
Which is less acidic than phenol?
A. $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$
B. $C{H_3}OH$
C. $p - nitrophenol$
D. ${H_2}O$
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: We can compare the acidity of alcohols in terms of ease of giving away protons.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define acids by using Arrhenius theory as well as Brönsted-Lowry theory. Both these theories define acids as ${H^ + }$ donors. Acids can be strong or weak depending upon how easily they can donate ${H^ + }$. This can be deduced by having a look at the group to which the proton is attached for that will affect the polarity of ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ bond by decreasing or increasing the electron density on oxygen.
We have some electron displacement effects with the help of which we can deduce whether the atom or group attached to the proton will increase or decrease the electron density. Inductive effect is an example. It arises as polarization of adjacent sigma bonds and based on this, groups or atoms can be classified as electron donating or electron withdrawing. For example, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing whereas methyl is an electron donating group.
Now, let’s have a look at the structures of all the given compounds and phenol:
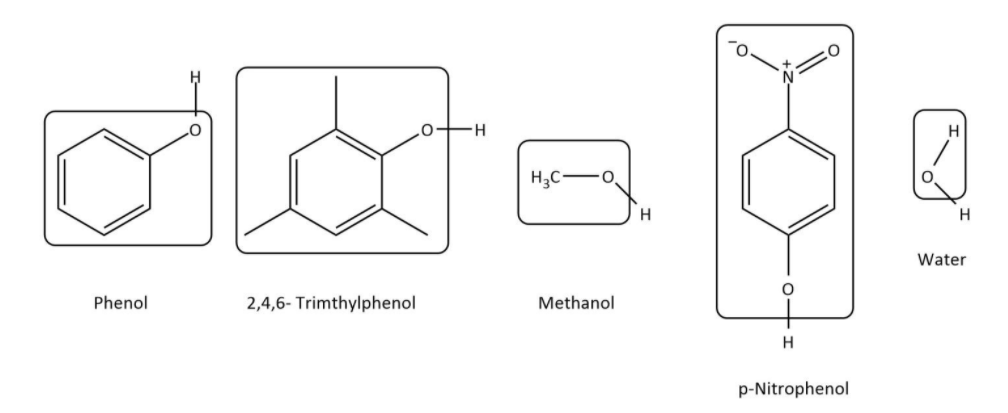
Now, we can see that in phenol, the group attached to $ - OH$ is benzyl; in $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, the attached group is methyl-substituted benzyl; in methanol, methyl group is attached to $ - OH$ group; in $p - nitrophenol$, the attached group is nitro-substituted benzyl and in water it is proton.
Now, we will compare the acidity of compounds with benzyl groups namely phenol, $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$and $p - nitrophenol$. In all of them phenol is there but in two cases it is substituted. In $p - nitrophenol$, the substituent is nitro group which is electron withdrawing which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ more polar and hence is more acidic than phenol. However, in $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, the substituent are methyl groups which are electron donating which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ less polar and hence is less acidic than phenol.
Now, let’s compare the acidity of phenol, methanol and water. In, phenol, ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ group is attached to benzyl group, at $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ more polar than it is in water whereas in methanol, ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ is attached to methyl group, at $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ less polar than it is in water. So, we can deduce that methanol is less acidic than water which is also less acidic than phenol.
Hence, it can be concluded that $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, $C{H_3}OH$and ${H_2}O$ are less acidic than phenol.
Therefore, the correct option is option A,B & D.
Note:
Water is a neutral molecule but it can act both as acid as well as base.
Complete step by step answer:
We can define acids by using Arrhenius theory as well as Brönsted-Lowry theory. Both these theories define acids as ${H^ + }$ donors. Acids can be strong or weak depending upon how easily they can donate ${H^ + }$. This can be deduced by having a look at the group to which the proton is attached for that will affect the polarity of ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ bond by decreasing or increasing the electron density on oxygen.
We have some electron displacement effects with the help of which we can deduce whether the atom or group attached to the proton will increase or decrease the electron density. Inductive effect is an example. It arises as polarization of adjacent sigma bonds and based on this, groups or atoms can be classified as electron donating or electron withdrawing. For example, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing whereas methyl is an electron donating group.
Now, let’s have a look at the structures of all the given compounds and phenol:

Now, we can see that in phenol, the group attached to $ - OH$ is benzyl; in $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, the attached group is methyl-substituted benzyl; in methanol, methyl group is attached to $ - OH$ group; in $p - nitrophenol$, the attached group is nitro-substituted benzyl and in water it is proton.
Now, we will compare the acidity of compounds with benzyl groups namely phenol, $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$and $p - nitrophenol$. In all of them phenol is there but in two cases it is substituted. In $p - nitrophenol$, the substituent is nitro group which is electron withdrawing which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ more polar and hence is more acidic than phenol. However, in $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, the substituent are methyl groups which are electron donating which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ less polar and hence is less acidic than phenol.
Now, let’s compare the acidity of phenol, methanol and water. In, phenol, ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ group is attached to benzyl group, at $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ more polar than it is in water whereas in methanol, ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ is attached to methyl group, at $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon which makes ${O^{\delta - }} - {H^{\delta + }}$ less polar than it is in water. So, we can deduce that methanol is less acidic than water which is also less acidic than phenol.
Hence, it can be concluded that $2,4,6 - trimethylphenol$, $C{H_3}OH$and ${H_2}O$ are less acidic than phenol.
Therefore, the correct option is option A,B & D.
Note:
Water is a neutral molecule but it can act both as acid as well as base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




