
Which is most acidic and why?
A.
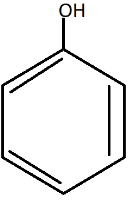
B.
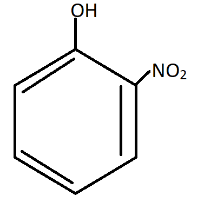
C.
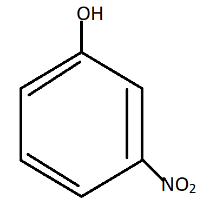
D.
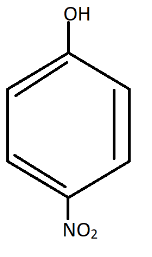




Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: Use the concept of inductive effect and mesomeric effect. Compare the inductive effect of the $N{O_2}$ group at different positions. Hydrogen bonding also plays an important role while comparing the acidity of compounds. It can be intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete answer: Let us suppose that ${H^ + }$from each compound is removed. Then, the remaining $Oxide{\text{ ion}}$ \[\left( {{O^ - }} \right)\]must be stabilized by the Nitro group.
$N{O_2}$ group has both $\left( { - I} \right)$and $\left( { - m} \right)$effect. Hence, it supports the acidic nature of compounds. With the help of $\left( { - m} \right)$effect, the conjugate base $\left( {Oxide{\text{ ion}}} \right)$gets stabilized after removal of ${H^ + }$.
Nitro is an electron withdrawing group. It will withdraw electrons of $Oxide{\text{ ion}}$\[\left( {{O^ - }} \right)\]through these two effects.
By inductive effect, it withdraws electrons, but it is an effect which is based on distance unlike mesomeric effect.
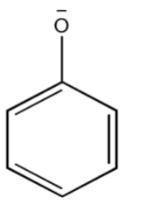
Thus, the $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$so formed after losing the proton ${H^ + }$must be stabilized by resonance. The negative charge present on $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$must be delocalized into a benzene ring.
Nitro group present at meta-position in$m - nitrophenol$, cannot stabilize $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$as compared to $o - nitrophenol$ and$p - nitrophenol$.
Also, in$p - nitrophenol$, there is a chance of hydrogen bonding. (Hydrogen from $OH$ and Nitrogen from $N{O_2}$ group).
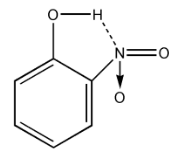
So, it is hard to lose the proton ${H^ + }$ due to $H - Bonding$ with $N{O_2}$ group.
Now, there will be more resonance effect, thus more stabilization of compound$p - nitrophenol$.
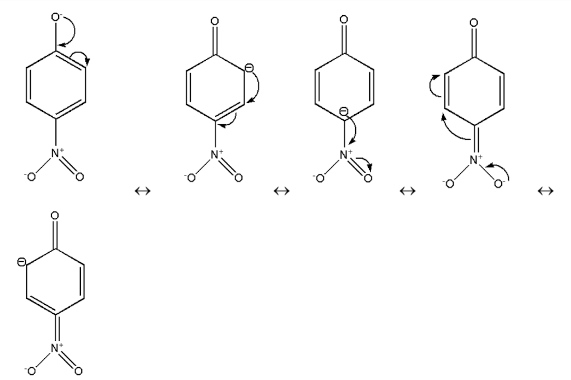 Therefore these are the resonating structures of $p - nitrophenol$.Thus, in $p - nitrophenol$ there is Stabilization due to resonance and inductive effect too.
Therefore these are the resonating structures of $p - nitrophenol$.Thus, in $p - nitrophenol$ there is Stabilization due to resonance and inductive effect too.
Hence, the correct answer is (D).
The most acidic is:
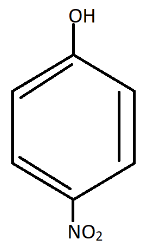
Additional information:
$N{O_2}$ Group do not show mesomeric effect of meta-position in benzene ring. Inductive effect is distance dependent. Hydrogen bonding occurs between Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Oxygen. Hydrogen bonding can be intermolecular and intramolecular.
Note:
While comparing the acidity of the different compounds, always remember the inductive effect and mesomeric effect. The stability of phenoxide ions gives us the order of acidity. More stable theoxide ${\text{ }}ion({O^ - })$, the more its acidity. The order of basicity is just the reverse of the order of acidity.
Complete answer: Let us suppose that ${H^ + }$from each compound is removed. Then, the remaining $Oxide{\text{ ion}}$ \[\left( {{O^ - }} \right)\]must be stabilized by the Nitro group.
$N{O_2}$ group has both $\left( { - I} \right)$and $\left( { - m} \right)$effect. Hence, it supports the acidic nature of compounds. With the help of $\left( { - m} \right)$effect, the conjugate base $\left( {Oxide{\text{ ion}}} \right)$gets stabilized after removal of ${H^ + }$.
Nitro is an electron withdrawing group. It will withdraw electrons of $Oxide{\text{ ion}}$\[\left( {{O^ - }} \right)\]through these two effects.
By inductive effect, it withdraws electrons, but it is an effect which is based on distance unlike mesomeric effect.

Thus, the $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$so formed after losing the proton ${H^ + }$must be stabilized by resonance. The negative charge present on $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$must be delocalized into a benzene ring.
Nitro group present at meta-position in$m - nitrophenol$, cannot stabilize $phenoxide{\text{ ion}}$as compared to $o - nitrophenol$ and$p - nitrophenol$.
Also, in$p - nitrophenol$, there is a chance of hydrogen bonding. (Hydrogen from $OH$ and Nitrogen from $N{O_2}$ group).

So, it is hard to lose the proton ${H^ + }$ due to $H - Bonding$ with $N{O_2}$ group.
Now, there will be more resonance effect, thus more stabilization of compound$p - nitrophenol$.

Hence, the correct answer is (D).
The most acidic is:

Additional information:
$N{O_2}$ Group do not show mesomeric effect of meta-position in benzene ring. Inductive effect is distance dependent. Hydrogen bonding occurs between Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Oxygen. Hydrogen bonding can be intermolecular and intramolecular.
Note:
While comparing the acidity of the different compounds, always remember the inductive effect and mesomeric effect. The stability of phenoxide ions gives us the order of acidity. More stable theoxide ${\text{ }}ion({O^ - })$, the more its acidity. The order of basicity is just the reverse of the order of acidity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




