
What is the wavelength of the wave ?
Answer
525k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will study the basic anatomy of a wave. This way, we can know all the basic components of a wave and also give information about their relation with each other.
Complete answer:
Now, the first thing we start off is by looking at what exactly is a wave? As we all are aware with the wave-particle duality. It states that a particle can also be represented in the form of a wave. Therefore, a wave can be interpreted as a transfer of energy through a point from one point to another. The examples of waves are: the water waves, the sound waves, the radio waves, etc.
Now, we come up to the concept of wavelength. What exactly do we mean by the word wavelength? We can define wavelength as a distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave. The measurement is taken in the direction of the wave. It is measured in the units of lengths such as meters, centimeters, millimeters, nanometers, etc. but mostly it is measured in terms of an angstrom.
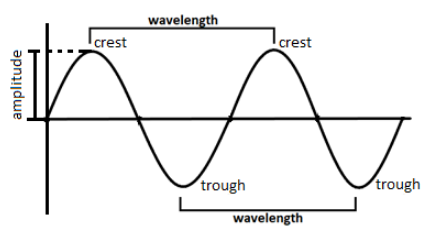
The equation by which the wavelength is represented is known as the wavelength formulae and we write it as,
Wavelength, $\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
Where $v$ is the velocity with which the wave is travelling and $f$ is the frequency of the wave.
The other important fact that we need to know is that the wavelength of the light varies with colours which implies that every colour which we see in nature has its own wavelength. The red colour has the longest wavelength whereas the violet colour has the shortest wavelength.
Note:The wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency as we can interpret from the formulae above. The higher the wavelength, the lower will be the frequency and vice versa. The UV radiation has a shorter wavelength compared to that of violet light and similarly the wavelength of infra-red light is longer than that of the red light.
Complete answer:
Now, the first thing we start off is by looking at what exactly is a wave? As we all are aware with the wave-particle duality. It states that a particle can also be represented in the form of a wave. Therefore, a wave can be interpreted as a transfer of energy through a point from one point to another. The examples of waves are: the water waves, the sound waves, the radio waves, etc.
Now, we come up to the concept of wavelength. What exactly do we mean by the word wavelength? We can define wavelength as a distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave. The measurement is taken in the direction of the wave. It is measured in the units of lengths such as meters, centimeters, millimeters, nanometers, etc. but mostly it is measured in terms of an angstrom.

The equation by which the wavelength is represented is known as the wavelength formulae and we write it as,
Wavelength, $\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
Where $v$ is the velocity with which the wave is travelling and $f$ is the frequency of the wave.
The other important fact that we need to know is that the wavelength of the light varies with colours which implies that every colour which we see in nature has its own wavelength. The red colour has the longest wavelength whereas the violet colour has the shortest wavelength.
Note:The wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency as we can interpret from the formulae above. The higher the wavelength, the lower will be the frequency and vice versa. The UV radiation has a shorter wavelength compared to that of violet light and similarly the wavelength of infra-red light is longer than that of the red light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




