
When does DNA copying occur?
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint DNA replication takes place during gamete formation. Between cell divisions, the cells are in interphase, during which there's cell growth, and therefore the genetic material, DNA, contained within the chromosomes is duplicated.
Complete answer:
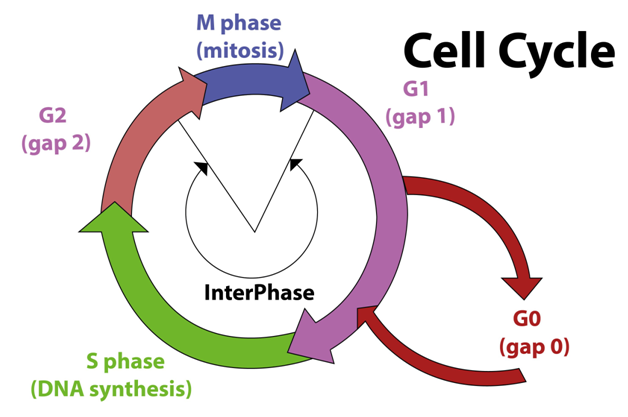
DNA copying which is also known as replication occurs during cell division. DNA replication is found to take place during the ‘S’ phase (synthesis phase) of the cell cycle. The ‘S’ phase of the cycle is followed by the ‘M’ phase or mitosis phase, where chromosomes segregate.
In the ‘S’ phase, the DNA content of chromosomes gets duplicated and it's a crucial step, in order that daughter cells contain an equivalent amount of DNA because of the parent cell. cellular division is required for growth differentiation and gamete formation. Interphase is further divided into three different types of stages ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$. DNA copying takes place within the S phase of the interphase nucleus.
Additional Information:
Interphase: Interphase is a long, non-dividing growing phase of the cell cycle, where the cell prepares itself for the division. It is further divided into three stages:
${ G }_{ 1 }$ Phase: This phase is considered as the interval between the mitosis phase and initiation of DNA replication. In this phase, the cell grows in size continuously and synthesizes nucleotides, ATP, amino acids, RNA, etc. Most of the organelles duplicate in this phase.
${ G }_{ 0 }$ Phase: The non-dividing cell enters the quiescent stage of the cell cycle. In this phase, the cell remains metabolically active but does not proliferate unless it is called on to do so.
S- Phase: It is also known as the synthesis phase. It is a phase in which the synthesis or replication of DNA takes place and there is a doubling of DNA. For example, if the DNA is 2N, then after the S phase the DNA becomes 4N. During this phase, DNA replication starts in the nucleus while the centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm.
${ G }_{ 2 }$ Phase: It is the second gap phase present between S and M phases.
M phase or mitotic phase is the phase where the actual cell division takes place. It consists of 2 processes, karyokinesis, and cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis: This phase marks the end of the cell division. The division of cytoplasm occurs in this phase. Cytokinesis is achieved by the formation of a furrow in the plasma membrane. It deepens and
ultimately divides the cell cytoplasm into two.
Note:
- Interphase is a biosynthetic phase in which the cell duplicates its organelles and replicates its DNA.
- Period of the cell cycle varies from organism to organism and also from cell to cell.
- Interphase is also called the Resting phase because it does not involve any activity related to cell division.
- Some cells which are present in adult animals do not divide e.g., nerve cells.
Complete answer:
DNA copying which is also known as replication occurs during cell division. DNA replication is found to take place during the ‘S’ phase (synthesis phase) of the cell cycle. The ‘S’ phase of the cycle is followed by the ‘M’ phase or mitosis phase, where chromosomes segregate.
In the ‘S’ phase, the DNA content of chromosomes gets duplicated and it's a crucial step, in order that daughter cells contain an equivalent amount of DNA because of the parent cell. cellular division is required for growth differentiation and gamete formation. Interphase is further divided into three different types of stages ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$. DNA copying takes place within the S phase of the interphase nucleus.
Additional Information:
Interphase: Interphase is a long, non-dividing growing phase of the cell cycle, where the cell prepares itself for the division. It is further divided into three stages:
${ G }_{ 1 }$ Phase: This phase is considered as the interval between the mitosis phase and initiation of DNA replication. In this phase, the cell grows in size continuously and synthesizes nucleotides, ATP, amino acids, RNA, etc. Most of the organelles duplicate in this phase.
${ G }_{ 0 }$ Phase: The non-dividing cell enters the quiescent stage of the cell cycle. In this phase, the cell remains metabolically active but does not proliferate unless it is called on to do so.
S- Phase: It is also known as the synthesis phase. It is a phase in which the synthesis or replication of DNA takes place and there is a doubling of DNA. For example, if the DNA is 2N, then after the S phase the DNA becomes 4N. During this phase, DNA replication starts in the nucleus while the centrioles duplicate in the cytoplasm.
${ G }_{ 2 }$ Phase: It is the second gap phase present between S and M phases.
M phase or mitotic phase is the phase where the actual cell division takes place. It consists of 2 processes, karyokinesis, and cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis: This phase marks the end of the cell division. The division of cytoplasm occurs in this phase. Cytokinesis is achieved by the formation of a furrow in the plasma membrane. It deepens and
ultimately divides the cell cytoplasm into two.

Note:
- Interphase is a biosynthetic phase in which the cell duplicates its organelles and replicates its DNA.
- Period of the cell cycle varies from organism to organism and also from cell to cell.
- Interphase is also called the Resting phase because it does not involve any activity related to cell division.
- Some cells which are present in adult animals do not divide e.g., nerve cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




