
What is product A ?
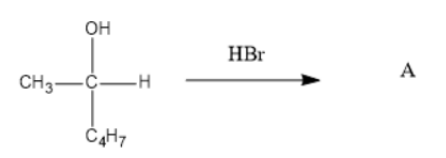

Answer
507k+ views
Hint :The reaction of Hydrogen Bromide which is an electron rich compound with an alkyl alcohol which is a leaving group. This is a type of nucleophilic substitution reaction. The product formed will be an alkyl hydrogen bromide along with water as a by-product.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a type of where leaving group which acquires an electron pair and leaves from the carbon due to presence of an electron rich compound which replaces this leaving group. The type of nucleophilic reaction that undergoes in the above reaction is nucleophilic substitution bimolecular mechanism i.e. $ {S_N}2 $ .
The order of alcohol relative reactivity is $ {3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } $ and the order of hydrogen halide is as follow: $ HI > HBr > HCl > HF $
In $ HI $ the iodide particle greatly favours the nucleophilic reaction than the bromide and chloride.
The alcohol provided in the question is secondary alcohol. When an alcohol is reacted with hydrogen halide it undergoes a nucleophilic reaction. The primary and secondary alcohol undergoes $ {S_N}2 $ .
The reaction is as follow:
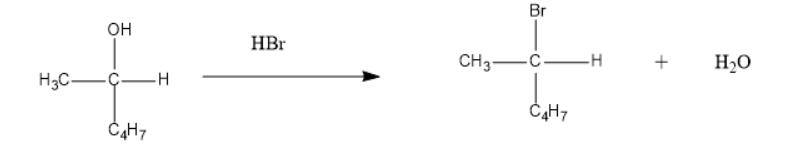
In the above reaction the breaking of bond at the one end and formation or making of bond occurs simultaneously. Therefore this $ {S_N}2 $ is a single step process and the rate of reaction depends on both the concentration of substrate as well as the nucleophile.
In addition to that the bromine atom being the electron rich compound replaces the leaving group which is a hydroxyl in this reaction.
Note :
Though primary and secondary alcohol undergoes nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reaction but tertiary alcohols nucleophilic unimolecular reaction more readily undergoes this reaction due to more crowding of the alkyl group.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is a type of where leaving group which acquires an electron pair and leaves from the carbon due to presence of an electron rich compound which replaces this leaving group. The type of nucleophilic reaction that undergoes in the above reaction is nucleophilic substitution bimolecular mechanism i.e. $ {S_N}2 $ .
The order of alcohol relative reactivity is $ {3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } $ and the order of hydrogen halide is as follow: $ HI > HBr > HCl > HF $
In $ HI $ the iodide particle greatly favours the nucleophilic reaction than the bromide and chloride.
The alcohol provided in the question is secondary alcohol. When an alcohol is reacted with hydrogen halide it undergoes a nucleophilic reaction. The primary and secondary alcohol undergoes $ {S_N}2 $ .
The reaction is as follow:

In the above reaction the breaking of bond at the one end and formation or making of bond occurs simultaneously. Therefore this $ {S_N}2 $ is a single step process and the rate of reaction depends on both the concentration of substrate as well as the nucleophile.
In addition to that the bromine atom being the electron rich compound replaces the leaving group which is a hydroxyl in this reaction.
Note :
Though primary and secondary alcohol undergoes nucleophilic substitution bimolecular reaction but tertiary alcohols nucleophilic unimolecular reaction more readily undergoes this reaction due to more crowding of the alkyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




