
What is the steric number of $N{H_3}$?
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: Steric number is the number of atoms, groups, or lone pairs around the central atom in a molecule. It determines the molecular geometry. Find out the number of lone pairs and bonded atoms in $N{H_3}$ using Lewis structure and calculate the steric number using the formula:
Steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to central atom)
Complete answer:
The steric number is defined as the number of atoms bonded to a central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs attached to the central atom. The steric number is used in the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry of a molecule.
The formula for calculating the steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to the central atom)
Drawing Lewis's structure is important to calculate the steric number.
First we will draw the Lewis structure of $N{H_3}$ as follows:
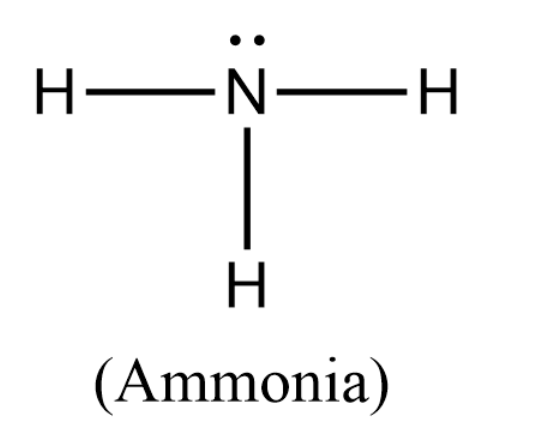
In the structure of ammonia, we can see that the nitrogen atom forms single bonds with three hydrogen atoms, with each of these bonds accounting for 2 valence electrons. The remaining 2 valence electrons are placed on the nitrogen atom as a lone pair of electrons.
Steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to central atom)
(For ammonia number of lone pairs$ = 1$ and number of bonded atoms $ = 3$)
Steric number$ = 1 + 3$
$ \Rightarrow 4$
Therefore the steric number of ammonia is $4$
Note:
The steric number also tells the hybridization of the central atom. In the case of ammonia, the steric number is $4$ and this implies that the hybridization of nitrogen atoms is $s{p^3}$. It also determines the bonded atom lone pair arrangement, the shape that maximizes the distances between the valence-shell electron pairs.
Steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to central atom)
Complete answer:
The steric number is defined as the number of atoms bonded to a central atom of a molecule plus the number of lone pairs attached to the central atom. The steric number is used in the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry of a molecule.
The formula for calculating the steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to the central atom)
Drawing Lewis's structure is important to calculate the steric number.
First we will draw the Lewis structure of $N{H_3}$ as follows:

In the structure of ammonia, we can see that the nitrogen atom forms single bonds with three hydrogen atoms, with each of these bonds accounting for 2 valence electrons. The remaining 2 valence electrons are placed on the nitrogen atom as a lone pair of electrons.
Steric number $ = $(number of lone pairs on central atom)$ + $(number of atoms bonded to central atom)
(For ammonia number of lone pairs$ = 1$ and number of bonded atoms $ = 3$)
Steric number$ = 1 + 3$
$ \Rightarrow 4$
Therefore the steric number of ammonia is $4$
Note:
The steric number also tells the hybridization of the central atom. In the case of ammonia, the steric number is $4$ and this implies that the hybridization of nitrogen atoms is $s{p^3}$. It also determines the bonded atom lone pair arrangement, the shape that maximizes the distances between the valence-shell electron pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




