
Which is not true of dicot root?
(a) Vascular bundles 15-20
(b) Radial vascular bundles
(c) Secondary growth
(d) Pith little or absent
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Diameter thickening occurs in the dicot root by the addition of vascular tissues. The vascular bundle has a simple xylem and phloem structure which is divided by nonconductive tissues. In dicot roots, there may not be a tissue composed of soft spongy parenchyma cells that store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. The number of bundles in dicotyledonous roots is limited.
Complete step by step answer:
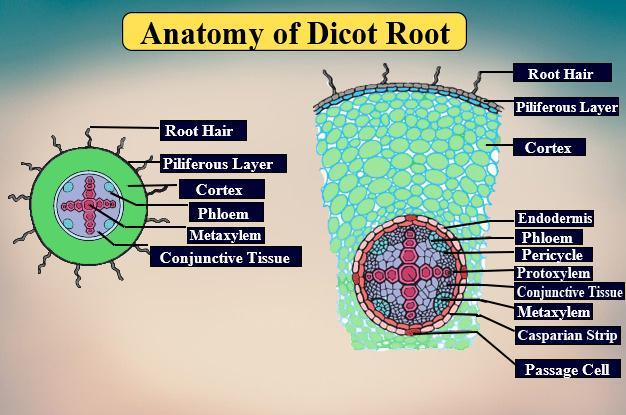
Radial vascular bundles are found in the Dicot root. There is a small parenchymatous pith in the middle. It may also be absent in dicot roots. Vascular bundles in the dicot root are 2 to 6 in number.
They differentiate into secondary growth xylem and phloem as cells of the vascular cambium divide, which increases the girth of dicot roots and stems.
Since the dicot roots have no central pith area, parenchyma serves as connective tissue in the region where the vascular structures of the dicot root are located.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Vascular bundles 15- 20’.
Additional information:
The conjunctive tissue in dicot roots has thin-walled parenchymatous cells lying between xylem and phloem classes.
Endodermis consists of one layer of barrel-shaped cells that are organized similarly without having intercellular spaces. There is a single-layered pericycle formed by thin-walled parenchyma cells next to the endodermis. The seat of origin of the lateral roots is the Pericycle. The cortex constitutes the thin-walled living parenchymal cells with leucoplast that turn sugar into starch grains. The epidermis is single-layered, with thin-walled cells.
Note: The vascular structures in dicot roots are located in the center of the root. In dicots, the arrangement of xylem and phloem is different from in monocots. In the center of the dicot root, the xylem is all placed and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated by the vascular cambium.
Complete step by step answer:
Radial vascular bundles are found in the Dicot root. There is a small parenchymatous pith in the middle. It may also be absent in dicot roots. Vascular bundles in the dicot root are 2 to 6 in number.
They differentiate into secondary growth xylem and phloem as cells of the vascular cambium divide, which increases the girth of dicot roots and stems.
Since the dicot roots have no central pith area, parenchyma serves as connective tissue in the region where the vascular structures of the dicot root are located.

So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Vascular bundles 15- 20’.
Additional information:
The conjunctive tissue in dicot roots has thin-walled parenchymatous cells lying between xylem and phloem classes.
Endodermis consists of one layer of barrel-shaped cells that are organized similarly without having intercellular spaces. There is a single-layered pericycle formed by thin-walled parenchyma cells next to the endodermis. The seat of origin of the lateral roots is the Pericycle. The cortex constitutes the thin-walled living parenchymal cells with leucoplast that turn sugar into starch grains. The epidermis is single-layered, with thin-walled cells.
Note: The vascular structures in dicot roots are located in the center of the root. In dicots, the arrangement of xylem and phloem is different from in monocots. In the center of the dicot root, the xylem is all placed and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated by the vascular cambium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




