
What is Thomson's atom?
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: Before answering this question, we should know about its discovery. William Thomson in 1900 proposed Thomson atomic model. It described the inner structure of the atom in a theoretical manner. Sir Joseph Thomson who had discovered the electron supported this strongly.
Complete answer:
J.J. Thomson discovered negatively charged particles by cathode ray tube experiment in the year 1897. The vacuum tube is a cathode ray tube. The negative particle that was discovered was called an electron.
There was an assumption by Thomson that an electron is 2000 times lighter than a proton and it is said thousands of electrons combine to form an atom. The atom was surrounded by a cloud that has positive charge as well as negative charge in the atomic structure model. Rutherford and he did the demonstration of the ionization of air with the help of an X-ray. They demonstrated it first before anybody else did. Thomson’s model of an atom is somewhat similar to the plum pudding model.
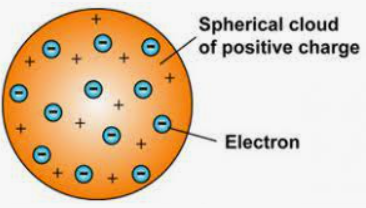
The postulates of Thomson’s atomic model are-
The atom has a positively charged sphere in which electrons are implanted.
There are negative and positive charges present in equal magnitude which makes the atom electrically neutral.
Thomson also compared this model to a watermelon in which the seeds of watermelon are negatively charged particles and the red part is the positively charged sphere.
Note:
The limitations of Thomson’s atomic model are-
How can a positive charge hold negatively charged electrons in an atom is not explained by this model. It fails to prove the stability of the atom. It also doesn’t tell about the position of the nucleus in an atom.
The scattering of alpha particles by thin metal foils is also not explained by this model.
There is also no proof of the experiment to support the theory.
Complete answer:
J.J. Thomson discovered negatively charged particles by cathode ray tube experiment in the year 1897. The vacuum tube is a cathode ray tube. The negative particle that was discovered was called an electron.
There was an assumption by Thomson that an electron is 2000 times lighter than a proton and it is said thousands of electrons combine to form an atom. The atom was surrounded by a cloud that has positive charge as well as negative charge in the atomic structure model. Rutherford and he did the demonstration of the ionization of air with the help of an X-ray. They demonstrated it first before anybody else did. Thomson’s model of an atom is somewhat similar to the plum pudding model.

The postulates of Thomson’s atomic model are-
The atom has a positively charged sphere in which electrons are implanted.
There are negative and positive charges present in equal magnitude which makes the atom electrically neutral.
Thomson also compared this model to a watermelon in which the seeds of watermelon are negatively charged particles and the red part is the positively charged sphere.
Note:
The limitations of Thomson’s atomic model are-
How can a positive charge hold negatively charged electrons in an atom is not explained by this model. It fails to prove the stability of the atom. It also doesn’t tell about the position of the nucleus in an atom.
The scattering of alpha particles by thin metal foils is also not explained by this model.
There is also no proof of the experiment to support the theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




