
Which chemical reaction takes place in the mitochondria? Which molecules are produced in this reaction?
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Mitochondria is a cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, semi-autonomous organelle. Mitochondria is considered as the powerhouse of the cell as the energy molecules ATP are produced in the mitochondria.
Complete answer: A cell organelle which is semi-autonomous in function and is bound by a double membrane is called mitochondria. It is found in all cells of eukaryotic organisms. However, it is absent in some cells of multicellular organisms.
-An example is the erythrocytes which are referred to as RBC of the human blood. The main function of the mitochondria is to produce ATP molecules which are a source of energy for most of the metabolic activities to be carried in the body. Hence it is called a powerhouse of the cell as it provides power in the form of ATP.
-Depending upon the cell type the number of mitochondria in the cell varies. Mitochondria perform the function of the conversion of ADP into ATP by oxidizing pyruvate, glucose, and NADH. These oxidizing substrates are formed in the cytosol of the cell.
-Oxidative phosphorylation is the chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. Oxygen is converted to water molecules in oxidative phosphorylation reactions. Tricarboxylic acid cycles take place in the matrix of mitochondria in eukaryotes.
-Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) is also called a citric acid cycle (CAC) or Krebs cycle. Each molecule of glucose requires two turns of the Krebs cycle. Products obtained after completion of two rounds of Krebs cycle are two GTP, two ubiquinol, six NADH, and four molecules of carbon dioxide.
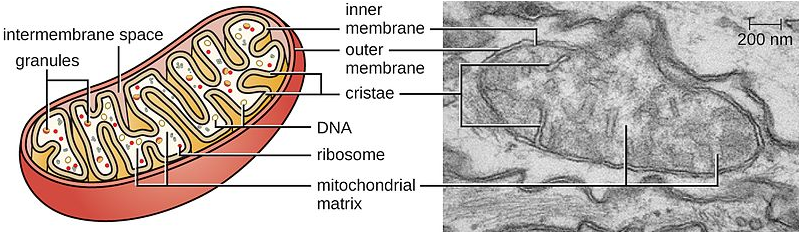
Note: The inner membrane of mitochondria contains proteins that are useful for the function of electron transport chain redox reactions, generation of ATP in the matrix of mitochondria, and for transporting the proteins in and out of the mitochondria. The enzyme ATP synthase is used for the production of ATP. Mitochondria also perform the function of regulating cellular metabolism.
Complete answer: A cell organelle which is semi-autonomous in function and is bound by a double membrane is called mitochondria. It is found in all cells of eukaryotic organisms. However, it is absent in some cells of multicellular organisms.
-An example is the erythrocytes which are referred to as RBC of the human blood. The main function of the mitochondria is to produce ATP molecules which are a source of energy for most of the metabolic activities to be carried in the body. Hence it is called a powerhouse of the cell as it provides power in the form of ATP.
-Depending upon the cell type the number of mitochondria in the cell varies. Mitochondria perform the function of the conversion of ADP into ATP by oxidizing pyruvate, glucose, and NADH. These oxidizing substrates are formed in the cytosol of the cell.
-Oxidative phosphorylation is the chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. Oxygen is converted to water molecules in oxidative phosphorylation reactions. Tricarboxylic acid cycles take place in the matrix of mitochondria in eukaryotes.
-Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) is also called a citric acid cycle (CAC) or Krebs cycle. Each molecule of glucose requires two turns of the Krebs cycle. Products obtained after completion of two rounds of Krebs cycle are two GTP, two ubiquinol, six NADH, and four molecules of carbon dioxide.

Note: The inner membrane of mitochondria contains proteins that are useful for the function of electron transport chain redox reactions, generation of ATP in the matrix of mitochondria, and for transporting the proteins in and out of the mitochondria. The enzyme ATP synthase is used for the production of ATP. Mitochondria also perform the function of regulating cellular metabolism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




