
What is parallelogram?
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: In a parallelogram, any two opposite sides are parallel to each other.
\[AB\parallel DC\] and \[AD\parallel BC\]
In a parallelogram, any two opposite sides are also equal to each other.
\[AB = DC\] and \[AD = BC\]
In a parallelogram, the opposite angles are also equal to each other.
Opposite angles are angles which do not have a common side, that is
\[\angle DAB = \angle DCB\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,\angle ABC = \angle ADC\]
The special cases of parallelogram are
1. All the sides are equal to each other, then the parallelogram is called rhombus.
2. If the opposite sides are equal and all the angles are \[{90^ \circ }\](right angles), then the parallelogram is a rectangle.
3. If all the four sides are equal and all the angles are \[{90^ \circ }\](right angles), then the parallelogram is a square or rhombus.
Complete step-by-step solution:
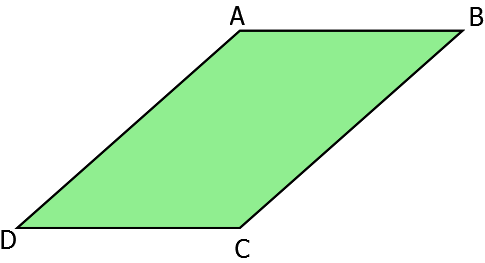
From the above figure we can see that the number of vertices is four and the number of sides are also four. This type of polygon is a quadrilateral.
Special case: If a parallelogram has one parallel side and the other two sides are non-parallel then the parallelogram is a trapezium.
Some properties of parallelogram:
The opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
The opposite angles are congruent.
The sum of the two consecutive angles are supplementary.
Two diagonals bisects each other.
If anyone of the angles is in the right angle, then all others will also be at the right angles.
Note: In a parallelogram, \[\angle A\& \angle D\] are supplementary angles because these interior angles lie on the same side of the transversal. The similar way of saying that \[\angle B\& \angle C\] are supplementary angles.
Therefore, we get \[\angle A + \angle D = {180^ \circ }\,\,\& \,\,\,\angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\].
\[AB\parallel DC\] and \[AD\parallel BC\]
In a parallelogram, any two opposite sides are also equal to each other.
\[AB = DC\] and \[AD = BC\]
In a parallelogram, the opposite angles are also equal to each other.
Opposite angles are angles which do not have a common side, that is
\[\angle DAB = \angle DCB\,\,{\text{and}}\,\,\angle ABC = \angle ADC\]
The special cases of parallelogram are
1. All the sides are equal to each other, then the parallelogram is called rhombus.
2. If the opposite sides are equal and all the angles are \[{90^ \circ }\](right angles), then the parallelogram is a rectangle.
3. If all the four sides are equal and all the angles are \[{90^ \circ }\](right angles), then the parallelogram is a square or rhombus.
Complete step-by-step solution:

From the above figure we can see that the number of vertices is four and the number of sides are also four. This type of polygon is a quadrilateral.
Special case: If a parallelogram has one parallel side and the other two sides are non-parallel then the parallelogram is a trapezium.
Some properties of parallelogram:
The opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
The opposite angles are congruent.
The sum of the two consecutive angles are supplementary.
Two diagonals bisects each other.
If anyone of the angles is in the right angle, then all others will also be at the right angles.
Note: In a parallelogram, \[\angle A\& \angle D\] are supplementary angles because these interior angles lie on the same side of the transversal. The similar way of saying that \[\angle B\& \angle C\] are supplementary angles.
Therefore, we get \[\angle A + \angle D = {180^ \circ }\,\,\& \,\,\,\angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





