
Which liquid can be dehydrated to produce ethene?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Dehydration is the process of removal of water molecules. These are the reverse of the hydration reaction. This process generally occurs in the presence of strong acids or high temperatures. These fall under the category of Elimination Reaction where hydrogen is removed from one atom and hydroxyl from the other one.
Complete answer:
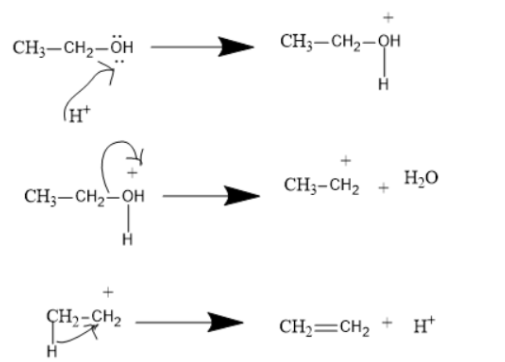
Ethyl Alcohol or Ethanol is dehydrated to produce Ethene or ethylene. There are some important characteristics regarding this particular reaction-
1. This reaction can take place in presence of strong acids like sulphuric acid or Phosphoric acid or in the presence of heat and a temperature not too high.(These catalysts reduce the Activation Energy required to convert reactant to product).
2. This Reaction is an Example of E2 Elimination. Ethyl alcohol is a primary alcohol so if it produces primary carbocation it will be very unstable (i.e. the E1 mechanism) and hence the loss of proton and that of water occurs at the same time in a single step reaction.
${C_2}{H_5}OH\xrightarrow{\Delta }{C_2}{H_4} + {H_2}O$

In this process the taking up of protons from the acid by oxygen of Alcohol and the removal of water molecules occurs in a single step, this is the most common way of elimination in ethanol.
However at some places the E1 reaction is also given however it is less favourable because the ethyl carbocation is very less stable.
Note:
In case of secondary and tertiary alcohol however we mostly prefer the E1 mechanism since the secondary and tertiary carbocation are very stable. Here the formation of carbocation is the rate determining step. These reactions are in more than one step. In some cases however dehydration produces Ether instead of producing alkene.
Complete answer:
Ethyl Alcohol or Ethanol is dehydrated to produce Ethene or ethylene. There are some important characteristics regarding this particular reaction-
1. This reaction can take place in presence of strong acids like sulphuric acid or Phosphoric acid or in the presence of heat and a temperature not too high.(These catalysts reduce the Activation Energy required to convert reactant to product).
2. This Reaction is an Example of E2 Elimination. Ethyl alcohol is a primary alcohol so if it produces primary carbocation it will be very unstable (i.e. the E1 mechanism) and hence the loss of proton and that of water occurs at the same time in a single step reaction.
${C_2}{H_5}OH\xrightarrow{\Delta }{C_2}{H_4} + {H_2}O$

In this process the taking up of protons from the acid by oxygen of Alcohol and the removal of water molecules occurs in a single step, this is the most common way of elimination in ethanol.
However at some places the E1 reaction is also given however it is less favourable because the ethyl carbocation is very less stable.

Note:
In case of secondary and tertiary alcohol however we mostly prefer the E1 mechanism since the secondary and tertiary carbocation are very stable. Here the formation of carbocation is the rate determining step. These reactions are in more than one step. In some cases however dehydration produces Ether instead of producing alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




