
Which is the accepted structure of ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ in gas phase?
(A)
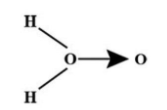
(B)
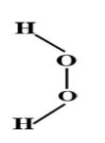
(C) both
(D) none


Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\] is not a planar molecule, there is an oxygen-oxygen bond which has 2 pairs of nonbonding electrons each. This creates a strong repulsion between the atoms of Hydrogen and the unbonded electrons of Oxygen.
Complete answer:
Let us start from the simplest thing we know is ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ a molecule that has 2 atoms of Hydrogen and 2 atoms of Oxygen. Also, Oxygen has six electrons in its outermost shell, which are called valence electrons. These electrons are used in the bond formation between atoms which give rise to a molecule or a compound.
In \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\], each Hydrogen is connected to any one of the Oxygen atoms. This Oxygen is further connected with the other Oxygen atom.
So, we get the skeletal or simple structure as H-O-O-H.
A single bond always consists of 2 electrons, where 1 electron is contributed by every atom. In the case of \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\], in the O-H bond, one electron is donated by Oxygen and the other by Hydrogen. Same is the case of the O-O bond.
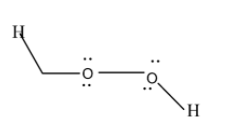
As you can see from the structure, both of the oxygen have some electrons left, which are not used in making bonds. These are called non-bonding electrons and this causes repulsion to occur (electrons are negatively charged and like charges repel). Due to this repulsion, there is a bent shape in this molecule.
Note:
Always remember that Hydrogen will make bonds with Oxygen due to a special property called “Hydrogen bonding”. Also, Hydrogen makes only one bond, by sharing only 1 electron as it has only 2 electrons in its outermost shell. Whereas, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, one with Hydrogen and with the other Oxygen. ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ is not planar, but known to have an “open-book structure”.
Complete answer:
Let us start from the simplest thing we know is ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ a molecule that has 2 atoms of Hydrogen and 2 atoms of Oxygen. Also, Oxygen has six electrons in its outermost shell, which are called valence electrons. These electrons are used in the bond formation between atoms which give rise to a molecule or a compound.
In \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\], each Hydrogen is connected to any one of the Oxygen atoms. This Oxygen is further connected with the other Oxygen atom.
So, we get the skeletal or simple structure as H-O-O-H.
A single bond always consists of 2 electrons, where 1 electron is contributed by every atom. In the case of \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\], in the O-H bond, one electron is donated by Oxygen and the other by Hydrogen. Same is the case of the O-O bond.

As you can see from the structure, both of the oxygen have some electrons left, which are not used in making bonds. These are called non-bonding electrons and this causes repulsion to occur (electrons are negatively charged and like charges repel). Due to this repulsion, there is a bent shape in this molecule.
Note:
Always remember that Hydrogen will make bonds with Oxygen due to a special property called “Hydrogen bonding”. Also, Hydrogen makes only one bond, by sharing only 1 electron as it has only 2 electrons in its outermost shell. Whereas, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, one with Hydrogen and with the other Oxygen. ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ is not planar, but known to have an “open-book structure”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




