
What is the range of projectiles?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: When the projectile touches a vertical velocity of zero, range is the highest height of the projectile, and then gravity will get over and accelerate the object descending. The horizontal displacement of the object projected is called the projectile range and depends on the object's initial velocity.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Projectile motion is when an object passes in the parabolic path; its path is termed its trajectory. Objects projected from and land on a similar horizontal surface will have a vertically balanced path. The time it needs from an object to be thrown and land is named the time of flight. This depends on the angle of projection and the initial velocity of the projectile.
A projectile is an object that provides an initial velocity, and gravity works on it. A projectile's horizontal range is the length along with the horizontal level. Moreover, it would move before it approaches the same vertical position as it began. After that, the horizontal range depends on the initial velocity, the projected angle θ, and the acceleration happening due to gravity. The horizontal range's unit is meter (m).
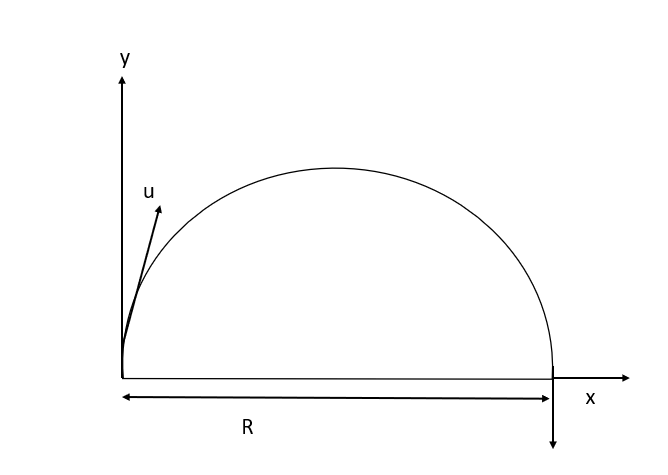
R is the range in the given figure.
The formula for range is:
$R = \dfrac{u^{2} sin 2\theta}{g}$
Where, u in initial velocity.
g is acceleration due to gravity.
Projectile motion is a motion where an object travels in a parabolic path. The path that the object obeys is called its trajectory.
Note:Projectile motion only happens when one force is exerted at the beginning of the trajectory, after which the only hindrance is from gravity. In physics, a projectile ejected with specific initial conditions will have a range. It may be more expected assuming a flat Earth with a regular gravity field and no air opposition.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Projectile motion is when an object passes in the parabolic path; its path is termed its trajectory. Objects projected from and land on a similar horizontal surface will have a vertically balanced path. The time it needs from an object to be thrown and land is named the time of flight. This depends on the angle of projection and the initial velocity of the projectile.
A projectile is an object that provides an initial velocity, and gravity works on it. A projectile's horizontal range is the length along with the horizontal level. Moreover, it would move before it approaches the same vertical position as it began. After that, the horizontal range depends on the initial velocity, the projected angle θ, and the acceleration happening due to gravity. The horizontal range's unit is meter (m).

R is the range in the given figure.
The formula for range is:
$R = \dfrac{u^{2} sin 2\theta}{g}$
Where, u in initial velocity.
g is acceleration due to gravity.
Projectile motion is a motion where an object travels in a parabolic path. The path that the object obeys is called its trajectory.
Note:Projectile motion only happens when one force is exerted at the beginning of the trajectory, after which the only hindrance is from gravity. In physics, a projectile ejected with specific initial conditions will have a range. It may be more expected assuming a flat Earth with a regular gravity field and no air opposition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




