
Which L-sugar on oxidation gives an optically active dibasic acid (\[2 - COOH\] groups)?
A.
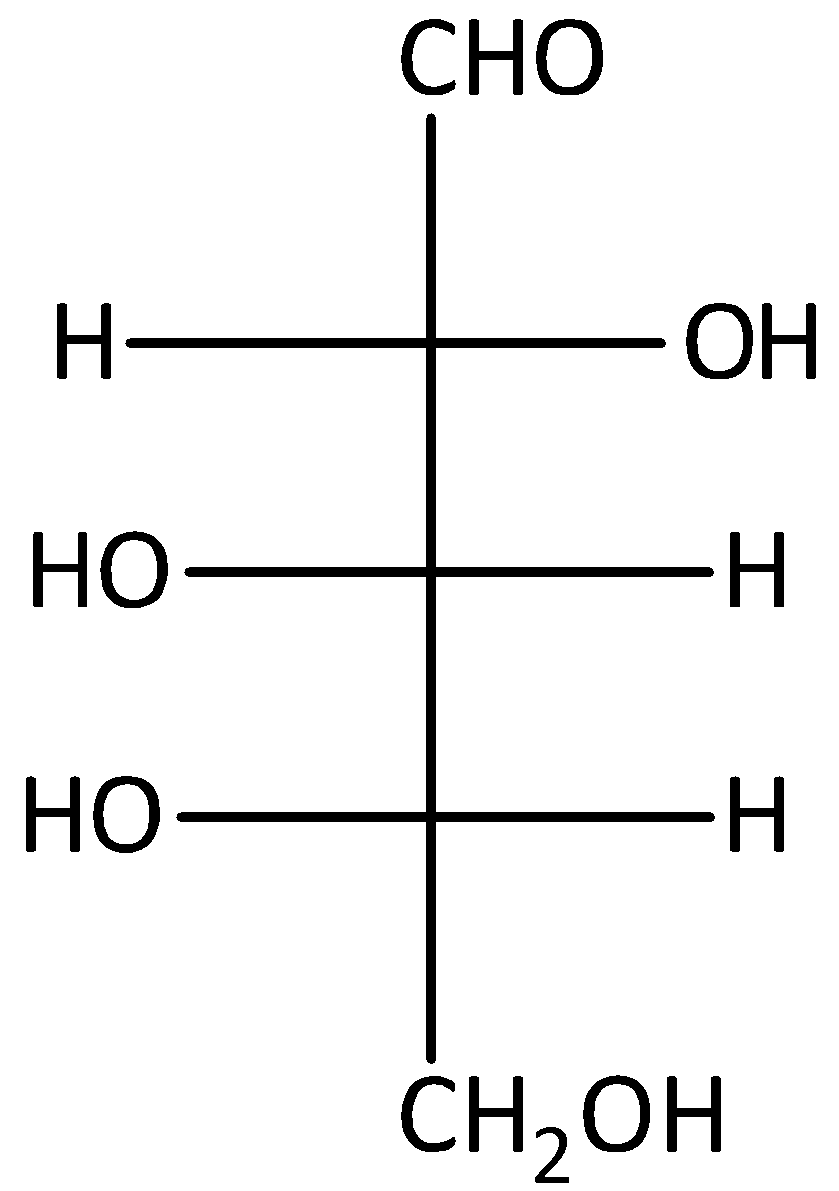
B.
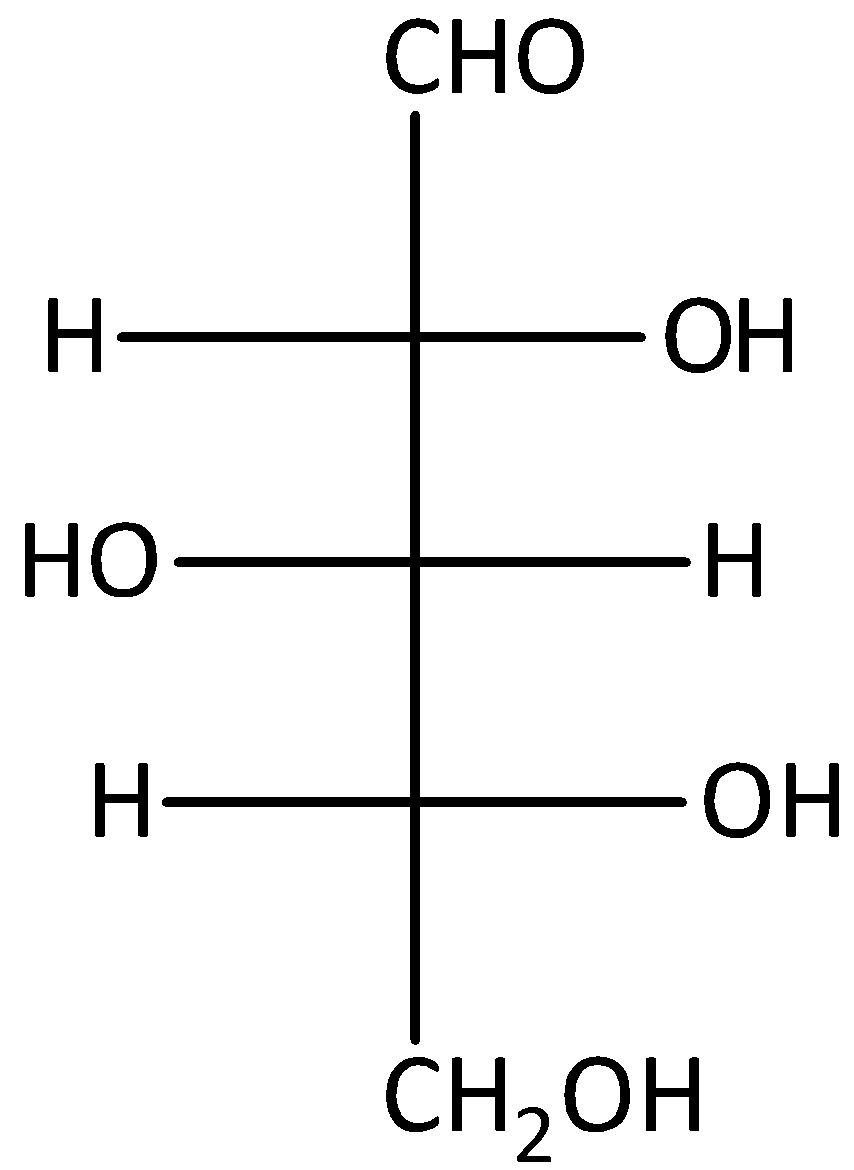
C.
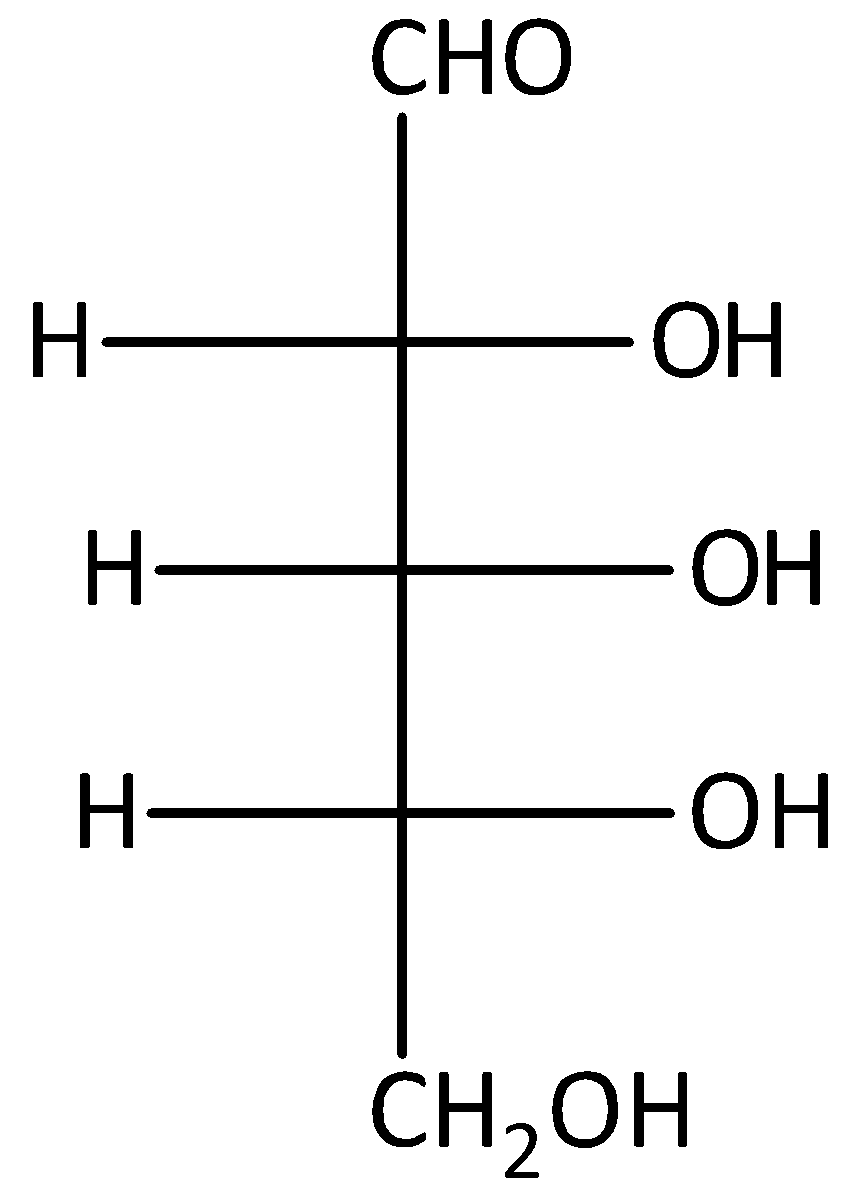
D.
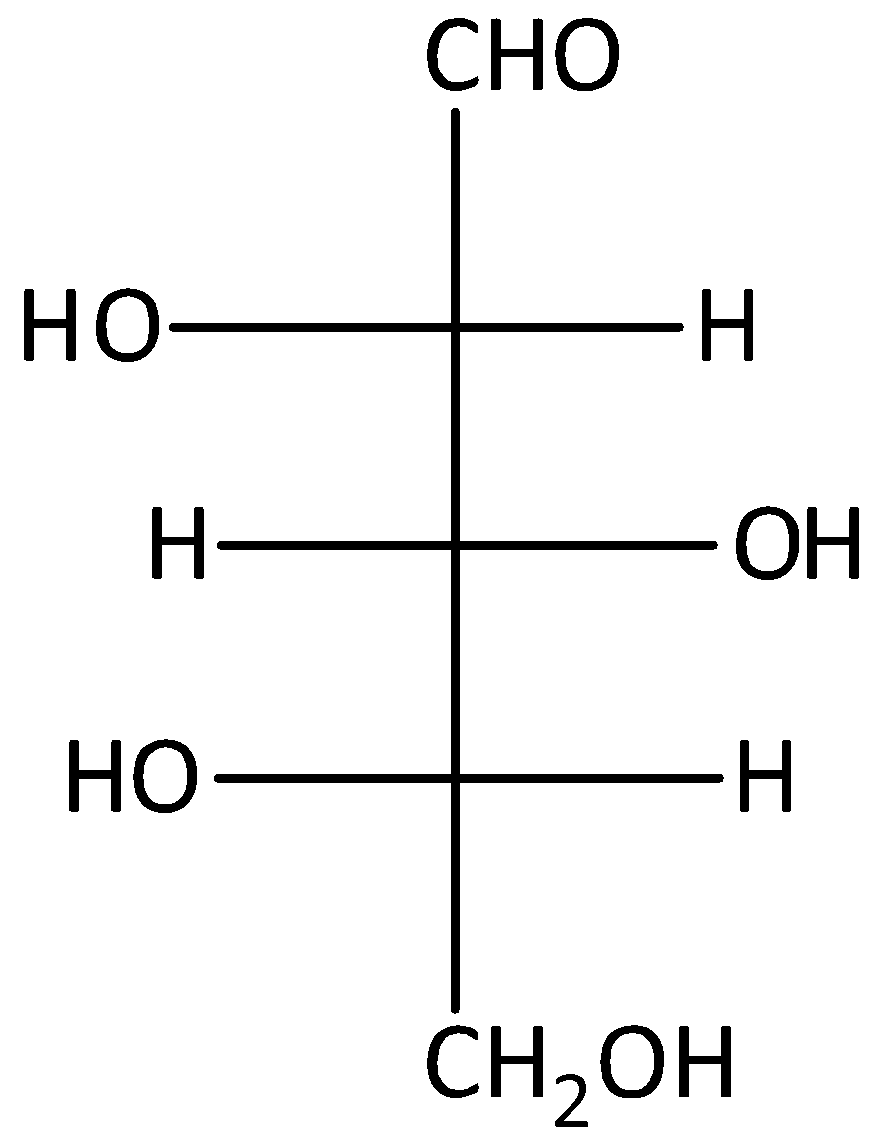




Answer
503.7k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the L-glucose is an organic compound having the formula, \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\] or it also written as, \[O = CH{\left[ {CH} \right]_5}H\]. The L-glucose is the l-isomer of the glucose. Naturally it will not occur in higher living organisms. And the molar mass of the l-glucose is equal to \[180.6g/mol\]. And it can be prepared by using D-glucose, by a convenient method and it can easily be prepared in the laboratory. The D-glucose is found in vegetables and plants naturally. The l-glucose is the primary source of energy in the living organism.
Complete answer:
It will give an optically active dibasic acid by undergoing oxidation. If the sugar is optically active, when it does not contain any plane of symmetry. According to the given options, option (A) and (D) are given the L-sugars after oxidation. But compounds (B) and (C) are D-sugars after oxidation. And the compound (A) gives the optically active mirror image on oxidation. Let’s see the reaction,
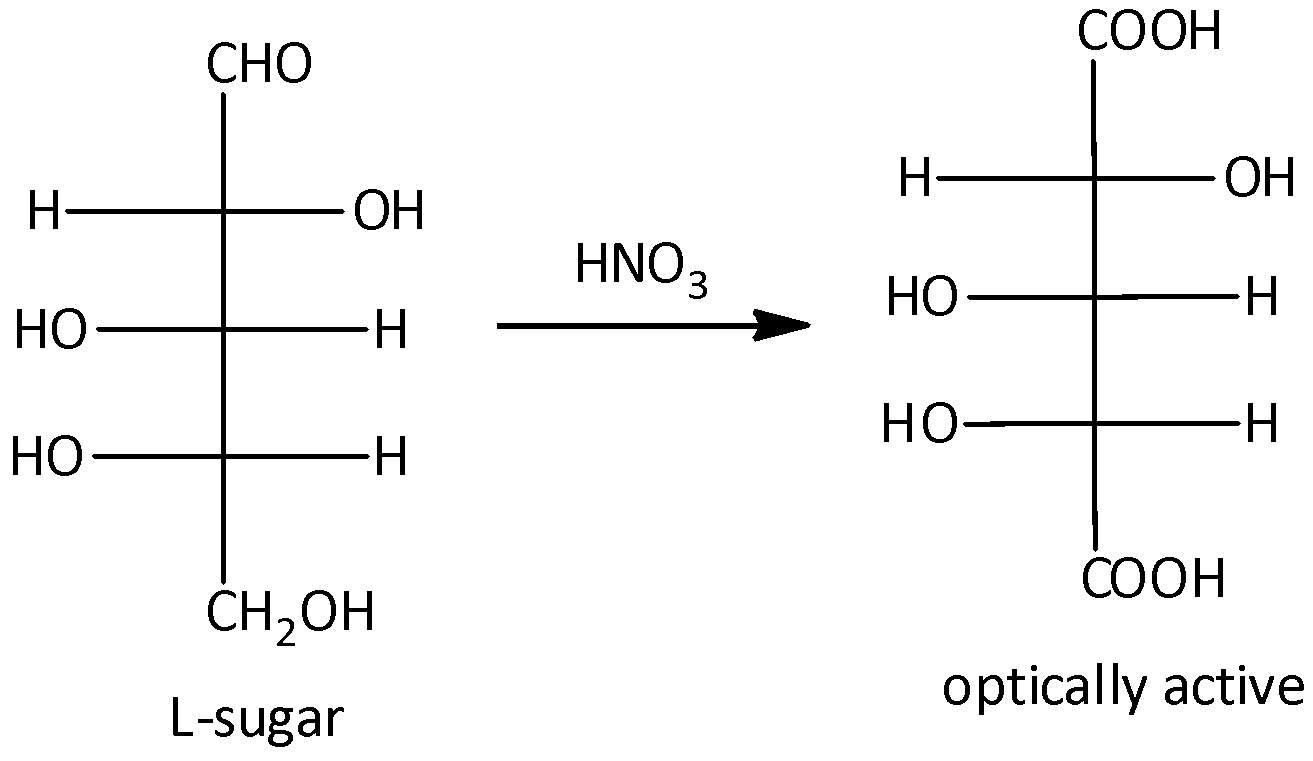
Hence, option (A) is correct.
The given compound B is D-glucose. Therefore, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (B) is incorrect.
The compound C is D-glucose. Therefore, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (C) is incorrect.
The given compound D is L-glucose. But, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note:
We have to remember that the oxidation – reduction reaction is also known as redox reaction. This is a type of chemical reaction that undergoes the transfer of electrons between two species. During a chemical reaction, the oxidation state of an atom, molecule or ion may change. It may increase or decrease the oxidation number by losing or gaining the electrons.
Complete answer:
It will give an optically active dibasic acid by undergoing oxidation. If the sugar is optically active, when it does not contain any plane of symmetry. According to the given options, option (A) and (D) are given the L-sugars after oxidation. But compounds (B) and (C) are D-sugars after oxidation. And the compound (A) gives the optically active mirror image on oxidation. Let’s see the reaction,

Hence, option (A) is correct.
The given compound B is D-glucose. Therefore, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (B) is incorrect.
The compound C is D-glucose. Therefore, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (C) is incorrect.
The given compound D is L-glucose. But, it will not give optically active dibasic acid on oxidation. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note:
We have to remember that the oxidation – reduction reaction is also known as redox reaction. This is a type of chemical reaction that undergoes the transfer of electrons between two species. During a chemical reaction, the oxidation state of an atom, molecule or ion may change. It may increase or decrease the oxidation number by losing or gaining the electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




