C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 2- Bromopropanoic acid and the structure of the acid is
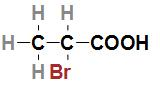
In the given structure we can see that the bromine atom which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached to the second carbon which is nearer to the –COOH group. As we know that bromine which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached nearer to the –COOH group so the given acid will have a $p{K_a}$ value which is lower than 3- Bromopropanoic acid and greater than 2- Fluoropropanoic acid and 3- Fluoropropanoic acid.
The order of the $p{K_a}$ values of the given acids are: $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ $ > $ $C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$ $ > $ $FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ $ > $ $C{H_3}CHFCOOH$
Therefore, $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ has a higher $p{K_a}$ value.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note: -COOH is an organic functional group which is known as Carboxylic acid. The name carboxyl is derived from carbonyl and hydroxyl, i.e. carb $ + $ oxyl as the two groups are directly linked to each other. It does not show the properties of the carbonyl group. It has its distinguishable properties and the acidic character is due to the presence of the replaceable hydrogen atom.
Some points to remember:
1.Higher the electronegativity halogen present in the acid molecule, the stronger is the acid and vice-versa.
2.The acidic strength of the acid decreases with an increase in distance of the halogen atom from –COOH group.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we will discuss the given options one by one.
First option is $C{H_3}CHFCOOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 2-Fluoropropanoic acid and the structure of this acid is
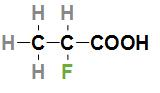
In the above structure, we can see that the fluorine atom is attached to the second carbon which is nearer to –COOH group. As we know fluorine is the most electronegative halogen atom and is attached nearer to the –COOH group so the given acid will have higher ${K_a}$ and lower $p{K_a}$ value.
Second option is $FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 3- Fluoropropanoic acid and the structure of this acid is
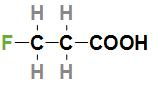
In the above structure, we can see that the fluorine atom is attached to the third carbon which is far from the –COOH group. As we know that fluorine is the most electronegative halogen atom and is attached far from the –COOH group so the given acid will have a $p{K_a}$ value which is more than 2- Fluoropropanoic acid but less than other the two acids which contain bromine.
Third option is $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 3- Bromopropanoic acid and the structure of the acid is
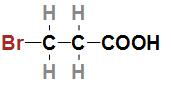
In the given structure we can see that the bromine atom which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached to the third carbon which is far from the –COOH group. As we know that bromine which is less electronegative than fluorine and is attached far from the –COOH group so the given acid will have a lower ${K_a}$ value and higher $p{K_a}$ value.
Fourth option is $C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$. The IUPAC name of the acid is 2- Bromopropanoic acid and the structure of the acid is
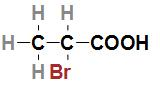
In the given structure we can see that the bromine atom which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached to the second carbon which is nearer to the –COOH group. As we know that bromine which is less electronegative than fluorine is attached nearer to the –COOH group so the given acid will have a $p{K_a}$ value which is lower than 3- Bromopropanoic acid and greater than 2- Fluoropropanoic acid and 3- Fluoropropanoic acid.
The order of the $p{K_a}$ values of the given acids are: $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ $ > $ $C{H_3}CHBrCOOH$ $ > $ $FC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ $ > $ $C{H_3}CHFCOOH$
Therefore, $BrC{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$ has a higher $p{K_a}$ value.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note: -COOH is an organic functional group which is known as Carboxylic acid. The name carboxyl is derived from carbonyl and hydroxyl, i.e. carb $ + $ oxyl as the two groups are directly linked to each other. It does not show the properties of the carbonyl group. It has its distinguishable properties and the acidic character is due to the presence of the replaceable hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




