
What is an apoplast?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: The word apoplast was developed by the German scientist E. Münch in 1930. According to him, the apoplast was a dead component in a plant body and it was more of an intercellular space in a plant that was only involved in water and nutrient transfer.
Complete answer:
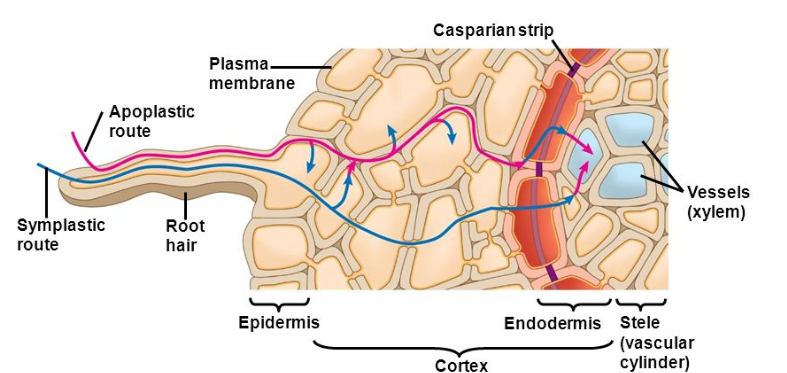
Also known as the key player in plant survival, the apoplast is also known as the intercellular space filled with gas and water, which is enclosed between cell membranes, the interfibrillar and intermicellar space of the cell walls, along with the xylem which extends to the rhizoplane and cuticle of the plants outer surface. An enormous variety of functions are performed by the apoplasm because its dynamic nature allows for a large number of important reactions to take place inside it. This includes nutrition and water transport, as well as the synthesis of cell wall components and other compounds.
It is in the apoplast, where after the cell wall components are liberated from the plasma membrane, then only the cell wall synthesis occurs. As a result, cell wall polymers are modified, degraded, and rearranged, depending on the state of cell growth and differentiation. The entire mechanism that occurs in the apoplast is considered as a passive absorption and this pathway is essential as it permits a solvent to diffuse through the tissue or an organ in a plant.
Note:
Symplast is located on the inside of the plasma membrane of a plant, water and low-molecular-weight solutes are allowed to readily flow through. Each symplast cell has several nuclei. Within the cytoplast or vacuoles of surrounding cells, water travels via a channel called the symplast pathway To proceed, however, water must pass through the Casparian strip, which forms an impassable barrier near the xylem.
Complete answer:
Also known as the key player in plant survival, the apoplast is also known as the intercellular space filled with gas and water, which is enclosed between cell membranes, the interfibrillar and intermicellar space of the cell walls, along with the xylem which extends to the rhizoplane and cuticle of the plants outer surface. An enormous variety of functions are performed by the apoplasm because its dynamic nature allows for a large number of important reactions to take place inside it. This includes nutrition and water transport, as well as the synthesis of cell wall components and other compounds.
It is in the apoplast, where after the cell wall components are liberated from the plasma membrane, then only the cell wall synthesis occurs. As a result, cell wall polymers are modified, degraded, and rearranged, depending on the state of cell growth and differentiation. The entire mechanism that occurs in the apoplast is considered as a passive absorption and this pathway is essential as it permits a solvent to diffuse through the tissue or an organ in a plant.
Note:
Symplast is located on the inside of the plasma membrane of a plant, water and low-molecular-weight solutes are allowed to readily flow through. Each symplast cell has several nuclei. Within the cytoplast or vacuoles of surrounding cells, water travels via a channel called the symplast pathway To proceed, however, water must pass through the Casparian strip, which forms an impassable barrier near the xylem.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




