
What is \[\tan 1x\] ?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: Sometimes \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] or \[\arctan x\] is also written in the form \[\tan 1x\] . So, \[\tan 1x\] is the compositional inverse of the trigonometric function tangent and it gives an answer in the form of an angle. It is basically used to find an angle from the trigonometric ratios.
Formula used: The formulas used are:
If
\[\begin{align}
& y=\tan x \\
& x={{\tan }^{-1}}y \\
\end{align}\]
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\pm {{\tan }^{-1}}y={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x\pm y}{1\pm xy} \right)\]
Derivative of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] :
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{1+{{x}^{2}}} \\
& x\ne +1,-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
\[\tan 1x\] is another form of the inverse of tangent function. It is also written in the form \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] or \[\arctan x\] . Now let us see some of its properties.
Addition of two tangent inverse functions:
If \[x\] and \[y\] are two angles, then,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\pm {{\tan }^{-1}}y={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x\pm y}{1\pm xy} \right)\]
Derivative of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] :
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{1+{{x}^{2}}} \\
& x\ne +1,-1 \\
\end{align}\]
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] can also be obtained by integrating the derivative within the limits \[0\] to \[x\] .
The graph of inverse tangent function:
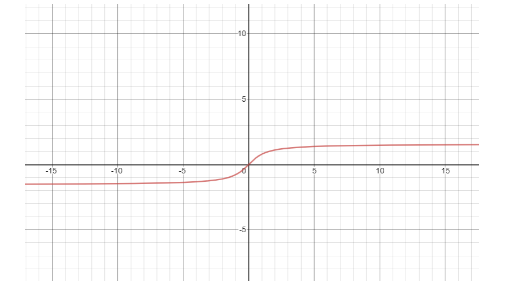
Other inverse tangent properties:
Domain of the ratio is all real numbers
Range of value in radians is \[-\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]<\[x\]<\[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Range of value in degrees is \[-90^\circ\] <\[x\]<\[90^\circ \]
The tangent inverse of infinity is:
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty \\
& {{\tan }^{-1}}\infty =\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: If we want to calculate an angle in a right angled triangle, then the inverse tangent function can be used for this. i.e. in a right angled triangle ABC
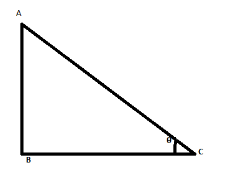
Angle, \[\theta \] can be calculated as:
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{AB}{BC} \right)\]
Where, \[AB\] is on the opposite side and \[BC\] is on the adjacent side.
It is to be noted that \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] should not be confused with \[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}\] because \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] is the inverse of the tangent function while \[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}\] is the cotangent i.e.
\[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{\tan x}=\cot x\]
As the tan inverse or \[\tan 1x\] gives the value in the form of an angle, so, the numbers between which the value of \[\tan 1x\] lies i.e. the range of \[\tan 1x\] is also calculated in degrees or radians.
Formula used: The formulas used are:
If
\[\begin{align}
& y=\tan x \\
& x={{\tan }^{-1}}y \\
\end{align}\]
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\pm {{\tan }^{-1}}y={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x\pm y}{1\pm xy} \right)\]
Derivative of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] :
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{1+{{x}^{2}}} \\
& x\ne +1,-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
\[\tan 1x\] is another form of the inverse of tangent function. It is also written in the form \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] or \[\arctan x\] . Now let us see some of its properties.
Addition of two tangent inverse functions:
If \[x\] and \[y\] are two angles, then,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\pm {{\tan }^{-1}}y={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{x\pm y}{1\pm xy} \right)\]
Derivative of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] :
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{1+{{x}^{2}}} \\
& x\ne +1,-1 \\
\end{align}\]
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] can also be obtained by integrating the derivative within the limits \[0\] to \[x\] .
The graph of inverse tangent function:

Other inverse tangent properties:
Domain of the ratio is all real numbers
Range of value in radians is \[-\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]<\[x\]<\[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
Range of value in degrees is \[-90^\circ\] <\[x\]<\[90^\circ \]
The tangent inverse of infinity is:
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \dfrac{\pi }{2}=\infty \\
& {{\tan }^{-1}}\infty =\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: If we want to calculate an angle in a right angled triangle, then the inverse tangent function can be used for this. i.e. in a right angled triangle ABC

Angle, \[\theta \] can be calculated as:
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{AB}{BC} \right)\]
Where, \[AB\] is on the opposite side and \[BC\] is on the adjacent side.
It is to be noted that \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] should not be confused with \[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}\] because \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] is the inverse of the tangent function while \[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}\] is the cotangent i.e.
\[{{\left( \tan x \right)}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{\tan x}=\cot x\]
As the tan inverse or \[\tan 1x\] gives the value in the form of an angle, so, the numbers between which the value of \[\tan 1x\] lies i.e. the range of \[\tan 1x\] is also calculated in degrees or radians.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




