
State Snell’s first and second law of refraction.
Answer
610.8k+ views
Hint: Refraction deals with bending of light at the interface of two mediums of different refractive index. So the angle associated with the incidence and refraction can have a relation to the refractive index of the two mediums.
Complete step by step answer:
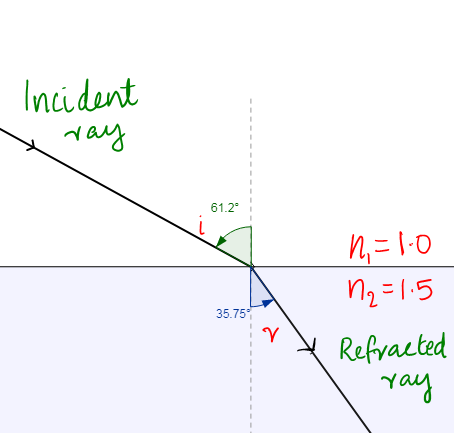
Snell’s First Law: It states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal lie on the same plane.
Snell’s second law: It states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalent to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
$\dfrac{\sin r}{\sin i}=\dfrac{{{\text{n}}_{\text{1}}}}{{{\text{n}}_{\text{2}}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{v}}_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{v}}_{\text{1}}}}$
Where,
${{\text{v}}_{2}}$ is the phase velocity of light in medium 2.
${{\text{v}}_{1}}$ is the phase velocity of light in medium 1.
${{\text{n}}_{\text{1}}}$ is the refractive index of medium 1.
${{\text{n}}_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium 2.
‘r’ is the angle of refraction.
‘i’ is the angle of incidence.
Additional Information:
Snell’s law is responsible for many physical phenomena like mirages, dispersion, apparent depth etc..
In optics, the refractive index of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how fast light travels through the material.
Note: Optical prisms and lenses use refraction to redirect light, as does the human eye. The refractive index of materials varies with the wavelength of light, and thus the angle of the refraction also varies correspondingly. This is called dispersion and causes prisms and rainbows to divide white light into its constituent spectral colors.
Complete step by step answer:

Snell’s First Law: It states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal lie on the same plane.
Snell’s second law: It states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalent to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction.
$\dfrac{\sin r}{\sin i}=\dfrac{{{\text{n}}_{\text{1}}}}{{{\text{n}}_{\text{2}}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{v}}_{\text{2}}}}{{{\text{v}}_{\text{1}}}}$
Where,
${{\text{v}}_{2}}$ is the phase velocity of light in medium 2.
${{\text{v}}_{1}}$ is the phase velocity of light in medium 1.
${{\text{n}}_{\text{1}}}$ is the refractive index of medium 1.
${{\text{n}}_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium 2.
‘r’ is the angle of refraction.
‘i’ is the angle of incidence.
Additional Information:
Snell’s law is responsible for many physical phenomena like mirages, dispersion, apparent depth etc..
In optics, the refractive index of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how fast light travels through the material.
Note: Optical prisms and lenses use refraction to redirect light, as does the human eye. The refractive index of materials varies with the wavelength of light, and thus the angle of the refraction also varies correspondingly. This is called dispersion and causes prisms and rainbows to divide white light into its constituent spectral colors.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




