
Which is the primary ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ acceptor for ${\text{C3}}$plant and ${\text{C4}}$plant?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The first organic compound produced in ${\text{C3}}$plants is a three-carbon compound while in the case of ${\text{C4}}$plants it is a four-carbon compound and due to this reason they differ from one another.
Complete answer:
${\text{C3}}$Plants: These plants are defined as the plants that show the ${\text{C3}}$ pathway. These plants utilize the Calvin cycle in the dark reaction of photosynthesis. ${\text{C3}}$plants don’t lose the water so they keep their stomata open for a longer time during the day. These plants intake carbon dioxide through minute pores present on the surface of leaves called stomata. Their leaves do not show kranz anatomy which is one of the features of ${\text{C4}}$plant.
Diagram showing the Calvin cycle:
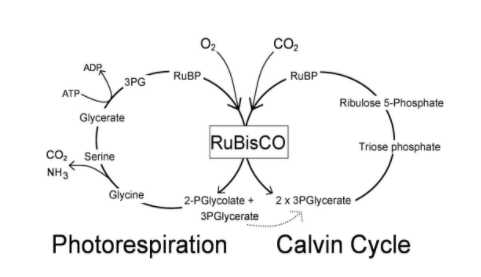
The primary ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ acceptor for ${\text{C3}}$ plants is RuBisCO (Ribulose-${\text{1}}$,${\text{5}}$-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) this enzyme catalyzes the entry of carbon dioxide into the photosynthetic metabolism and it is found in the chloroplast that plays a vital role during the Calvin cycle. Examples of ${\text{C3}}$plants are eucalyptus, sunflower, etc.
${\text{C4}}$Plants: These plants are defined as the plants that utilize the ${\text{C4}}$ pathway or Hatch-slack pathway at the time of dark reaction. They use ${\text{C4}}$ photosynthesis to avoid photorespiration. These types of plants are best suited for hot, dry climates and they produce more energy than the ${\text{C3}}$ plants. Leaves of these plants show kranz anatomy is a specialized structure present in${\text{C4}}$where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle-sheath cells in a ring-like pattern.
Diagram showing ${\text{C4}}$pathway:
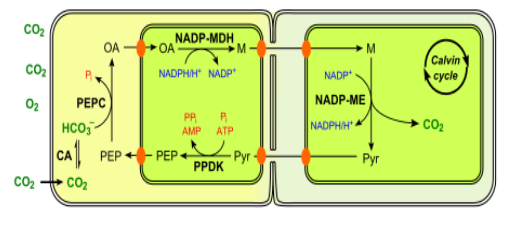
The primary ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ acceptor for${\text{C4}}$plants is PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate) and it is located in the mesophyll cells and an essential enzyme in ${\text{C4}}$plants. Examples of ${\text{C4}}$plants are crops of maize, millets, etc.
Note: Carbon fixation in ${\text{C3}}$plants takes place only at a single place i.e. only one chloroplast is involved while in ${\text{C4}}$plants it takes place twice first in the mesophyll cells and second in the bundle-sheath cells i.e. two chloroplasts are involved.
Complete answer:
${\text{C3}}$Plants: These plants are defined as the plants that show the ${\text{C3}}$ pathway. These plants utilize the Calvin cycle in the dark reaction of photosynthesis. ${\text{C3}}$plants don’t lose the water so they keep their stomata open for a longer time during the day. These plants intake carbon dioxide through minute pores present on the surface of leaves called stomata. Their leaves do not show kranz anatomy which is one of the features of ${\text{C4}}$plant.
Diagram showing the Calvin cycle:

The primary ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ acceptor for ${\text{C3}}$ plants is RuBisCO (Ribulose-${\text{1}}$,${\text{5}}$-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) this enzyme catalyzes the entry of carbon dioxide into the photosynthetic metabolism and it is found in the chloroplast that plays a vital role during the Calvin cycle. Examples of ${\text{C3}}$plants are eucalyptus, sunflower, etc.
${\text{C4}}$Plants: These plants are defined as the plants that utilize the ${\text{C4}}$ pathway or Hatch-slack pathway at the time of dark reaction. They use ${\text{C4}}$ photosynthesis to avoid photorespiration. These types of plants are best suited for hot, dry climates and they produce more energy than the ${\text{C3}}$ plants. Leaves of these plants show kranz anatomy is a specialized structure present in${\text{C4}}$where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle-sheath cells in a ring-like pattern.
Diagram showing ${\text{C4}}$pathway:

The primary ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ acceptor for${\text{C4}}$plants is PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate) and it is located in the mesophyll cells and an essential enzyme in ${\text{C4}}$plants. Examples of ${\text{C4}}$plants are crops of maize, millets, etc.
Note: Carbon fixation in ${\text{C3}}$plants takes place only at a single place i.e. only one chloroplast is involved while in ${\text{C4}}$plants it takes place twice first in the mesophyll cells and second in the bundle-sheath cells i.e. two chloroplasts are involved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




