
Which of the compounds will give \[{S_n}1\] reaction?
a.
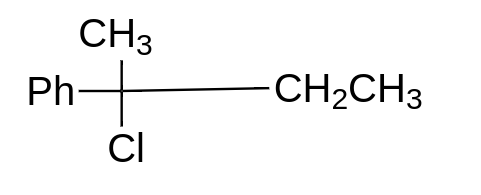
b.$C{H_3} - Cl$
c.$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Br$
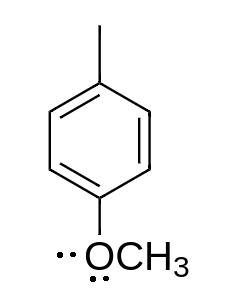
d.


Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Basically there are two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions, that is, ${S_n}1$ and ${S_n}2$ reaction. Here we are asked about the ${S_n}1$ reaction, so this reaction is a unimolecular reaction and the rate of this reaction is dependent on the concentration of only one reactant.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which a nucleophile which is electron-rich, attacks electrophile which is positively charged, in order to replace the leaving group. There are two types of nucleophilic reactions, that is, ${S_n}1$ and ${S_n}2$ reactions. So, ${S_n}1$ reaction is known as a unimolecular reaction, so its rate is dependent upon the concentration of only one reactant. This is a two-step reaction. Whereas ${S_n}2$ reaction is a one-step process and is bi-molecular, so its rate is dependent upon both the concentration present in the reaction.
In ${S_n}1$ reaction, tertiary carbocations are considered to be most stable, therefore tertiary carbocations are most reactive towards ${S_n}1$ reaction as compared to primary and secondary. As more is the stability of carbocation, more is the reactivity.
So, as per the stability of the carbocation,
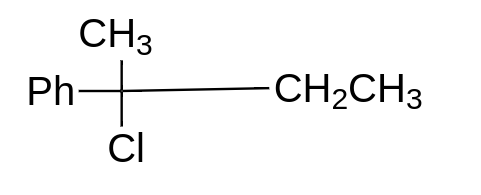
option (A) will give ${S_n}1$ reaction, because here, the formation of stable tertiary carbocation will take place, so this will give us ${S_n}1$ reaction. This molecule will always go for ${S_n}1$ reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is option (A).
Note :
Since, we know that ${S_n}1$ is a unimolecular reaction, so its rate will be dependent upon halo alkenes only not on nucleophiles. There are several other factors on which ${S_n}1$ reaction depends, such as polar protic solvent is required here in this, the better-leaving group should be there, that increases the rate of the reaction, weak nucleophiles are preferred.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which a nucleophile which is electron-rich, attacks electrophile which is positively charged, in order to replace the leaving group. There are two types of nucleophilic reactions, that is, ${S_n}1$ and ${S_n}2$ reactions. So, ${S_n}1$ reaction is known as a unimolecular reaction, so its rate is dependent upon the concentration of only one reactant. This is a two-step reaction. Whereas ${S_n}2$ reaction is a one-step process and is bi-molecular, so its rate is dependent upon both the concentration present in the reaction.
In ${S_n}1$ reaction, tertiary carbocations are considered to be most stable, therefore tertiary carbocations are most reactive towards ${S_n}1$ reaction as compared to primary and secondary. As more is the stability of carbocation, more is the reactivity.
So, as per the stability of the carbocation,

option (A) will give ${S_n}1$ reaction, because here, the formation of stable tertiary carbocation will take place, so this will give us ${S_n}1$ reaction. This molecule will always go for ${S_n}1$ reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is option (A).
Note :
Since, we know that ${S_n}1$ is a unimolecular reaction, so its rate will be dependent upon halo alkenes only not on nucleophiles. There are several other factors on which ${S_n}1$ reaction depends, such as polar protic solvent is required here in this, the better-leaving group should be there, that increases the rate of the reaction, weak nucleophiles are preferred.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




