
Where is the tricuspid valve found?
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Valve is a flap-like structure that directs the one-way flow of fluid. In addition to it, the tricuspid valve is also called a right atrioventricular valve which directs the flow of deoxygenated blood from the atrium to the ventricle.
Complete answer: Heart is a hollow muscular organ that consists of four chambers. They consist of two atria and two ventricles. The upper chamber of the heart where the blood is collected is called atria and the lower chambers where the blood is poured from the atria is called ventricles. The right atrium consists of the deoxygenated blood collected by all parts of the body via superior and inferior vena cava. Oxygenated blood is conducted to the left atrium from the lungs via pulmonary veins. The flow of blood from the atria to the ventricles is guarded by a flap-like structure called a valve. Between the right atrium and right ventricle, a flap-like structure called a tricuspid valve is present. It prevents the backward flow of blood and ensures only one-way conduction of the blood. The tricuspid valve is so called because of its three leaflets namely anterior, posterior, and septal leaflets. The tricuspid valve is also called a right atrioventricular valve. The flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle is guarded by a bicuspid valve. The bicuspid valve is also called the mitral valve. The conduction of oxygenated blood to all body parts is done by blood vessels called arteries and the veins carry deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body to the right atrium of the heart by superior and inferior vena cava.
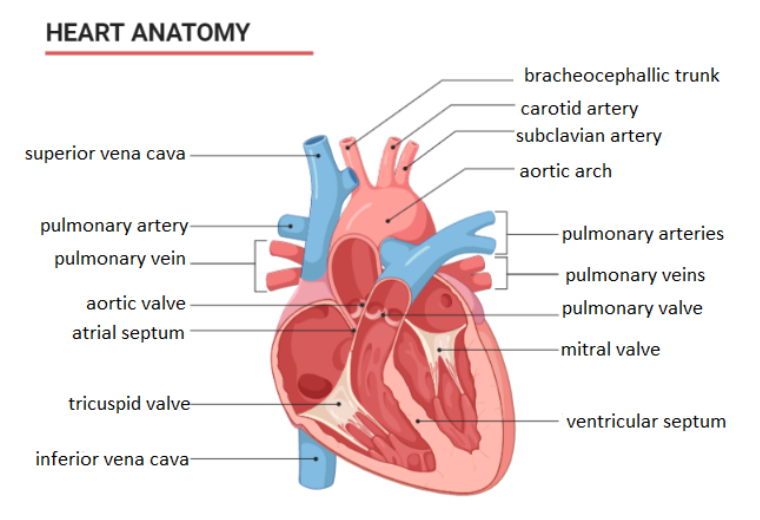
Note: Although veins carry deoxygenated blood and arteries carry oxygenated blood there is an exception in pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins. Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation whereas pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. This type of circulation between the lungs and heart is called pulmonary circulation.
Complete answer: Heart is a hollow muscular organ that consists of four chambers. They consist of two atria and two ventricles. The upper chamber of the heart where the blood is collected is called atria and the lower chambers where the blood is poured from the atria is called ventricles. The right atrium consists of the deoxygenated blood collected by all parts of the body via superior and inferior vena cava. Oxygenated blood is conducted to the left atrium from the lungs via pulmonary veins. The flow of blood from the atria to the ventricles is guarded by a flap-like structure called a valve. Between the right atrium and right ventricle, a flap-like structure called a tricuspid valve is present. It prevents the backward flow of blood and ensures only one-way conduction of the blood. The tricuspid valve is so called because of its three leaflets namely anterior, posterior, and septal leaflets. The tricuspid valve is also called a right atrioventricular valve. The flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle is guarded by a bicuspid valve. The bicuspid valve is also called the mitral valve. The conduction of oxygenated blood to all body parts is done by blood vessels called arteries and the veins carry deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body to the right atrium of the heart by superior and inferior vena cava.

Note: Although veins carry deoxygenated blood and arteries carry oxygenated blood there is an exception in pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins. Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation whereas pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. This type of circulation between the lungs and heart is called pulmonary circulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




