
Which cell is the largest cell in the male human body?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: The largest cell in the male human body is a nerve cell or neuron. These nerve cells are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system as well as responsible for receiving sensory input and sending signals. Neurons are produced by the process of neurogenesis. There are about 10-20 billion neurons estimated in the cerebral cortex and 55-70 billion neurons in the cerebellum of the human brain.
Complete answer:
In the male human body, nerve cells are more tightly packed and more numerous, unlike the female human body. It is 1 meter in length and 100 microns in diameter. Nerve cell is also the longest cell in the human body.
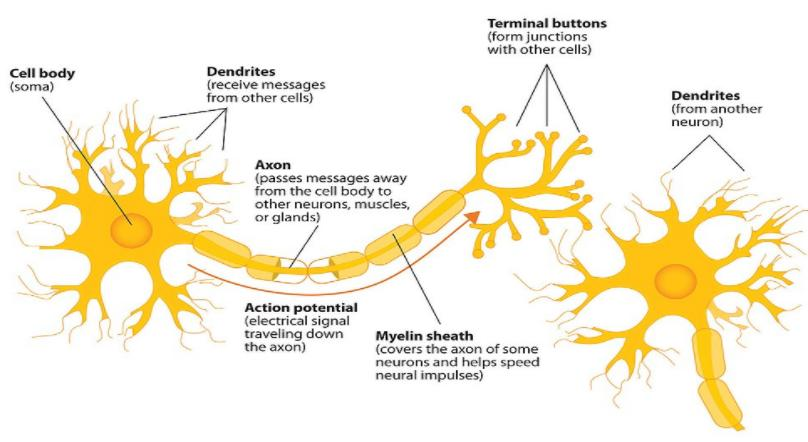
Nerve cells are the primary components of the nervous system, along with the glial cells which provide structural and metabolic support to them. A typical neuron mainly contains a cell body (called soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is the body of the neuron which contains the nucleus and gives space to most of the protein for their synthesis.
Neurons are excitable (generate and propagate electrical signals when excited) and secretory (secrete neurotransmitters) cells. They consist of specialized projections called axons which allow them to transmit electrical and chemical signals to the other cells. They can also receive these signals via dendrites.
Note:
Based on the function, neurons are mainly 3 types; sensory neuron (respond to stimuli and send signals to the spinal cord and brain), motor neurons (receive signals from the spinal cord and brain) and interneurons (connect neurons to other neurons within the same region and send information between sensory neurons and motor neurons).
Complete answer:
In the male human body, nerve cells are more tightly packed and more numerous, unlike the female human body. It is 1 meter in length and 100 microns in diameter. Nerve cell is also the longest cell in the human body.
Nerve cells are the primary components of the nervous system, along with the glial cells which provide structural and metabolic support to them. A typical neuron mainly contains a cell body (called soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is the body of the neuron which contains the nucleus and gives space to most of the protein for their synthesis.
Neurons are excitable (generate and propagate electrical signals when excited) and secretory (secrete neurotransmitters) cells. They consist of specialized projections called axons which allow them to transmit electrical and chemical signals to the other cells. They can also receive these signals via dendrites.

Note:
Based on the function, neurons are mainly 3 types; sensory neuron (respond to stimuli and send signals to the spinal cord and brain), motor neurons (receive signals from the spinal cord and brain) and interneurons (connect neurons to other neurons within the same region and send information between sensory neurons and motor neurons).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




