
What's auxiliary motion?
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: Movement of any object from one position to a different position with reference to the observer is named Motion. Motion Along a Straight Line: When an object moves along a line , the motion of the thing is named rectilinear motion. For example; motion of a car on the highway.
Complete answer:
To produce an honest quality of fabric and to stop damages it's required to possess some stop motion provided on the loom. These extra motions are mentioned as auxiliary motions.These motions aren't mandatory but are often essential permanently quality products.
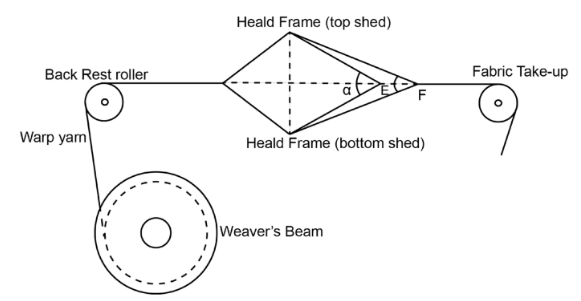
In the world of mechanics, there are four basic sorts of motion. These four are rotary, oscillating, linear and reciprocating. all moves during a slightly different way and every type is achieved using different mechanical means help us understand linear motion and motion control.
There are differing types of motion: translational, rotational, periodic, and non periodic movement. A kind of motion during which all parts of an object move an equivalent distance during a given time is called translational motion.
Note: Motion is caused by forces.A stationary object doesn't move unless a force acts thereon to start it going. Once it's moving, it carries on at an equivalent speed and within the same direction unless a force makes it speed up, change direction or hamper and stop.
Complete answer:
To produce an honest quality of fabric and to stop damages it's required to possess some stop motion provided on the loom. These extra motions are mentioned as auxiliary motions.These motions aren't mandatory but are often essential permanently quality products.

In the world of mechanics, there are four basic sorts of motion. These four are rotary, oscillating, linear and reciprocating. all moves during a slightly different way and every type is achieved using different mechanical means help us understand linear motion and motion control.
There are differing types of motion: translational, rotational, periodic, and non periodic movement. A kind of motion during which all parts of an object move an equivalent distance during a given time is called translational motion.
Note: Motion is caused by forces.A stationary object doesn't move unless a force acts thereon to start it going. Once it's moving, it carries on at an equivalent speed and within the same direction unless a force makes it speed up, change direction or hamper and stop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




