
What is Polymorphism in Lysosome?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: Cell organelles as we know are the components of a cell. They are useful for performing different activities of the cell just like the organ system in the body. Cells perform different activities like- cell repair, blood formation, repair damaged tissues etc. cells have various components including plasma membrane, chromosomes, cell organelles.
Complete explanation:
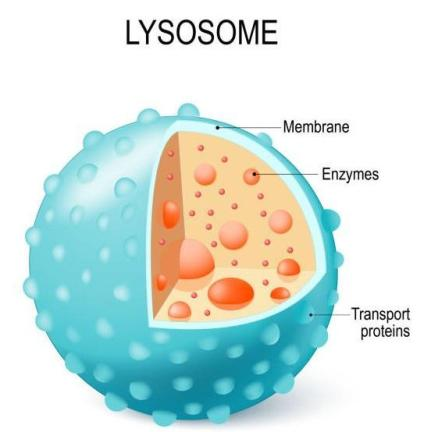
Lysosomes are nothing but suicidal bags of cells as they burst and destroy all the metabolic wastes of the cell produced during or throughout the cell activities. Polymorphism is defined as the structure which has different forms or morphology that is known as polymorphism. Cell organelles also possess polymorphism. It is an important aspect of the organelle.
Various Polymorphism forms are being identified by the lysozyme organelle such as- primary lysosome, secondary lysosome, residual bodies and autophagic vacuoles.
Primary lysosomes are the first Polymorphism structures, they are released from vesicles like Golgi apparatus: Golgi bodies are stained reticular structures present near the nucleus. They consist of flat, disc-shaped sacs or cisternae. They are stacked parallel to each other. Many cisternae are present in Golgi complex.
Secondary lysosome is formed from the combination of the primary lysosome and the Pinosome. Their major function includes digesting the food compartments and contracting digestive particles.
Note:
As we discussed various organelles. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organelles are 80s and 70s. ribosomes are the headquarters for the polypeptide synthesis. Hence, polypeptides are the building blocks of our body. And as cells are multicellular structures. So, it helps in all vital components in our bodies. Ribosome’s main function include protein synthesis as proteins or polypeptides are formed from the surface of ribosomal membrane. Hence, they are called the protein factory of the cell engine.
Complete explanation:
Lysosomes are nothing but suicidal bags of cells as they burst and destroy all the metabolic wastes of the cell produced during or throughout the cell activities. Polymorphism is defined as the structure which has different forms or morphology that is known as polymorphism. Cell organelles also possess polymorphism. It is an important aspect of the organelle.
Various Polymorphism forms are being identified by the lysozyme organelle such as- primary lysosome, secondary lysosome, residual bodies and autophagic vacuoles.
Primary lysosomes are the first Polymorphism structures, they are released from vesicles like Golgi apparatus: Golgi bodies are stained reticular structures present near the nucleus. They consist of flat, disc-shaped sacs or cisternae. They are stacked parallel to each other. Many cisternae are present in Golgi complex.
Secondary lysosome is formed from the combination of the primary lysosome and the Pinosome. Their major function includes digesting the food compartments and contracting digestive particles.

Note:
As we discussed various organelles. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organelles are 80s and 70s. ribosomes are the headquarters for the polypeptide synthesis. Hence, polypeptides are the building blocks of our body. And as cells are multicellular structures. So, it helps in all vital components in our bodies. Ribosome’s main function include protein synthesis as proteins or polypeptides are formed from the surface of ribosomal membrane. Hence, they are called the protein factory of the cell engine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




