
What occurs during Translation?
Answer
481.5k+ views
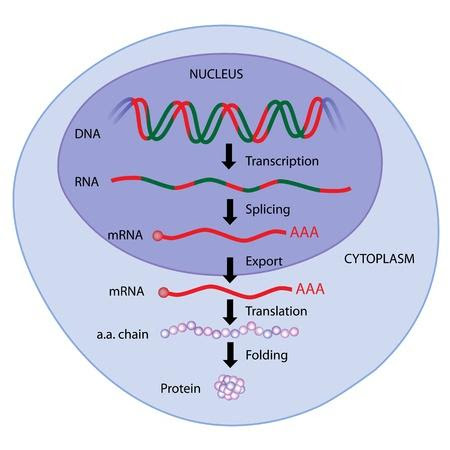
Hint: Translation is the process of synthesis of proteins which typically occurs in the ribosome. Translation is the process where DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is translated into mRNA proteins. During translation a sequence (mRNA) is being read using the genetic code, which is a set of rules defining mRNA sequence to be translated into the codes of amino acids, which are building blocks of proteins.
Complete answer-
Translation or protein synthesis is the next or second step of synthesis of proteins from DNA. According to central dogma the theory proves that first DNA rises to RNA and RNA helps in synthesis of proteins from RNA structures. If it is reversed it can only happen in case of bacteria or prokaryotes.
The stages in translation are- initiation, elongation and termination. These three steps are the major steps for protein synthesis. If it is reversed it is known as reverse transcriptase. First step is the initiation step where a start codon $5'$AUG is needed. That codon is specific to amino acid methionine which is always near to the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain. At the $5'$ cap of mRNA, the small subunits of the ribosome bind and the larger subunits bind to the initiation complex.
Second step is elongation- ribosomes have binding sites called P site and A site. One holds the peptide chain and another accepts the tRNA respectively. Methionine moves along the P site to A site a to get attached with new amino acid there, hence the elongation of peptide begins. mRNA translation works conjugation with tRNA and ribosomes in both present in the cytoplasm to create protein in a process known as translation.
Last step is the termination step- where stop codons enter into the A site. There is no tRNA molecule binding hence, P site becomes hydrolyze and releases the polypeptide into cytoplasm and small and large subunits of the ribosome dissociates.
Note:
In any DNA strand the strands initiating the template specially show-case this hydroxyl group. DNA sequence is stored in long sequences and maintained in a data bank. DNA sequences are placed in compact structures. Introns are in RNA which do not directly code for proteins. Introns are removed during the precursor messenger RNA or pre-mRNA.
Complete answer-
Translation or protein synthesis is the next or second step of synthesis of proteins from DNA. According to central dogma the theory proves that first DNA rises to RNA and RNA helps in synthesis of proteins from RNA structures. If it is reversed it can only happen in case of bacteria or prokaryotes.
The stages in translation are- initiation, elongation and termination. These three steps are the major steps for protein synthesis. If it is reversed it is known as reverse transcriptase. First step is the initiation step where a start codon $5'$AUG is needed. That codon is specific to amino acid methionine which is always near to the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain. At the $5'$ cap of mRNA, the small subunits of the ribosome bind and the larger subunits bind to the initiation complex.
Second step is elongation- ribosomes have binding sites called P site and A site. One holds the peptide chain and another accepts the tRNA respectively. Methionine moves along the P site to A site a to get attached with new amino acid there, hence the elongation of peptide begins. mRNA translation works conjugation with tRNA and ribosomes in both present in the cytoplasm to create protein in a process known as translation.
Last step is the termination step- where stop codons enter into the A site. There is no tRNA molecule binding hence, P site becomes hydrolyze and releases the polypeptide into cytoplasm and small and large subunits of the ribosome dissociates.

Note:
In any DNA strand the strands initiating the template specially show-case this hydroxyl group. DNA sequence is stored in long sequences and maintained in a data bank. DNA sequences are placed in compact structures. Introns are in RNA which do not directly code for proteins. Introns are removed during the precursor messenger RNA or pre-mRNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




