
What is the function of a goblet cell?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Goblet cells are those that are concerned with mucus production in the body. They function exactly like exocrine (duct bearing) glands secreting mucus into respective organs.
Complete answer:
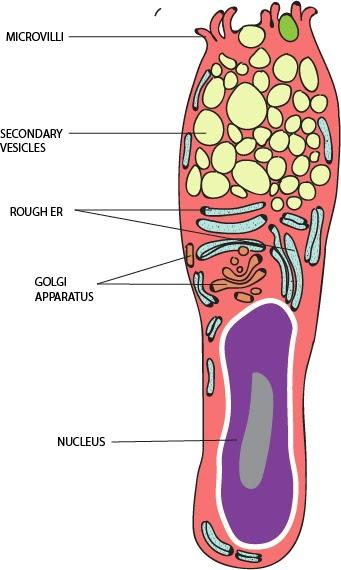
Goblet cells are merocrine producers of semi-solid and salty fluid called mucus. Though they are not glands yet their method of functioning makes it appear as an exocrine gland (that uses ducts to secrete its fluid). However, its structure is such that its opening is through a duct like villi (hair like structure) that imparts secreting mucus a gland like image.
Following are enlisted few of the functions of the goblet cells:
1. Manufacturing of mucus that helps in absorption of nutrients directly into the blood.
2. Frames a protective mucosal layer that engulfs harmful microorganisms thus, protects the organ.
3. Production of moisty mucus that provides lubrication to the organs while functioning.
Mucus is one of the most important fluids produced in the body. It is a kind of a glycoprotein that has comparatively higher molecular weight than others. Its physical state varies from semi-solid to liquid depending upon its need. It serves various functions while reciting inside the organ. It is generally produced in the inner lining of the organ through goblet cells. These goblet cells are producers of the mucosal layer inside any organ, especially the small and
large intestines.
Note:
The entire epithelial length of intestines have a covering of mucus as it helps in digestion. It is generally found in the epithelium layer of various organs in order to provide protection along with lubrication.
Complete answer:
Goblet cells are merocrine producers of semi-solid and salty fluid called mucus. Though they are not glands yet their method of functioning makes it appear as an exocrine gland (that uses ducts to secrete its fluid). However, its structure is such that its opening is through a duct like villi (hair like structure) that imparts secreting mucus a gland like image.
Following are enlisted few of the functions of the goblet cells:
1. Manufacturing of mucus that helps in absorption of nutrients directly into the blood.
2. Frames a protective mucosal layer that engulfs harmful microorganisms thus, protects the organ.
3. Production of moisty mucus that provides lubrication to the organs while functioning.
Mucus is one of the most important fluids produced in the body. It is a kind of a glycoprotein that has comparatively higher molecular weight than others. Its physical state varies from semi-solid to liquid depending upon its need. It serves various functions while reciting inside the organ. It is generally produced in the inner lining of the organ through goblet cells. These goblet cells are producers of the mucosal layer inside any organ, especially the small and
large intestines.

Note:
The entire epithelial length of intestines have a covering of mucus as it helps in digestion. It is generally found in the epithelium layer of various organs in order to provide protection along with lubrication.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




