
which muscle is responsible for respiration.
(a)Diaphragm
(b)Muscle tissue
(c)Heart
(d)Lungs
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: It is a dome-shaped, thin muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity due to the elastic recoil of the lungs and surface tension, relaxed normal expiration is a passive process. Inspiration muscles elevate the ribs and sternum, and they are weakened by the expiration muscles.
Complete answer:
-The diaphragm and external intercostals are the main inspiratory muscles.
-The diaphragm is a double-domed layer of internal skeletal muscle separating the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity.
-The diaphragm is the main inspiratory muscle, it contracts and travels in the lower direction during inspiration, raising the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity and causing lung expansion, in turn drawing the air in.
-The diaphragm contracts during inhalation, so that its middle moves caudally (downward) and its edges (upward) travel cranially.
-The abdominal cavity is compressed, the ribs are lifted up and out, and the thoracic cavity is thus extended. It pulls oxygen into the lungs through this expansion.
-Elastic recoil of the lungs allows the thoracic cavity to contract as the diaphragm relaxes, pushing air out of the lungs and returning to its dome-shape.
-Between the ribs, intercostal muscles are attached and are important in manipulating the width of the rib cage.
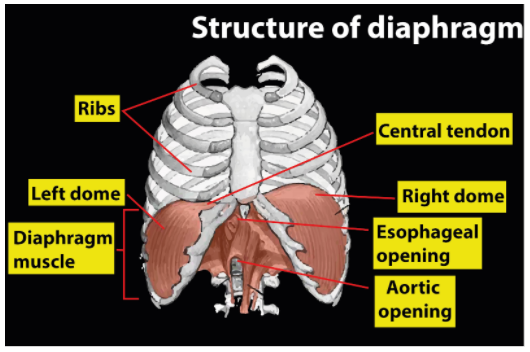
So, the correct answer is ‘Diaphragm’.
Note: -The diaphragm also assists in non-respiratory functions, helping to remove vomit, feces, and urine from the body by raising intra-abdominal pressure and avoiding acid reflux by adding pressure to the oesophagus when it travels through the esophageal hiatus.
Complete answer:
-The diaphragm and external intercostals are the main inspiratory muscles.
-The diaphragm is a double-domed layer of internal skeletal muscle separating the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity.
-The diaphragm is the main inspiratory muscle, it contracts and travels in the lower direction during inspiration, raising the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity and causing lung expansion, in turn drawing the air in.
-The diaphragm contracts during inhalation, so that its middle moves caudally (downward) and its edges (upward) travel cranially.
-The abdominal cavity is compressed, the ribs are lifted up and out, and the thoracic cavity is thus extended. It pulls oxygen into the lungs through this expansion.
-Elastic recoil of the lungs allows the thoracic cavity to contract as the diaphragm relaxes, pushing air out of the lungs and returning to its dome-shape.
-Between the ribs, intercostal muscles are attached and are important in manipulating the width of the rib cage.

So, the correct answer is ‘Diaphragm’.
Note: -The diaphragm also assists in non-respiratory functions, helping to remove vomit, feces, and urine from the body by raising intra-abdominal pressure and avoiding acid reflux by adding pressure to the oesophagus when it travels through the esophageal hiatus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




