
Where is your stomach located?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: The stomach is a hollow organ and is a sac-like expansion of the digestive system. It is present between the esophagus and small intestine. It serves as a temporary storage spot for food and aids in the mechanical distribution of food before food is passed into the intestine. The stomach possesses digestive glands and hence, some of the digestive processes take place in the stomach. The empty stomach in humans is 12 inches long and 6 inches wide.
Complete answer
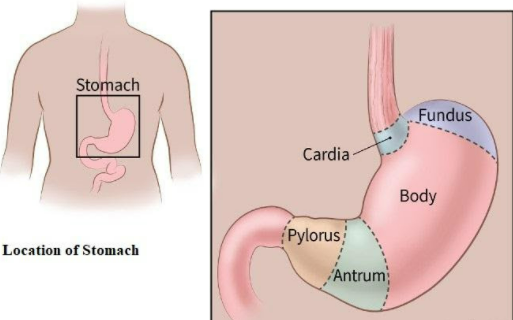
Fig: Region of Stomach. Displays the magnified view of the stomach and its regions.
The stomach is located in the abdominal cavity. It is present on the left side of the upper part of the abdominal cavity. The stomach is located below the liver and next to the spleen. The esophagus is capable to enter the stomach only after piercing via the diaphragm, separating the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The outlet of the stomach is through the duodenum, which is a part of the small intestine. The lower part of the rib cage aids in the partial protection of the stomach.
On the left side of the upper abdomen, a muscular organ is present, which is the stomach. It receives food from the esophagus. As the food enters the end part of the esophagus, it enters the stomach via a muscular valve, which is called the lower esophageal sphincter. The stomach secretes enzymes and acids that are used to digest food.
Note:
The stomach carries out many functions. Since it is a temporary storage organ, the urge for eating often is reduced. It secretes mucus, gastric hormone, hydrochloric acid, and pepsin. Pepsin enzyme is a proteolytic enzyme and carries out the digestive process. Due to hydrochloric acid, microorganisms can’t invade the gastrointestinal tract as higher pH prevents the microbes from surviving. Further, the stomach absorbs some water and alcohol.
Complete answer

Fig: Region of Stomach. Displays the magnified view of the stomach and its regions.
The stomach is located in the abdominal cavity. It is present on the left side of the upper part of the abdominal cavity. The stomach is located below the liver and next to the spleen. The esophagus is capable to enter the stomach only after piercing via the diaphragm, separating the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The outlet of the stomach is through the duodenum, which is a part of the small intestine. The lower part of the rib cage aids in the partial protection of the stomach.
On the left side of the upper abdomen, a muscular organ is present, which is the stomach. It receives food from the esophagus. As the food enters the end part of the esophagus, it enters the stomach via a muscular valve, which is called the lower esophageal sphincter. The stomach secretes enzymes and acids that are used to digest food.
Note:
The stomach carries out many functions. Since it is a temporary storage organ, the urge for eating often is reduced. It secretes mucus, gastric hormone, hydrochloric acid, and pepsin. Pepsin enzyme is a proteolytic enzyme and carries out the digestive process. Due to hydrochloric acid, microorganisms can’t invade the gastrointestinal tract as higher pH prevents the microbes from surviving. Further, the stomach absorbs some water and alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




