
Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation?
A.
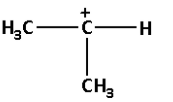
B.

C.
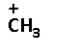
D.
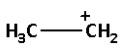


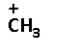
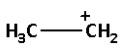
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: We know that carbocation is a positively charged carbon atom. The carbocation with the least partial positive charge is more stable. This is because the charge is distributed among neighbouring carbons. Higher the charge density on the carbon atom, more unstable is the carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
->The effect regarding the transmission of unequal sharing of the bonding electrons through a chain of atoms in a molecule which leads to permanent dipole in a bond is known as the inductive effect.
->The methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ group pushes electron density towards the carbon having positive charge and shows an inductive effect. As the methyl group pushes electron density towards the carbon having positive charge the charge density on the carbocation decreases.
Thus, more the number of methyl groups, more stable is the carbocation.
->We are given four carbocations. Carbocation (A) has two methyl groups, carbocation (B) has three methyl groups, carbocation (C) has no methyl group but has three hydrogen atoms and carbocation (D) has one methyl group.
Thus, carbocation (B) has the highest number of methyl groups and so it is the most stable carbocation.
Thus, the correct option is (B).
Note:
When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group it is known as a primary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to three other alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than the primary carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
->The effect regarding the transmission of unequal sharing of the bonding electrons through a chain of atoms in a molecule which leads to permanent dipole in a bond is known as the inductive effect.
->The methyl $\left( { - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ group pushes electron density towards the carbon having positive charge and shows an inductive effect. As the methyl group pushes electron density towards the carbon having positive charge the charge density on the carbocation decreases.
Thus, more the number of methyl groups, more stable is the carbocation.
->We are given four carbocations. Carbocation (A) has two methyl groups, carbocation (B) has three methyl groups, carbocation (C) has no methyl group but has three hydrogen atoms and carbocation (D) has one methyl group.
Thus, carbocation (B) has the highest number of methyl groups and so it is the most stable carbocation.
Thus, the correct option is (B).
Note:
When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group it is known as a primary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to two other alkyl groups it is known as a secondary carbocation. When a carbon atom carrying a positive charge is attached to three other alkyl groups it is known as a tertiary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation which is more stable than the primary carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




