
What is the classification of bones?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Bones are rigid muscles that provide shape and strength to the body of a vast majority of vertebrates. Different types of bones function together to form the skeletal system. The bones are of different sizes and shapes depending on the specific function it does.
Complete answer:
There are 206 bones in the human body. The basis of classification of bones depends on their shape. The different types of bones present in the human body are:
Long bones: These bones possess a cylindrical shape, and are longer than the other bones. The locations of these types of bones are in the arms (E.g.: Radius, Ulna and Humerus) and legs (Eg: Tibia, Fibula and Femur). These bones function as levers and help in movement, working in association with various muscles.
Short bones: These bones take up club- like shapes. The length, breadth and thickness of these bones are approximately equal. Carpals and Tarsals of the fingers are examples of these types of bones. These bones provide stability as well as support during movements.
Flat bones: These are thinned and curved bones. Ribs, scapulae, sternum and cranial bones are the examples belonging to this category.
Irregular bones: These bones possess a complex shape. Facial bones as well as vertebrae are the examples. These function as protective structures to the internal organs.
Sesamoid bones: These are round bones which are small in size. They are embedded onto tendons. Patellae is an example for this category. These bones help in protecting the tendons from the various compressive forces.
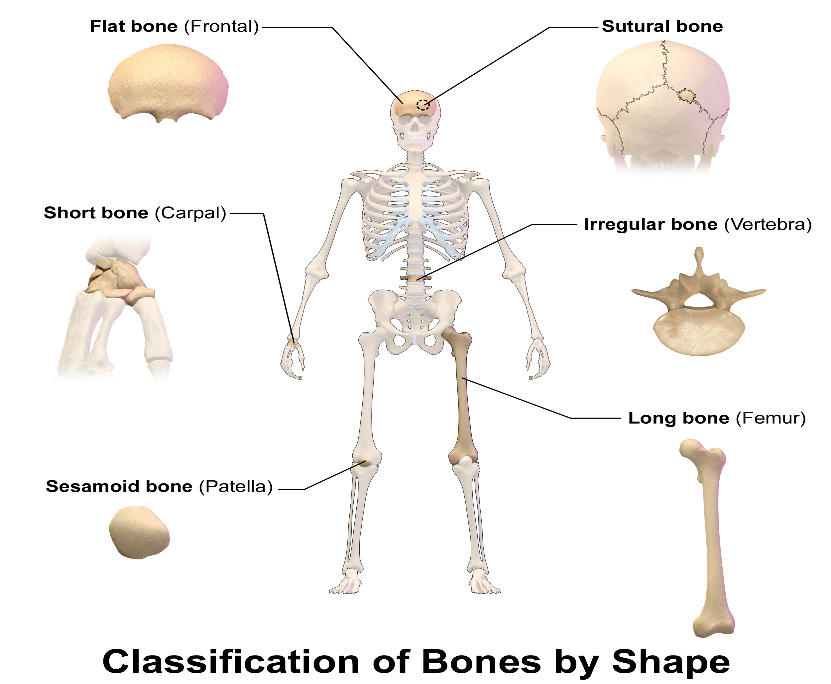
Figure: Classification of bones by shape
Note:
The major functions carried out by bones are in facilitating movements, they provide a structural framework to the body. It also helps in functioning as a hard outer cage for protecting the softer internal organs inside. It also functions as a factory where blood cells are produced from the bone marrow.
Complete answer:
There are 206 bones in the human body. The basis of classification of bones depends on their shape. The different types of bones present in the human body are:
Long bones: These bones possess a cylindrical shape, and are longer than the other bones. The locations of these types of bones are in the arms (E.g.: Radius, Ulna and Humerus) and legs (Eg: Tibia, Fibula and Femur). These bones function as levers and help in movement, working in association with various muscles.
Short bones: These bones take up club- like shapes. The length, breadth and thickness of these bones are approximately equal. Carpals and Tarsals of the fingers are examples of these types of bones. These bones provide stability as well as support during movements.
Flat bones: These are thinned and curved bones. Ribs, scapulae, sternum and cranial bones are the examples belonging to this category.
Irregular bones: These bones possess a complex shape. Facial bones as well as vertebrae are the examples. These function as protective structures to the internal organs.
Sesamoid bones: These are round bones which are small in size. They are embedded onto tendons. Patellae is an example for this category. These bones help in protecting the tendons from the various compressive forces.

Figure: Classification of bones by shape
Note:
The major functions carried out by bones are in facilitating movements, they provide a structural framework to the body. It also helps in functioning as a hard outer cage for protecting the softer internal organs inside. It also functions as a factory where blood cells are produced from the bone marrow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




