
What is the hybridization in \[HCl\]?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is a hypothetical concept adopted to explain geometry and bond properties of polyatomic molecules. This is hydrochloric acid in the aqueous form and hydrogen chloride if it is in gas form.
Complete answer:
Before going to the hybridization of hydrochloric acid, it is important to know the Lewis dot structure of it. In simple words, Lewis dot structure is the distribution of electrons around the atoms which helps us to find out the number and types of bonds in the compound.
Chlorine, being a halogen, needs one electron to complete its octet. Likewise, hydrogen also needs one more electron to attain an octet because hydrogen’s outermost shell can hold upto two electrons. The Lewis dot structure will be:
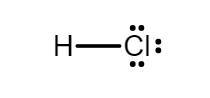
According to the VSEPR theory, \[HCl\] has linear molecular geometry/shape and tetrahedral electron geometry. The bond angle is ${180^\circ }$. Hydrochloric acid is an $AX{E_3}$ type molecule where,
A= the central atom= chlorine, X= atom bonded to A= hydrogen, E=lone pair on A= $3$
Hydrochloric acid has no hybridization, because \[HCl\] being a linear diatomic molecule, has a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom bonded covalently. So there is no need for any extra stability.
Note:
Being a diatomic molecule, it only had one atom as a surrounding atom. Thus there can be only one possibility of structure and so extra stability is needed for this molecule. Hybridization of a molecule can be predicted either from the VSEPR theory chart or using the formula:
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$
Here, H= hybridization, V= number of valence electrons, M= number of monovalent atoms, C= charge of the cation, A= charge of the anion.
Complete answer:
Before going to the hybridization of hydrochloric acid, it is important to know the Lewis dot structure of it. In simple words, Lewis dot structure is the distribution of electrons around the atoms which helps us to find out the number and types of bonds in the compound.
Chlorine, being a halogen, needs one electron to complete its octet. Likewise, hydrogen also needs one more electron to attain an octet because hydrogen’s outermost shell can hold upto two electrons. The Lewis dot structure will be:

According to the VSEPR theory, \[HCl\] has linear molecular geometry/shape and tetrahedral electron geometry. The bond angle is ${180^\circ }$. Hydrochloric acid is an $AX{E_3}$ type molecule where,
A= the central atom= chlorine, X= atom bonded to A= hydrogen, E=lone pair on A= $3$
Hydrochloric acid has no hybridization, because \[HCl\] being a linear diatomic molecule, has a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom bonded covalently. So there is no need for any extra stability.
Note:
Being a diatomic molecule, it only had one atom as a surrounding atom. Thus there can be only one possibility of structure and so extra stability is needed for this molecule. Hybridization of a molecule can be predicted either from the VSEPR theory chart or using the formula:
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$
Here, H= hybridization, V= number of valence electrons, M= number of monovalent atoms, C= charge of the cation, A= charge of the anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




