
Which hybridization results in non-planar orbitals?
(A)- $sp$
(B)- $s{{p}^{2}}$
(C)- $s{{p}^{3}}$
(D)- $ds{{p}^{2}}$
Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals of comparable energies belonging to the same shell, to form new orbitals of equal energy and shape. Angle between the four hybrid orbitals in $s{{p}^{3}}$-hybridization is ${{109}^{o}}{{28}^{\prime }}$.
Complete answer:
The shapes of molecules can be determined from the type hybridization the molecule is undergoing. Let us now discuss the shapes of the hybrid orbitals resulting from the above given hybridizations.
sp-hybridization
One s and one p orbital of the same shell of an atom combine or hybridize together to form two identical hybrid orbitals. The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals.
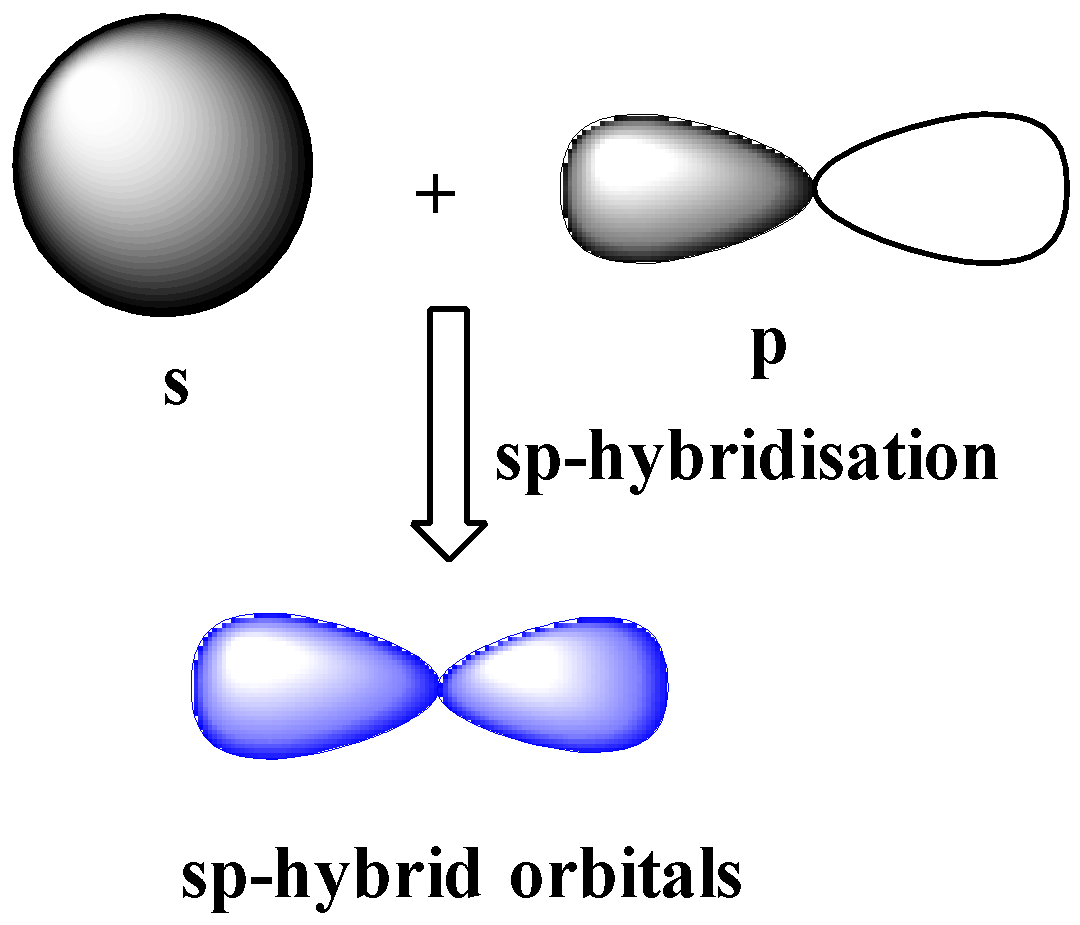
The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals have ${{180}^{o}}$ angle between then and are collinear.
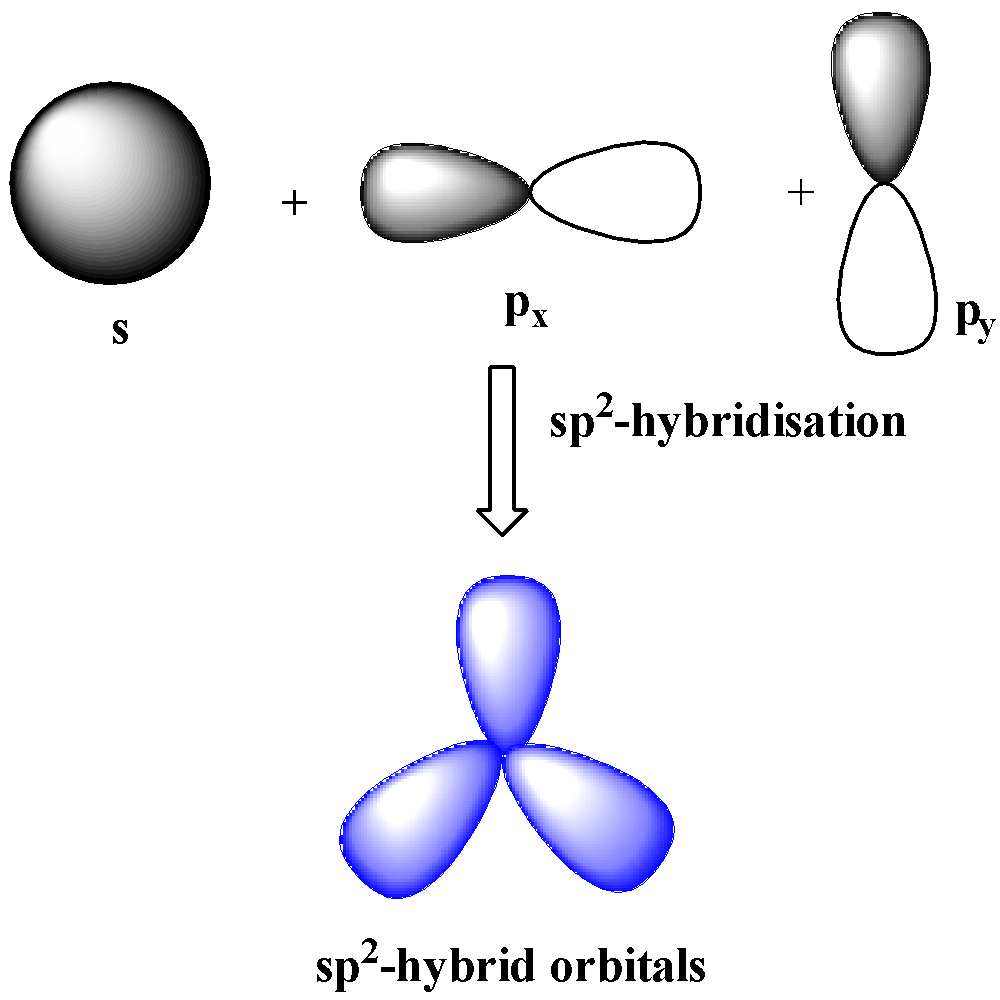
$s{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization
When one s and two p orbitals of the same shell mix together to form three orbitals of equal energy and identical shape, the hybridization is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. The three hybrid orbitals make ${{120}^{o}}$ with one another and are in the same plane. $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization leads to trigonal planar geometry.
$s{{p}^{3}}$-hybridization
One s and three p-orbitals belong to the same shell mix together to four new equivalent orbitals.
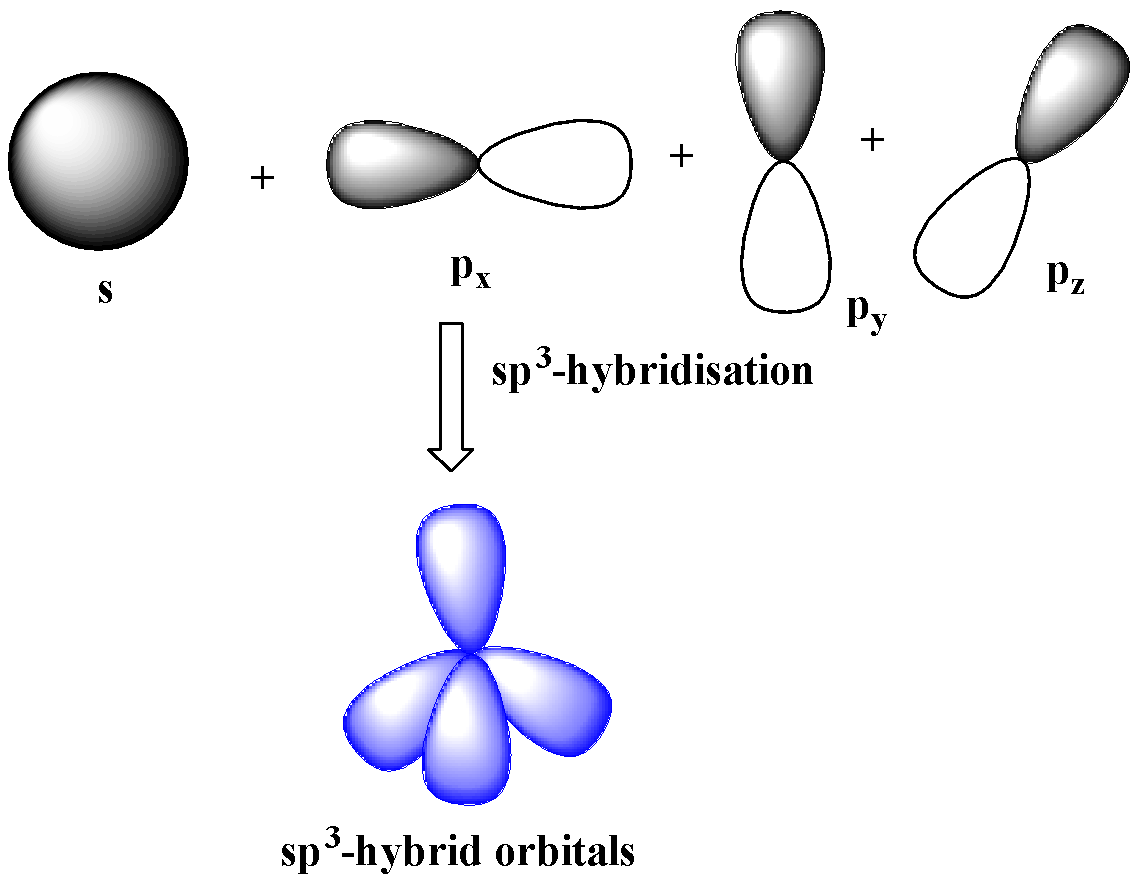

These orbitals rearranged in a regular tetrahedron making an angle of ${{109.5}^{o}}$ with one another. Therefore, these orbitals are non-planar.
$ds{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization
In this type of hybridization, one d (${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$) orbital of lower shell and one s and p orbital of the next shell mix together to form four orbitals of identical shapes and equal energy.
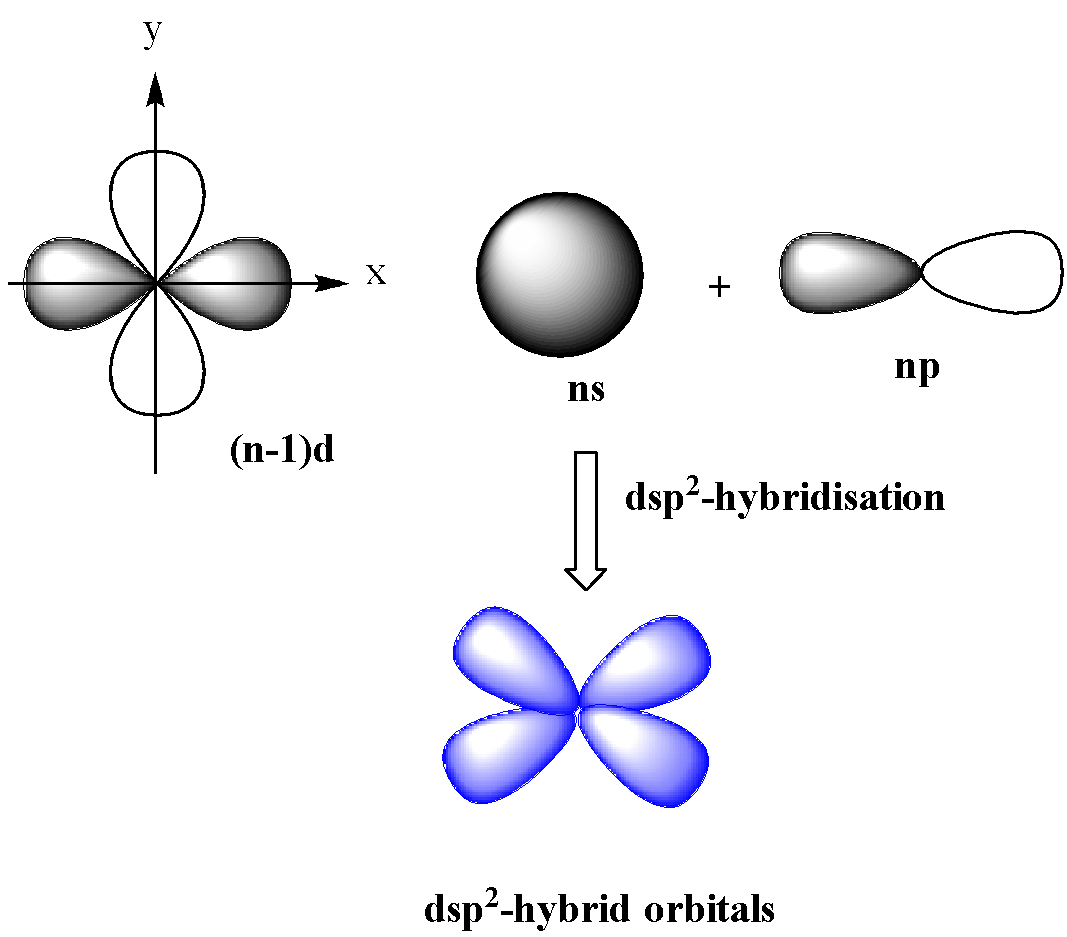
These orbitals are in the same plane having an angle of ${{90}^{o}}$ with one another. $ds{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization gives square planar geometry.
Based on the above discussion, we can see that $s{{p}^{3}}$-hybridization leads to non-planar orbitals.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Do not confuse yourself between $ds{{p}^{2}}$ and $s{{p}^{3}}$. Both involve the hybridization of four orbitals. But the orbitals involved in hybridization are different in the two cases. $s{{p}^{3}}$ leads to non-planar tetrahedral geometry whereas $ds{{p}^{2}}$ leads to square planar geometry.
Complete answer:
The shapes of molecules can be determined from the type hybridization the molecule is undergoing. Let us now discuss the shapes of the hybrid orbitals resulting from the above given hybridizations.
sp-hybridization
One s and one p orbital of the same shell of an atom combine or hybridize together to form two identical hybrid orbitals. The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals.

The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals have ${{180}^{o}}$ angle between then and are collinear.
$s{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization
When one s and two p orbitals of the same shell mix together to form three orbitals of equal energy and identical shape, the hybridization is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. The three hybrid orbitals make ${{120}^{o}}$ with one another and are in the same plane. $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization leads to trigonal planar geometry.

$s{{p}^{3}}$-hybridization
One s and three p-orbitals belong to the same shell mix together to four new equivalent orbitals.

These orbitals rearranged in a regular tetrahedron making an angle of ${{109.5}^{o}}$ with one another. Therefore, these orbitals are non-planar.
$ds{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization
In this type of hybridization, one d (${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$) orbital of lower shell and one s and p orbital of the next shell mix together to form four orbitals of identical shapes and equal energy.

These orbitals are in the same plane having an angle of ${{90}^{o}}$ with one another. $ds{{p}^{2}}$-hybridization gives square planar geometry.
Based on the above discussion, we can see that $s{{p}^{3}}$-hybridization leads to non-planar orbitals.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Do not confuse yourself between $ds{{p}^{2}}$ and $s{{p}^{3}}$. Both involve the hybridization of four orbitals. But the orbitals involved in hybridization are different in the two cases. $s{{p}^{3}}$ leads to non-planar tetrahedral geometry whereas $ds{{p}^{2}}$ leads to square planar geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




