
Which of the following 3d orbitals has electron density in all three axes?
A. $3{d_{xy}}$
B. $3{d_{yz}}$
C. $3{d_{{z^2}}}$
D. $3{d_{zx}}$
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Electron density or electronic density is the measure of the probability of an electron present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any given point. Moreover, to solve this question we need to know the shapes of the d orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron density is a scalar quantity that depends on three spatial variables. It is basically the measure of the probability of an electron being present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any point. In case of molecules, regions of large density are usually found around the atom and its bonds. Further, in case of delocalized or conjugated systems such as phenol, benzene and other compounds such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll, the electron density is significant in an entire region i.e. in case of benzene, they are found above and below planar ring.
Now, let’s discuss the d-orbitals. There are five d-orbitals ${d_{xy,}}{d_{yz,}}{d_{zx}},{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}},{d_{{z^2}}}$. As we can see that ${d_{{z^2}}}$ orbital has one lobe and along z axis and donut shaped electron cloud is perpendicular to it in xy plane while all other d-orbitals have two dumbbells either along the axis ${d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$ or in between the axis i.e. ${d_{xy,}}{d_{yz,}}{d_{zx}}$.
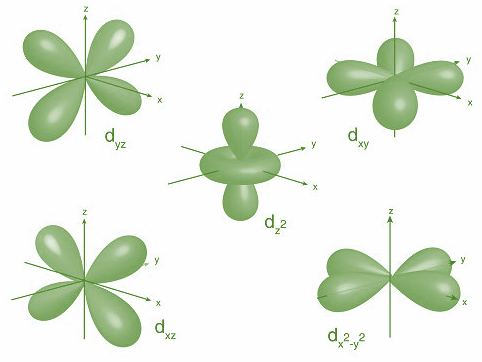
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Spin density is the electron density applied to free radicals. It refers to the total electron density of electrons of one spin minus the total electron density of the electrons of the other spin. Another way to measure it experimentally is by electron spin resonance.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron density is a scalar quantity that depends on three spatial variables. It is basically the measure of the probability of an electron being present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any point. In case of molecules, regions of large density are usually found around the atom and its bonds. Further, in case of delocalized or conjugated systems such as phenol, benzene and other compounds such as hemoglobin and chlorophyll, the electron density is significant in an entire region i.e. in case of benzene, they are found above and below planar ring.
Now, let’s discuss the d-orbitals. There are five d-orbitals ${d_{xy,}}{d_{yz,}}{d_{zx}},{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}},{d_{{z^2}}}$. As we can see that ${d_{{z^2}}}$ orbital has one lobe and along z axis and donut shaped electron cloud is perpendicular to it in xy plane while all other d-orbitals have two dumbbells either along the axis ${d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$ or in between the axis i.e. ${d_{xy,}}{d_{yz,}}{d_{zx}}$.

Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Spin density is the electron density applied to free radicals. It refers to the total electron density of electrons of one spin minus the total electron density of the electrons of the other spin. Another way to measure it experimentally is by electron spin resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




