
What is meant by Hybridization?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: We have to know that, in science, orbital hybridization is the idea of blending nuclear orbitals into new cross breed orbitals (with various energies, shapes, and so on, than the part nuclear orbitals) reasonable for the matching of electrons to frame substance bonds in valence bond hypothesis.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, in a carbon particle, which structures four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital consolidates with three valence-shell p orbitals to shape four comparable $s{p^3}$ combinations, which are organized in a tetrahedral course of action around the carbon to cling to four unique molecules. Mixture orbitals are valuable in the clarification of sub-atomic math and nuclear holding properties and are evenly arranged in space. Generally crossover orbitals are framed by blending nuclear orbitals of similar energies.
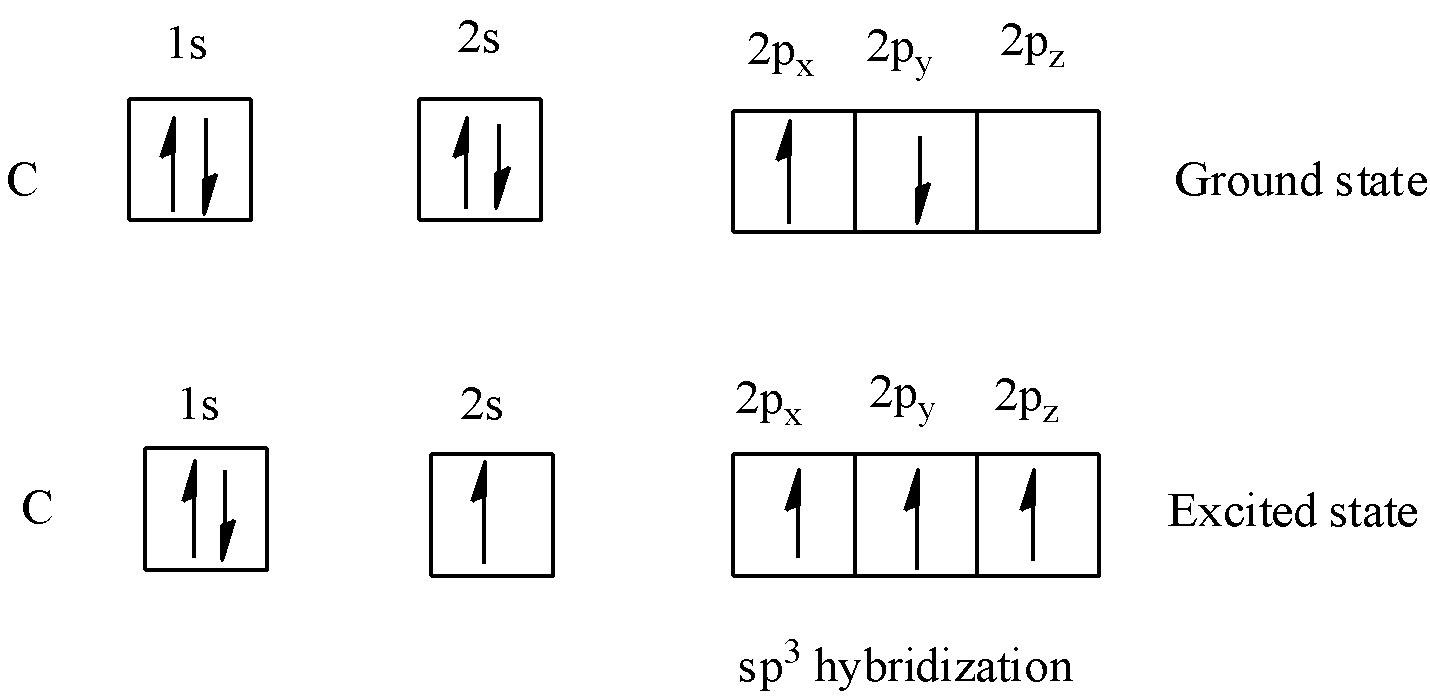
We have to know that orbitals are a model portrayal of the conduct of electrons inside particles. On account of straightforward hybridization, this guess depends on nuclear orbitals, like those acquired for the hydrogen particle, the lone nonpartisan molecule for which the Schrödinger condition can be settled precisely. In heavier iotas, like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, the nuclear orbitals utilized are the $2s$ , and $2p$ orbitals, like energized state orbitals for hydrogen.
Note:
We know that hybridization assists with clarifying particle shape, since the points between bonds are roughly equivalent to the points between cross breed orbitals. This is as opposed to valence shell electron-pair aversion hypothesis, which can be utilized to foresee sub-atomic calculation dependent on observational principles instead of on valence-bond or orbital speculations.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, in a carbon particle, which structures four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital consolidates with three valence-shell p orbitals to shape four comparable $s{p^3}$ combinations, which are organized in a tetrahedral course of action around the carbon to cling to four unique molecules. Mixture orbitals are valuable in the clarification of sub-atomic math and nuclear holding properties and are evenly arranged in space. Generally crossover orbitals are framed by blending nuclear orbitals of similar energies.

We have to know that orbitals are a model portrayal of the conduct of electrons inside particles. On account of straightforward hybridization, this guess depends on nuclear orbitals, like those acquired for the hydrogen particle, the lone nonpartisan molecule for which the Schrödinger condition can be settled precisely. In heavier iotas, like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, the nuclear orbitals utilized are the $2s$ , and $2p$ orbitals, like energized state orbitals for hydrogen.
Note:
We know that hybridization assists with clarifying particle shape, since the points between bonds are roughly equivalent to the points between cross breed orbitals. This is as opposed to valence shell electron-pair aversion hypothesis, which can be utilized to foresee sub-atomic calculation dependent on observational principles instead of on valence-bond or orbital speculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




