
What is the Carbylamine reaction?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, first we need to understand how carbylamines are formed. Carbylamine are formed when we perform the test to detect primary amines. Then, in the whole Carbylamine chemical test there are different compounds that are formed when amine is added to the reaction. Remember that the reaction is carried out in two steps for the formation of isocyanides.
Complete step by step answer:
The carbylamine reaction is also known as Hoffmann's isocyanide synthesis. Now, we need to understand what happens in this chemical reaction. The carbylamine reaction involves synthesis of an isocyanide when primary amine, chloroform, and a base are reacted. The reaction involves conversion of dichlorocarbene which acts to be an intermediate in the reaction. .
Just refer to this reaction where you can see the synthesis of tert-butyl isocyanide from tert-butylamine in the presence of a catalytic amount which involves phase transfer of the catalyst benzyltriethylammonium chloride.
Likewise to carbylamine reactions there are reactions for aniline which is used to prepare secondary amines.
Now, let’s refer to the mechanism of the carbylamine reaction:
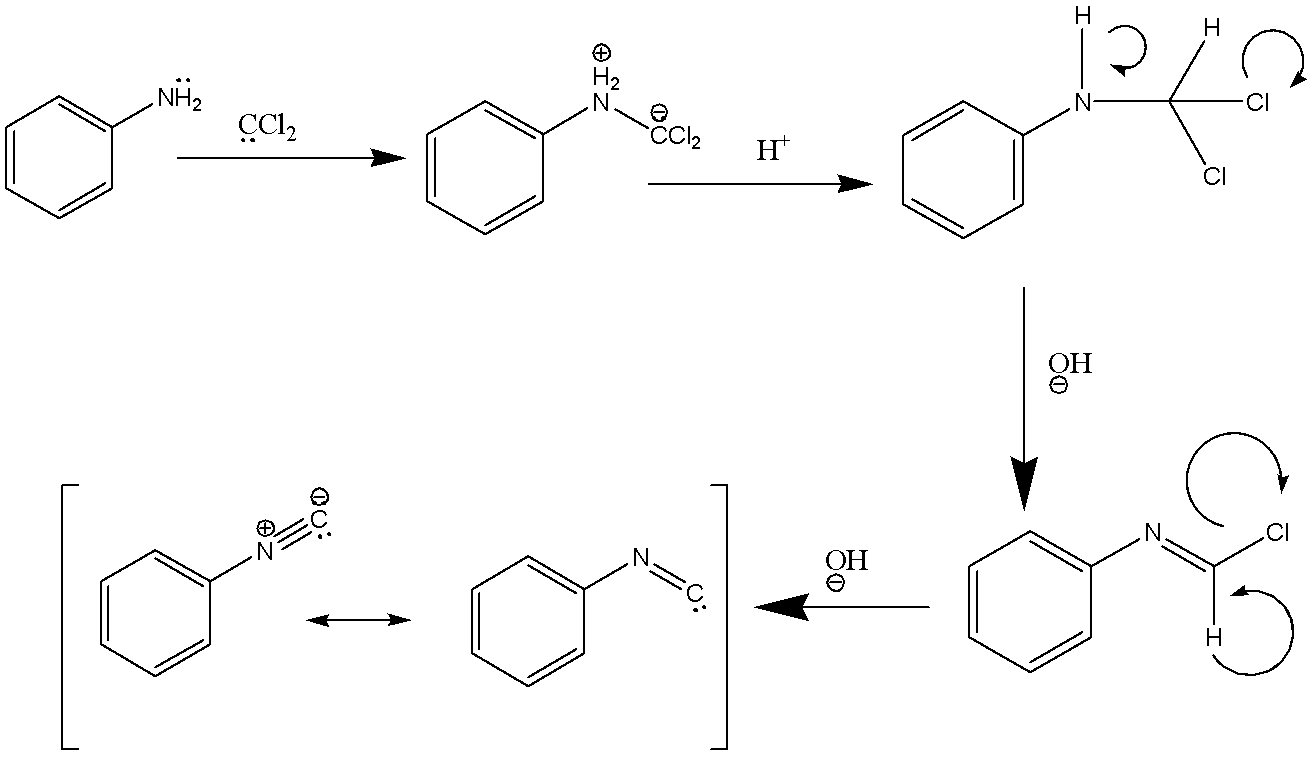
The mechanism of the carbylamine reaction involves the addition of amine to dichlorocarbene which is a reactive intermediate generated by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. There are two successive base-mediated in the dehydrochlorination of chloroform that result in the formation of an isocyanide.
Note:
We must know that an effective method to test primary amines, this carbylamine reaction can be further used as a chemical test. Also known as Saytzeff's isocyanide test in which the analyte is heated in the presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform. If a primary amine is found which is indicated by a foul odor then isocyanides is formed.
Complete step by step answer:
The carbylamine reaction is also known as Hoffmann's isocyanide synthesis. Now, we need to understand what happens in this chemical reaction. The carbylamine reaction involves synthesis of an isocyanide when primary amine, chloroform, and a base are reacted. The reaction involves conversion of dichlorocarbene which acts to be an intermediate in the reaction. .
Just refer to this reaction where you can see the synthesis of tert-butyl isocyanide from tert-butylamine in the presence of a catalytic amount which involves phase transfer of the catalyst benzyltriethylammonium chloride.
\[M{e_3}CN{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + 3NaOH \to M{e_3}CNC + 3NaCl + 3{H_2}O\]
Likewise to carbylamine reactions there are reactions for aniline which is used to prepare secondary amines.
Now, let’s refer to the mechanism of the carbylamine reaction:
The mechanism of the carbylamine reaction involves the addition of amine to dichlorocarbene which is a reactive intermediate generated by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. There are two successive base-mediated in the dehydrochlorination of chloroform that result in the formation of an isocyanide.

Note:
We must know that an effective method to test primary amines, this carbylamine reaction can be further used as a chemical test. Also known as Saytzeff's isocyanide test in which the analyte is heated in the presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide and chloroform. If a primary amine is found which is indicated by a foul odor then isocyanides is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




