
What is meiosis?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: It is a mechanism in which a single cell splits twice to create four cells that hold half of the original genetic material. These cells, sperm in males, eggs in females, are our sex cells. During this process, one cell divides twice to form four daughter cells.
Complete step by step answer:
The fusion of two gametes, each with a complete haploid set of chromosomes, includes the production of offspring by sexual reproduction. Gametes are produced from diploid specialist cells. This specialized kind of cell division decreases the chromosome number by half results in the development of haploid daughter cells. It's called meiosis, this kind of separation.
Meiosis ensures the generation of haploid phase in the life cycle of sexually reproducing species whereas fertilization restores the diploid phase. During gametogenesis in plants and animals, we come across meiosis. This leads to haploid gametes being created.
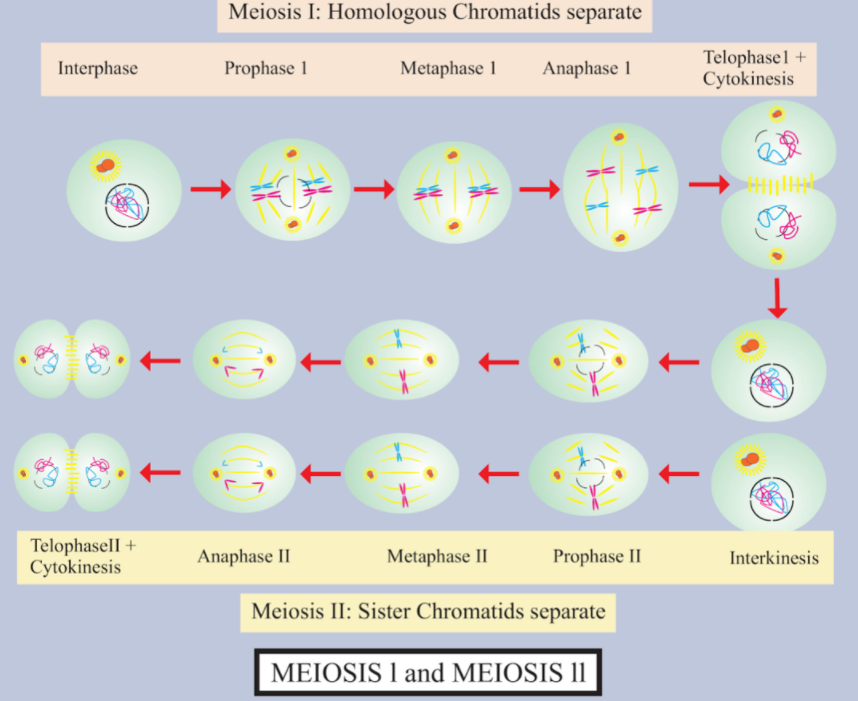
The following are the key characteristics of meiosis:
Meiosis requires two consecutive cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis I and meiosis II but just a single cycle of DNA replication.
After replication of the parental chromosomes to produce identical sister chromatids at the S stage, Meiosis I is initiated.
Meiosis requires pairing and recombination of homologous chromosomes.
At the termination of meiosis II, four haploid cells are produced.
Additional information: Mitosis is a cell replication or reproduction process through which two genetically identical daughter cells are formed by one cell. The term mitosis is strictly applied to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes, the structures carrying genetic information.
Note: A reduction of the ploidy (number of chromosomes) of the gametes from diploid (2n or two sets of 23 chromosomes) to haploid (1n or a set of 23 chromosomes) is the primary function of meiosis. In order to produce genetic diversity among the progeny, two main roles of meiosis are to halve the DNA content and to reshuffle the genetic content of the organism.
Complete step by step answer:
The fusion of two gametes, each with a complete haploid set of chromosomes, includes the production of offspring by sexual reproduction. Gametes are produced from diploid specialist cells. This specialized kind of cell division decreases the chromosome number by half results in the development of haploid daughter cells. It's called meiosis, this kind of separation.
Meiosis ensures the generation of haploid phase in the life cycle of sexually reproducing species whereas fertilization restores the diploid phase. During gametogenesis in plants and animals, we come across meiosis. This leads to haploid gametes being created.

The following are the key characteristics of meiosis:
Meiosis requires two consecutive cycles of nuclear and cell division called meiosis I and meiosis II but just a single cycle of DNA replication.
After replication of the parental chromosomes to produce identical sister chromatids at the S stage, Meiosis I is initiated.
Meiosis requires pairing and recombination of homologous chromosomes.
At the termination of meiosis II, four haploid cells are produced.
Additional information: Mitosis is a cell replication or reproduction process through which two genetically identical daughter cells are formed by one cell. The term mitosis is strictly applied to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes, the structures carrying genetic information.
Note: A reduction of the ploidy (number of chromosomes) of the gametes from diploid (2n or two sets of 23 chromosomes) to haploid (1n or a set of 23 chromosomes) is the primary function of meiosis. In order to produce genetic diversity among the progeny, two main roles of meiosis are to halve the DNA content and to reshuffle the genetic content of the organism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




