
What is the most stable carbocation?
Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint: Carbocation is an ion bearing positively-charged carbon atom with six electrons in their valence shell which make them electron deficient. They are highly unstable electrophiles and quickly react with nucleophiles to form a new bond. Due to their reactivity with heteroatoms, carbocations are very useful intermediates in many organic reactions.
Complete answer:
There are mainly four different types of carbocation named on the basis of the carbon groups bonded with carbon. The different types of carbocation are methyl, primary, secondary and tertiary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Methyl carbocation: When no carbon is attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as methyl carbocation.
$ \bullet $Primary carbocation: When one carbon is attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as primary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Secondary carbocation: When two carbon are attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as secondary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Tertiary carbocation: When three carbons are attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as three carbocation.
The stability of carbocations depends on the following factors:
$1.$Resonance: The stability of carbocations are directly proportional to resonance. More the number of resonating structures, more is the stability of carbocation.
$2.$Hyperconjugation and inductive effect: Increasing substitution increases the hyperconjugation and thus it increases the stability.
$3.$Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the capacity of an atom to attract electrons. The electronegativity of a carbon with positive charge directly affects the stability of carbocations. Hence, more the electronegativity, more is the stability.
Therefore, from the above points we can say that tertiary carbocations are the most stable carbocation.
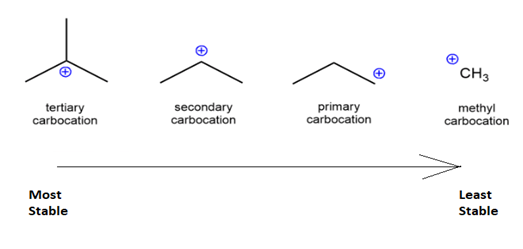
Fig: Stability of carbocation.
Note:
The formation of carbocation depends on two fundamental steps:
$1.$Cleavage of carbon bond: Whenever there is a cleavage of a bond, the leaving group takes away the shared electrons; thus making the carbon atom as electron deficient and as a result a positive charge is developed with the formation of a carbocation.
$2.$Electrophilic addition: In this case, electrophile attacks on the unsaturated points resulting in the formation of pi bond and formation of carbocation.
Complete answer:
There are mainly four different types of carbocation named on the basis of the carbon groups bonded with carbon. The different types of carbocation are methyl, primary, secondary and tertiary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Methyl carbocation: When no carbon is attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as methyl carbocation.
$ \bullet $Primary carbocation: When one carbon is attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as primary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Secondary carbocation: When two carbon are attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as secondary carbocation.
$ \bullet $Tertiary carbocation: When three carbons are attached to the carbon with positive charge, it is known as three carbocation.
The stability of carbocations depends on the following factors:
$1.$Resonance: The stability of carbocations are directly proportional to resonance. More the number of resonating structures, more is the stability of carbocation.
$2.$Hyperconjugation and inductive effect: Increasing substitution increases the hyperconjugation and thus it increases the stability.
$3.$Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the capacity of an atom to attract electrons. The electronegativity of a carbon with positive charge directly affects the stability of carbocations. Hence, more the electronegativity, more is the stability.
Therefore, from the above points we can say that tertiary carbocations are the most stable carbocation.

Fig: Stability of carbocation.
Note:
The formation of carbocation depends on two fundamental steps:
$1.$Cleavage of carbon bond: Whenever there is a cleavage of a bond, the leaving group takes away the shared electrons; thus making the carbon atom as electron deficient and as a result a positive charge is developed with the formation of a carbocation.
$2.$Electrophilic addition: In this case, electrophile attacks on the unsaturated points resulting in the formation of pi bond and formation of carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




