
Which is the unit of polarizability of a molecule?
A) ${{\text{C}}^2}{{\text{m}}^{\text{1}}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$
B) ${{\text{C}}^2}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}{{\text{N}}^{\text{1}}}$
C) ${{\text{C}}^{ - 2}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{1}}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$
D) ${{\text{C}}^2}{{\text{m}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Polarizability determines the response of a molecule to an external field.
Formula Used: Polarizability is given by, $\alpha = \dfrac{p}{E}$ , where $p$ represents the electric dipole moment of the molecule and $E$ is the incident electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Define polarizability of a molecule.
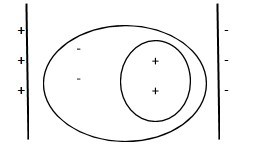
When a molecule is placed in an electric field of strength $E$ a charge separation of electrons and positive charges takes place. This causes the formation of a dipole moment $p$ inside the molecule. It is called induced dipole moment.
The induced dipole moment $p$ is directly proportional to strength of the electric field $E$
i.e., $p \propto E$ or, $p = \alpha E$ .
where, $\alpha $ is the constant of proportionality called polarizability.
Thus, polarizability of the molecule is defined as the dipole moment induced in the molecule by an electric field of unit strength. It determines the relative tendency or dynamic response of the molecule when it gets distorted by an external electrical field.
Step 2: Express the relation for polarizability in terms of the units of the induced dipole moment and electric field strength.
We have, $p = \alpha E$ .
This implies that $\alpha = \dfrac{p}{E}$ .
The unit of dipole moment is ${{\text{C}}^1}{{\text{m}}^1}$and that of electric field strength is ${{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}{{\text{N}}^1}$ .
Substituting these units in the relation for polarizability we get, $\alpha = \dfrac{{{{\text{C}}^1}{{\text{m}}^1}}}{{{{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}{{\text{N}}^1}}}$ .
Finally, we have the unit of polarizability as ${{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^1}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$ .
Therefore, the correct option is a) ${{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^1}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$ .
Note: Charge separation of electrons and positive charges lead to the creation of electric dipoles (an electric dipole is a couple of opposite charges separated by some distance) and thereby induce a dipole moment inside the molecule. Electric field is the force by charge. Thus, has a unit of ${{\text{N}}^1}{{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Formula Used: Polarizability is given by, $\alpha = \dfrac{p}{E}$ , where $p$ represents the electric dipole moment of the molecule and $E$ is the incident electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Define polarizability of a molecule.

When a molecule is placed in an electric field of strength $E$ a charge separation of electrons and positive charges takes place. This causes the formation of a dipole moment $p$ inside the molecule. It is called induced dipole moment.
The induced dipole moment $p$ is directly proportional to strength of the electric field $E$
i.e., $p \propto E$ or, $p = \alpha E$ .
where, $\alpha $ is the constant of proportionality called polarizability.
Thus, polarizability of the molecule is defined as the dipole moment induced in the molecule by an electric field of unit strength. It determines the relative tendency or dynamic response of the molecule when it gets distorted by an external electrical field.
Step 2: Express the relation for polarizability in terms of the units of the induced dipole moment and electric field strength.
We have, $p = \alpha E$ .
This implies that $\alpha = \dfrac{p}{E}$ .
The unit of dipole moment is ${{\text{C}}^1}{{\text{m}}^1}$and that of electric field strength is ${{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}{{\text{N}}^1}$ .
Substituting these units in the relation for polarizability we get, $\alpha = \dfrac{{{{\text{C}}^1}{{\text{m}}^1}}}{{{{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}{{\text{N}}^1}}}$ .
Finally, we have the unit of polarizability as ${{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^1}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$ .
Therefore, the correct option is a) ${{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}{{\text{m}}^1}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - 1}}}}$ .
Note: Charge separation of electrons and positive charges lead to the creation of electric dipoles (an electric dipole is a couple of opposite charges separated by some distance) and thereby induce a dipole moment inside the molecule. Electric field is the force by charge. Thus, has a unit of ${{\text{N}}^1}{{\text{C}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




