
What is the Scattering angle?
Answer
498k+ views
Hint: Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes in which localised non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass cause moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, to deviate from a straight trajectory. This also includes divergence of reflected radiation from the angle anticipated by the law of reflection in traditional usage.
Complete answer:
Small-angle scattering (SAS) is a scattering technique that involves deflecting collimated radiation away from the straight path when it contacts objects considerably bigger than the wavelength of the radiation. Because the deflection is tiny ( $ 0.1 - 10^\circ $ ), the moniker "small-angle" was coined. The size, shape, and orientation of structures in a sample may be determined using SAS methods. SAS is a strong approach for studying large-scale structures with dimensions ranging from tens of thousands to tens of thousands of angstroms.
The SAS method's most essential characteristic is its ability to analyse the underlying structure of disordered systems, and it's often the only option to get direct structural information on systems with a random arrangement of density inhomogeneities at such vast sizes. The SAS approach is now a self-contained area of structural analysis of matter, with well-developed experimental and theoretical techniques and a large range of examined objects. Small angle neutron scattering (SANS) or small angle X-ray scattering (SAS) are two terms that can be used interchangeably (SAXS).
The angle at which a light beam is deflected by a particle when it comes into contact with it is known as the scattering angle.
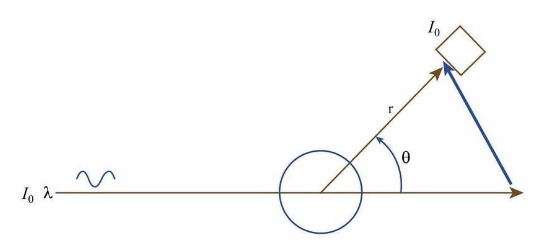
Here $ \theta $ is the scattered angle.
Note:
Single scattering occurs when radiation is dispersed by only one localised scattering site. Scattering centres are frequently clustered together; in such circumstances, radiation may scatter several times, resulting in multiple scattering. The main difference between single and multiple scattering effects is that single scattering can usually be treated as a random phenomenon, whereas multiple scattering can be modelled as a more deterministic process, despite the fact that the combined results of a large number of scattering events tend to average out. Diffusion theory may often be used to simulate multiple scattering.
Complete answer:
Small-angle scattering (SAS) is a scattering technique that involves deflecting collimated radiation away from the straight path when it contacts objects considerably bigger than the wavelength of the radiation. Because the deflection is tiny ( $ 0.1 - 10^\circ $ ), the moniker "small-angle" was coined. The size, shape, and orientation of structures in a sample may be determined using SAS methods. SAS is a strong approach for studying large-scale structures with dimensions ranging from tens of thousands to tens of thousands of angstroms.
The SAS method's most essential characteristic is its ability to analyse the underlying structure of disordered systems, and it's often the only option to get direct structural information on systems with a random arrangement of density inhomogeneities at such vast sizes. The SAS approach is now a self-contained area of structural analysis of matter, with well-developed experimental and theoretical techniques and a large range of examined objects. Small angle neutron scattering (SANS) or small angle X-ray scattering (SAS) are two terms that can be used interchangeably (SAXS).
The angle at which a light beam is deflected by a particle when it comes into contact with it is known as the scattering angle.

Here $ \theta $ is the scattered angle.
Note:
Single scattering occurs when radiation is dispersed by only one localised scattering site. Scattering centres are frequently clustered together; in such circumstances, radiation may scatter several times, resulting in multiple scattering. The main difference between single and multiple scattering effects is that single scattering can usually be treated as a random phenomenon, whereas multiple scattering can be modelled as a more deterministic process, despite the fact that the combined results of a large number of scattering events tend to average out. Diffusion theory may often be used to simulate multiple scattering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




