
Which kind of point defect is found in \[KCl\] crystal ?
A. Frenkel
B. Schottky
C. Linear
D. Impurity
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: There are three types of point defects ie stoichiometric defect, Frenkle defect and schottky defect. These are the imperfections in crystal lattice due to missing atoms or ions, it creates a vacancy for extra atoms or ions.
Complete step by step answer: $KCl$ is an ionic compound, having small difference in size of cations and anions present in the crystal lattice.
In such compounds, more examples :
$NaCl,KBr,CsCl\;and\;AgBr,$the point defect seen is schottky defect. Schottky defects consist of cations and anions in stoichiometric ratio that are unoccupied.
Simple structure of ionic crystal is ${A^ - }{B^ + }.$
This defect was named after walter H schottky, who demonstrated that in crystal lattice, oppositely charged ions ie. Cation and anion leave their sites and get incorporated at surface for instance and create oppositely charged vacancies in stoichiometric units and maintain overall neutral charge on ionic solid .
Two dimensional diagram of this defeat for $KCl$ is :-
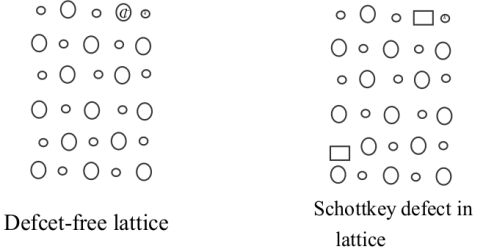
Due to schottky defect, the density of the solid crystal lattice becomes lower than actual theoretical density.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Both anion and cation leave the solid crystal and permanently move out of it. Generally , the number of Vacancies formed is two.
The number of schottky defects can be calculated by using the formula
$ns = Next\left( {\frac{{ - \Delta Hs}}{{2RT}}} \right)$
Where, $ns = $ number of Schottky defects per unit volume.
$R = $gas constant
$\Delta H = $enthalpy of defect formation
$T = $ Temperature in kelvin.
Complete step by step answer: $KCl$ is an ionic compound, having small difference in size of cations and anions present in the crystal lattice.
In such compounds, more examples :
$NaCl,KBr,CsCl\;and\;AgBr,$the point defect seen is schottky defect. Schottky defects consist of cations and anions in stoichiometric ratio that are unoccupied.
Simple structure of ionic crystal is ${A^ - }{B^ + }.$
This defect was named after walter H schottky, who demonstrated that in crystal lattice, oppositely charged ions ie. Cation and anion leave their sites and get incorporated at surface for instance and create oppositely charged vacancies in stoichiometric units and maintain overall neutral charge on ionic solid .
Two dimensional diagram of this defeat for $KCl$ is :-

Due to schottky defect, the density of the solid crystal lattice becomes lower than actual theoretical density.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Both anion and cation leave the solid crystal and permanently move out of it. Generally , the number of Vacancies formed is two.
The number of schottky defects can be calculated by using the formula
$ns = Next\left( {\frac{{ - \Delta Hs}}{{2RT}}} \right)$
Where, $ns = $ number of Schottky defects per unit volume.
$R = $gas constant
$\Delta H = $enthalpy of defect formation
$T = $ Temperature in kelvin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




