
Which has the fast reaction with KOH (aq)
A.
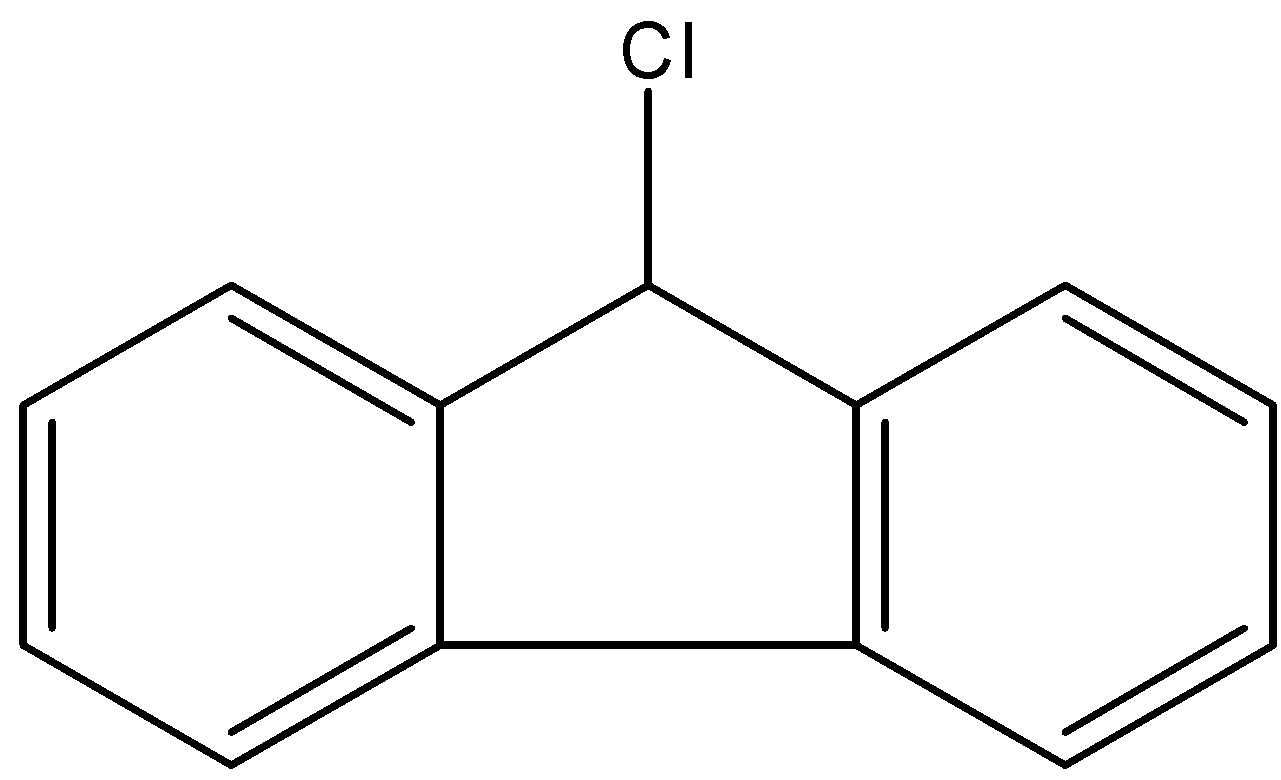
B.
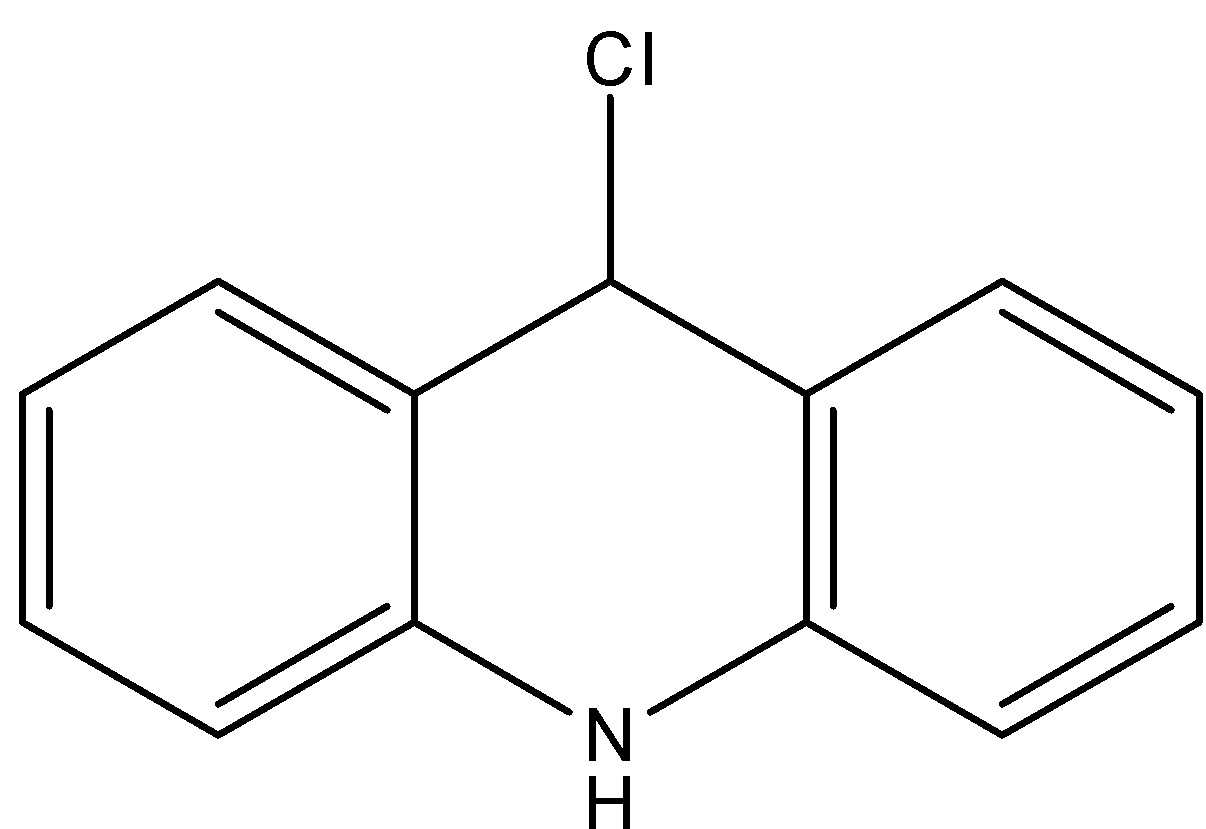
C.
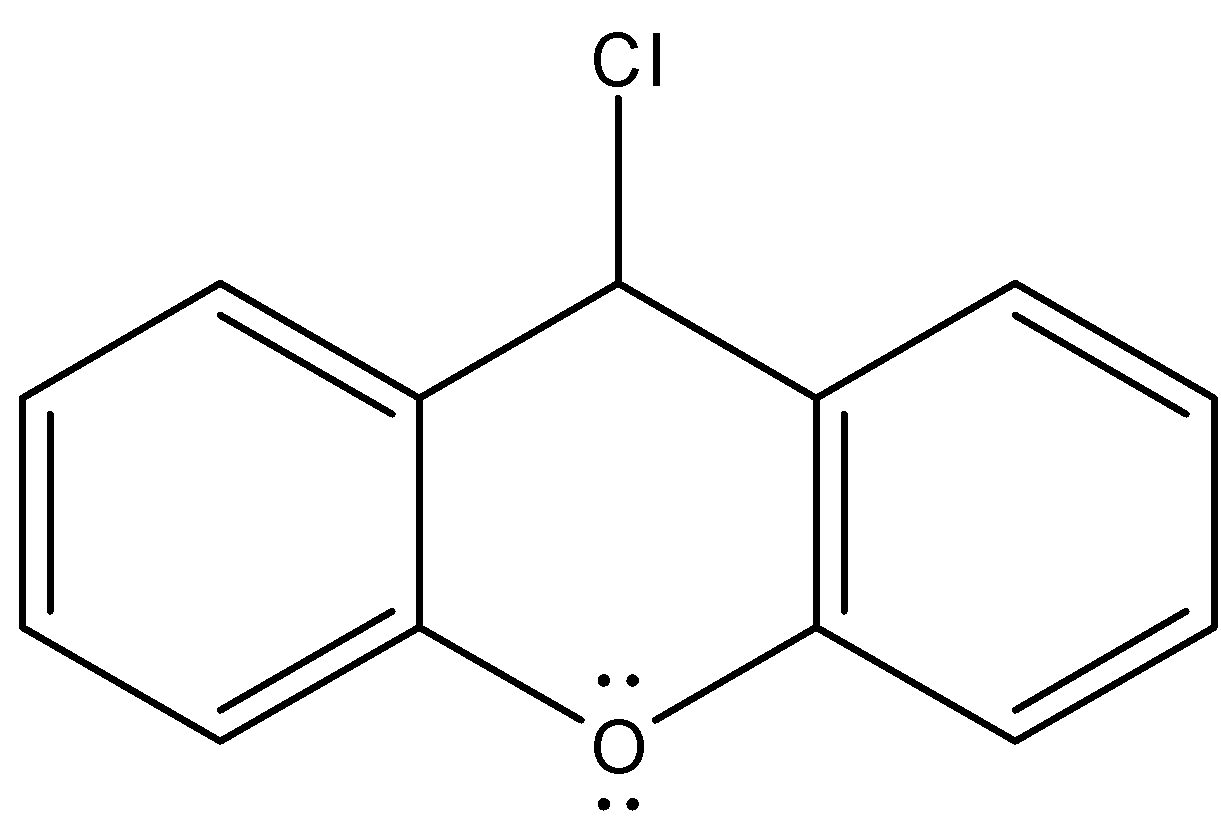
D.
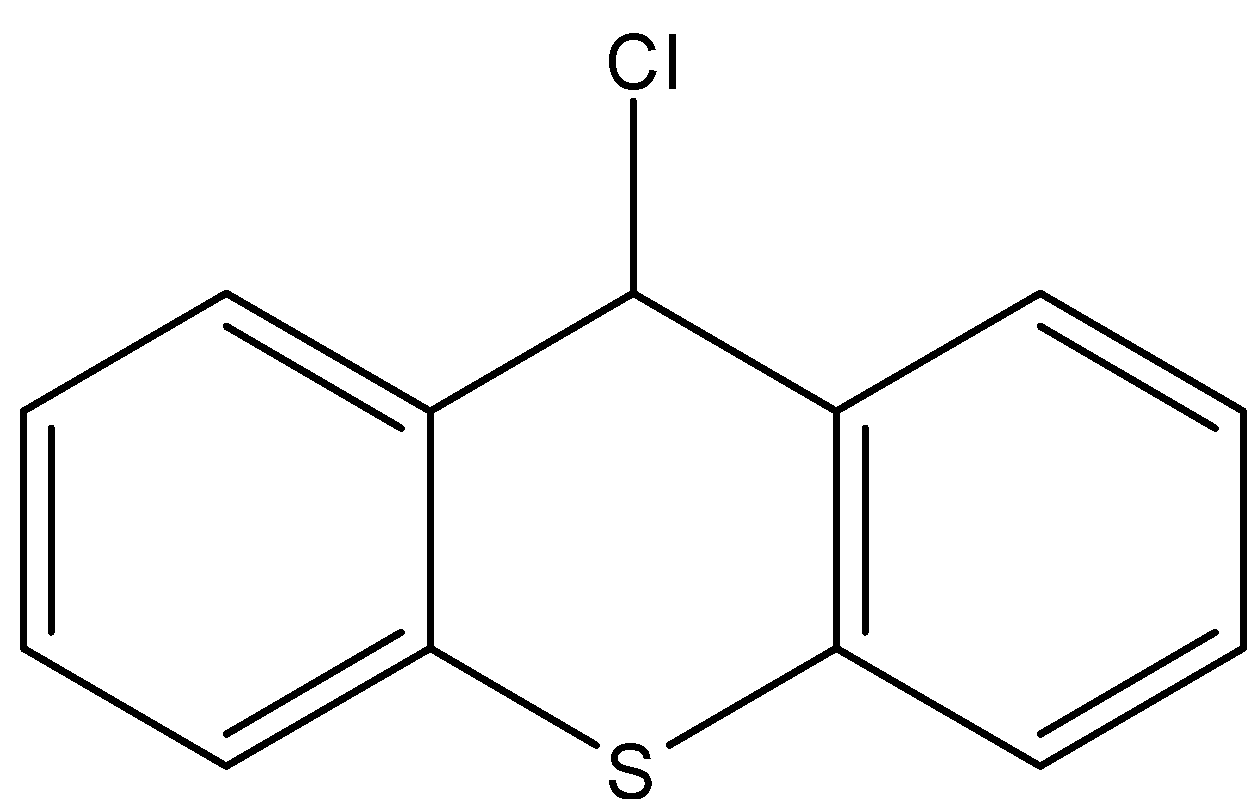




Answer
532.2k+ views
Hint: The unstable compounds only undergo reaction with KOH. If the compound is going to get resonance because of the neighboring atoms then the compound is more stable than the ordinary organic compound.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is given to find the compound which is going to react with KOH among the given options.
- Coming to the given options, option A.
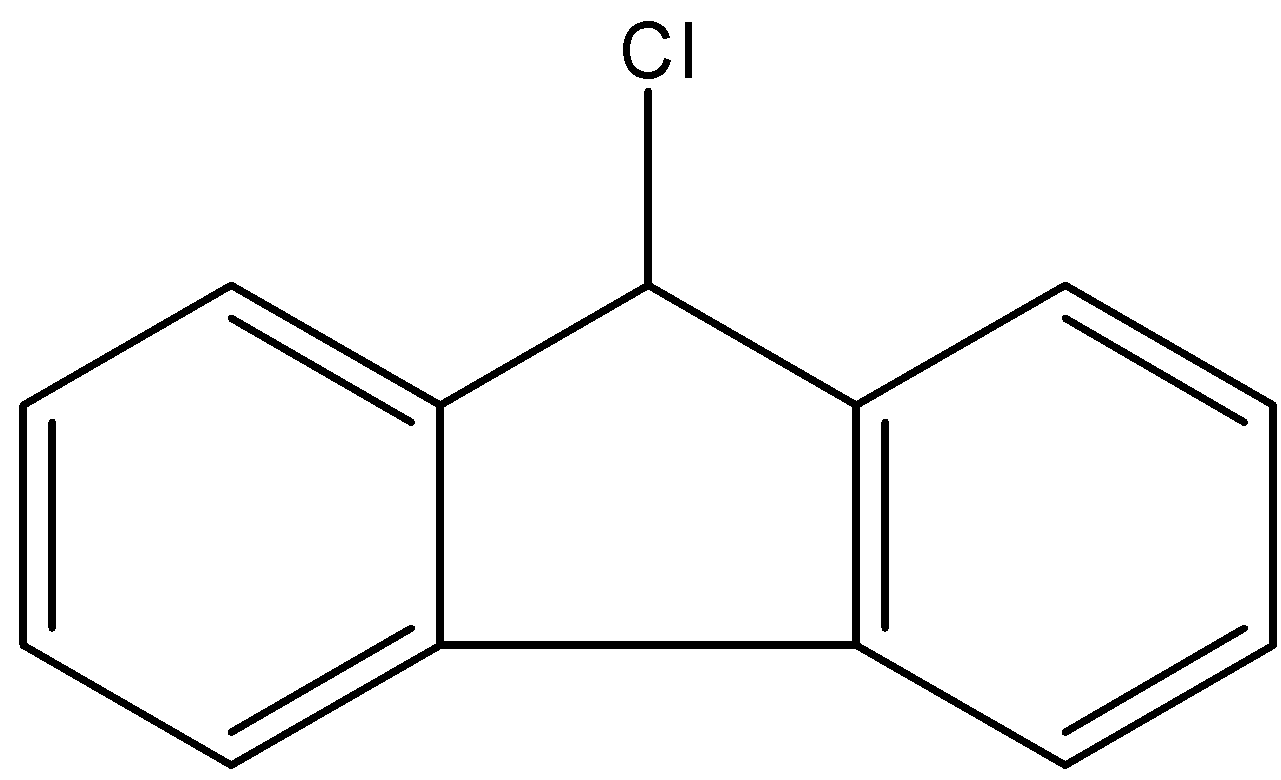
- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.
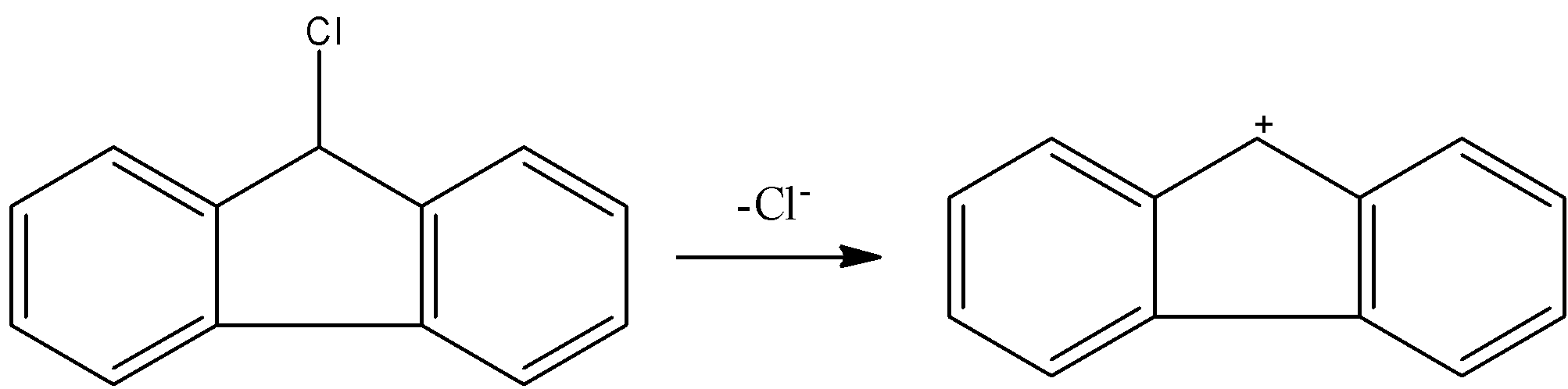
- Now we can see clearly that no neighbor atom existed to stabilize the cationic species which is produced from the compound A.
- Therefore compound A is going to react with KOH.
- Coming to option B,
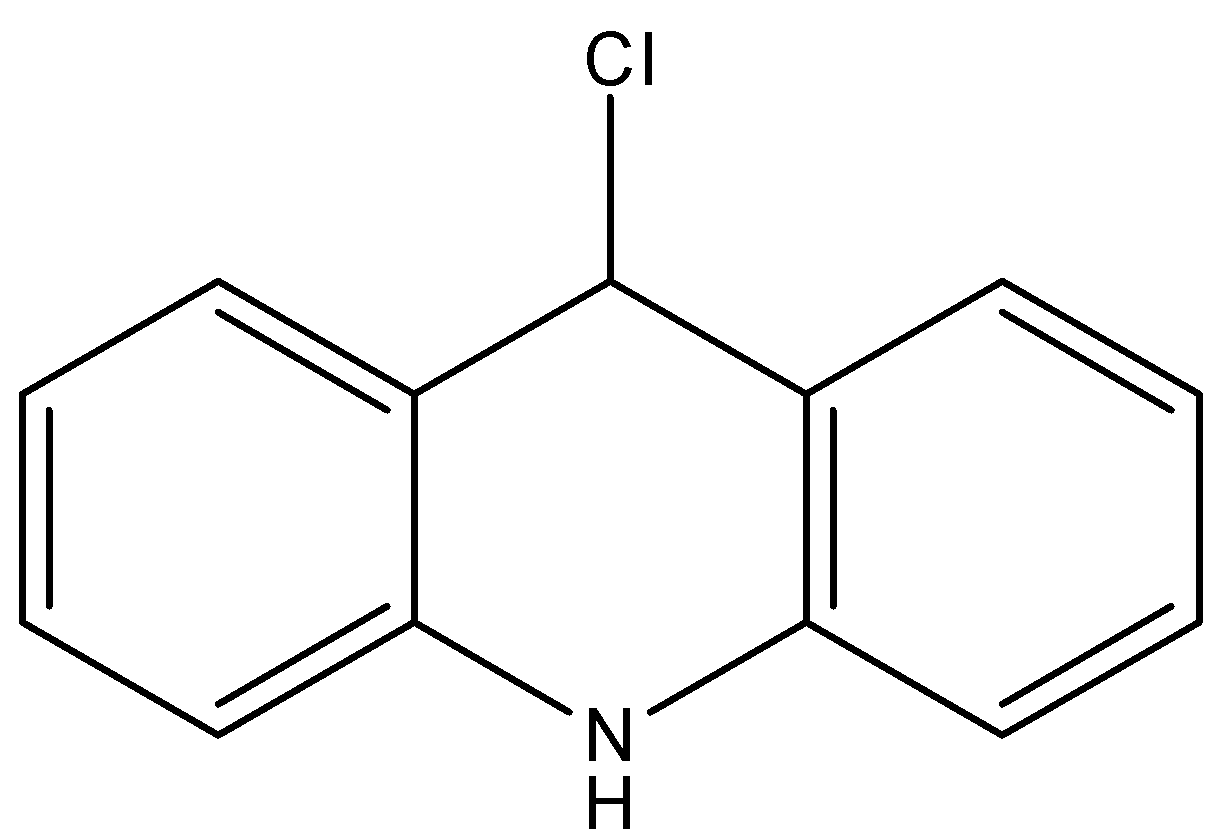
- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.
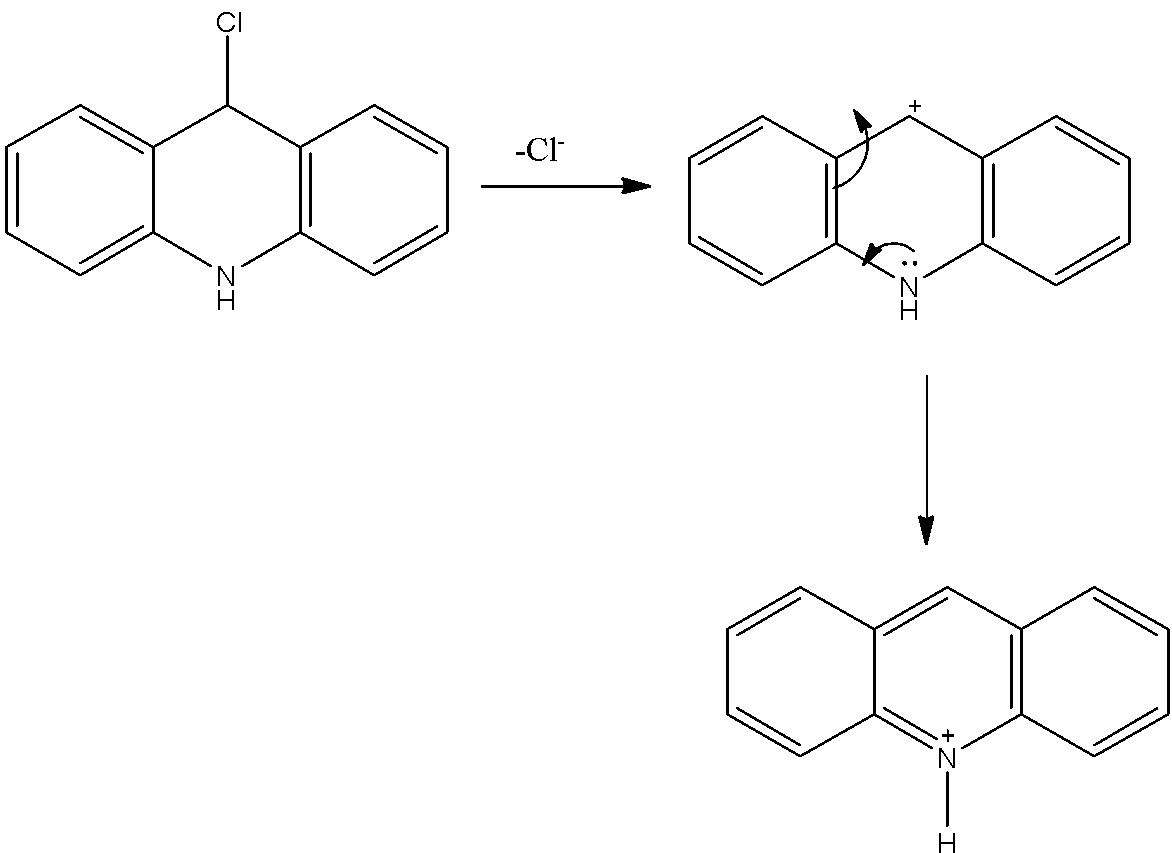
- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
- Coming to option C,
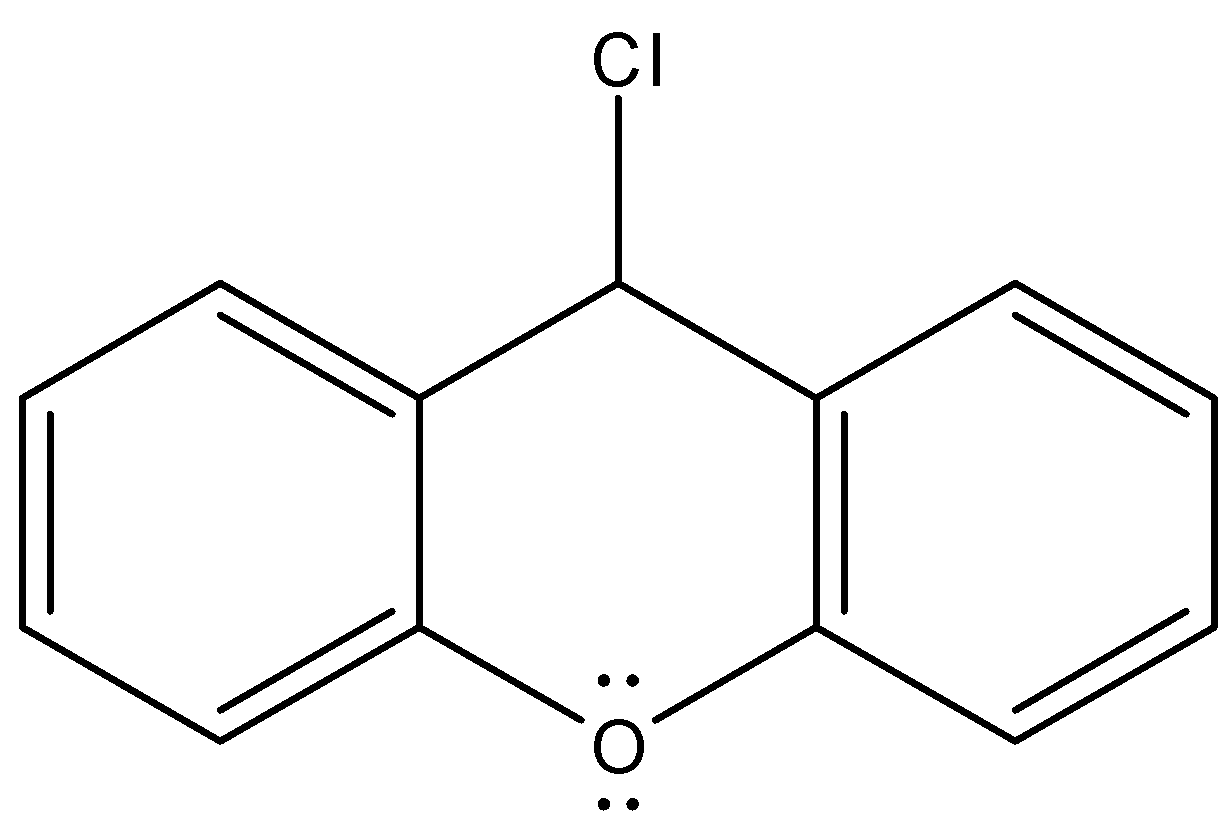
- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.
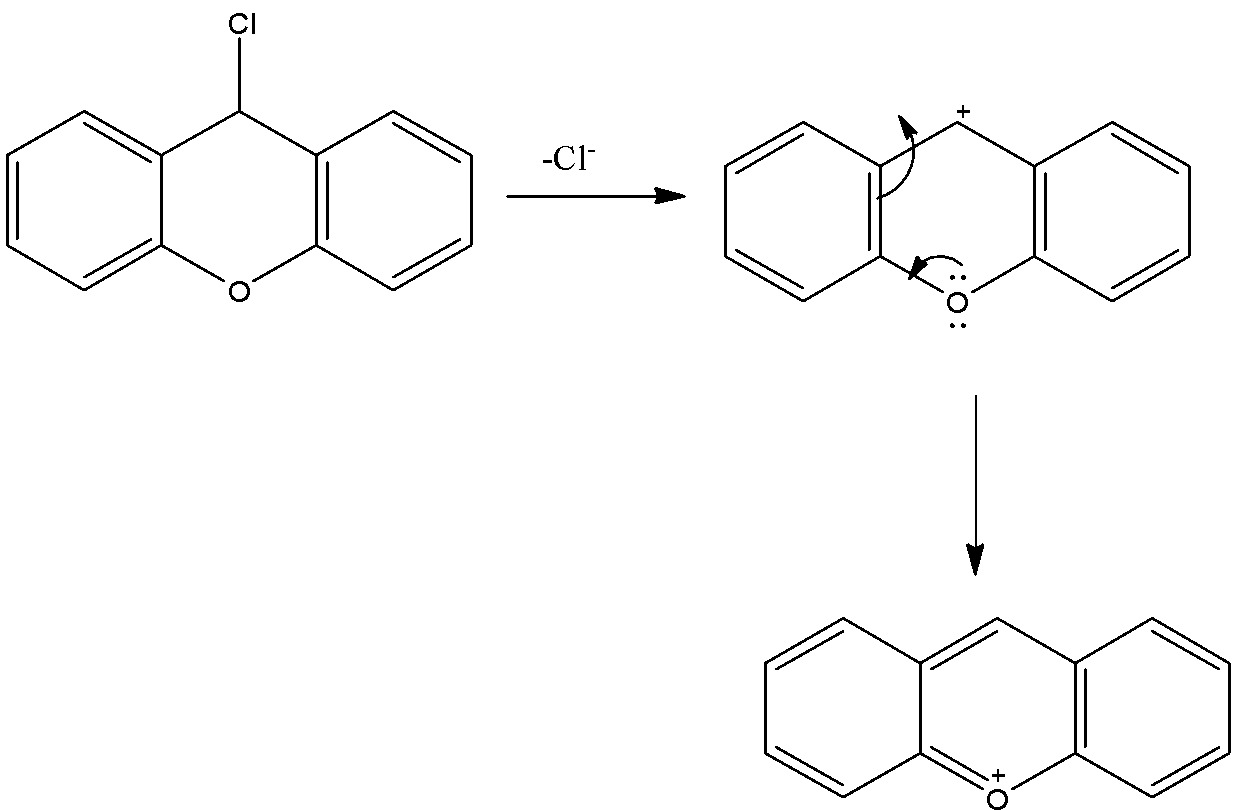
- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
- Coming to option D,
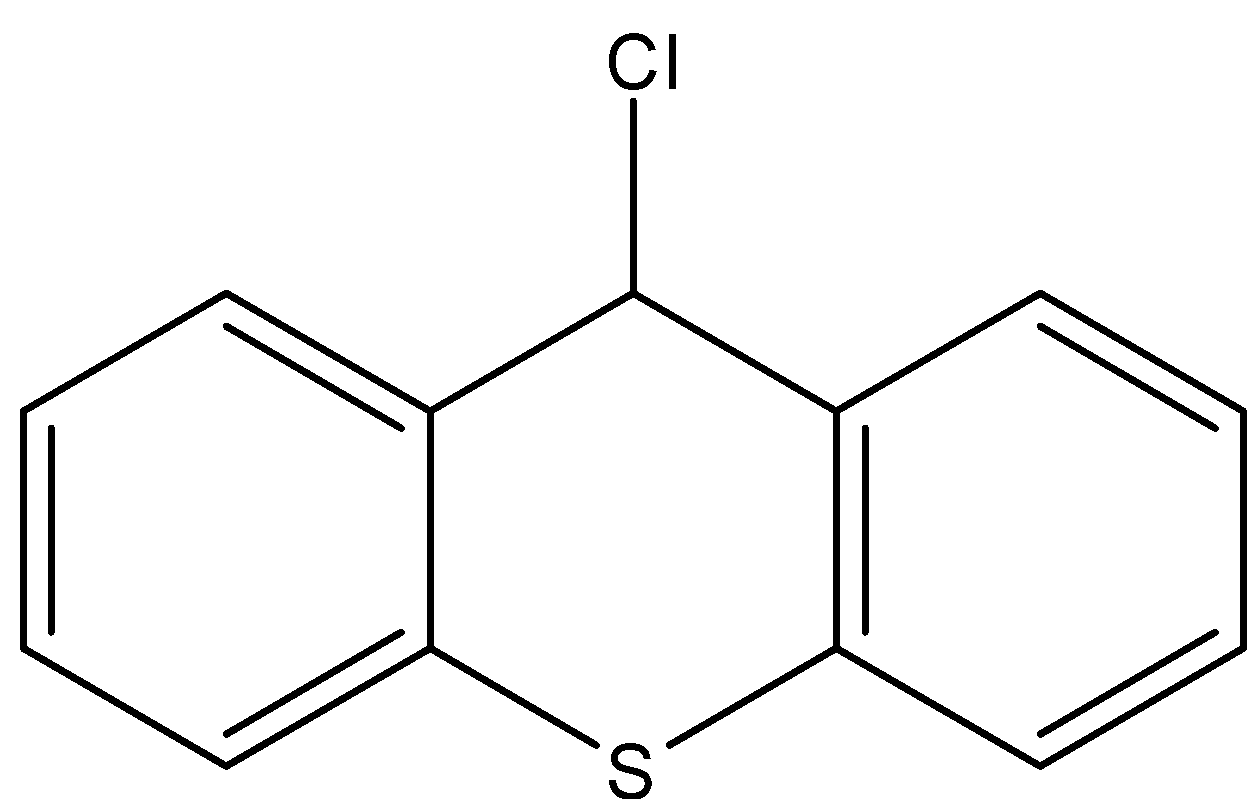
- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.
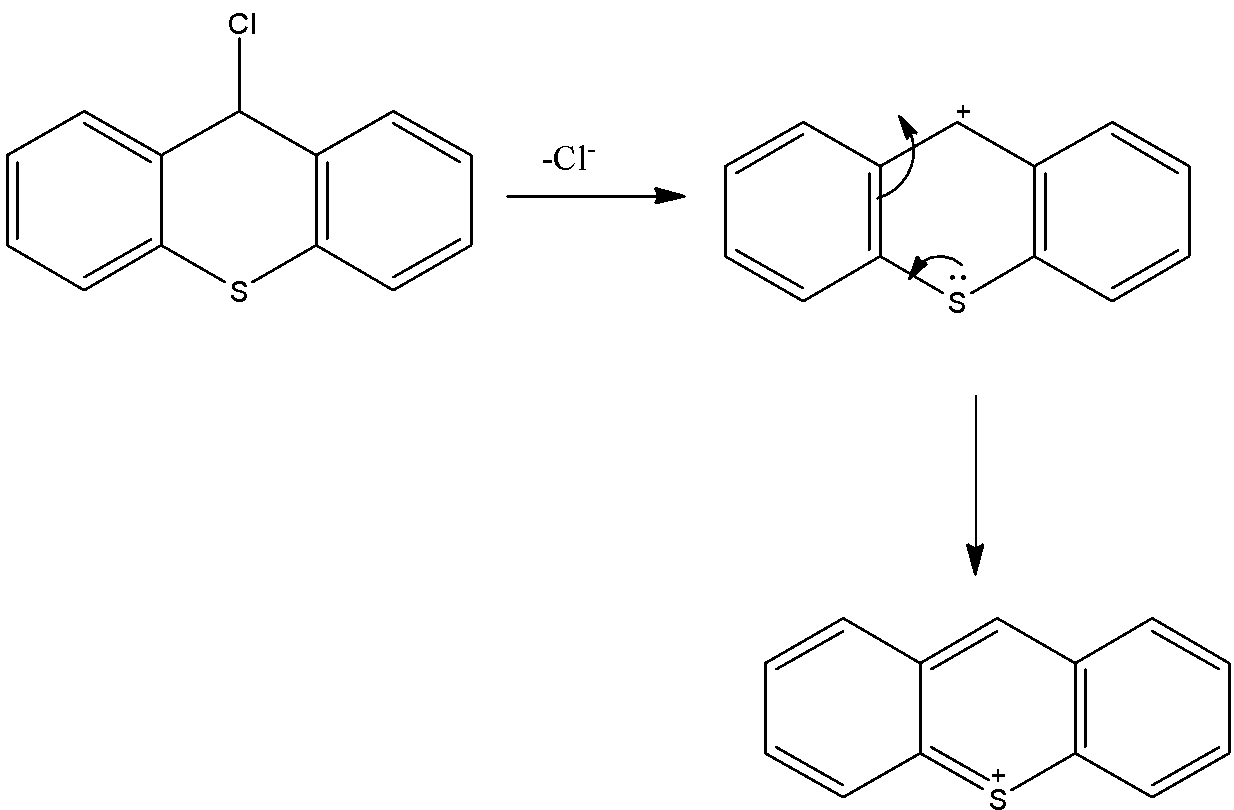
- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
If the cation which formed by the liberation of the halide is going to get stability due to the electron donation of the neighboring groups then the molecule is more stable than the normal compounds which do not have the neighboring group which donate electrons.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is given to find the compound which is going to react with KOH among the given options.
- Coming to the given options, option A.

- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.

- Now we can see clearly that no neighbor atom existed to stabilize the cationic species which is produced from the compound A.
- Therefore compound A is going to react with KOH.
- Coming to option B,

- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.

- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
- Coming to option C,

- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.

- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
- Coming to option D,

- If the chlorine atom comes out from the given organic compound we will get the following structure.

- The cation which is produced by the liberation of the chlorine atoms is stabilized by the neighboring nitrogen atom.
- Therefore the compound B is stable and won’t react with KOH.
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
If the cation which formed by the liberation of the halide is going to get stability due to the electron donation of the neighboring groups then the molecule is more stable than the normal compounds which do not have the neighboring group which donate electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




