
What is an allosteric enzyme?
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint: They are the enzymes that help in the change in the structure of the molecule when it is bound to the molecule. This also changes the affinity of the binding of the molecules. It helps in the process of metabolism.
Complete answer:
An allosteric enzyme is an enzyme that binds to the allosteric modulator that changes the conformational structure and when binds to the ligands then it results in the change in the structure of the ligand. This concept is called the allosteric concept which affects the binding of the ligand at one point and also affects the binding of the ligand at another point. This process helps in the functioning of the various metabolism regulation, cell signaling along with various other biological processes. In biochemistry, allostery is found to be the binding of the protein to an effector molecule instead of the active site of the enzyme.
The point at which the effector molecule binds is called the allosteric site. At this site, the protein binds to the effector molecule and may result in the conformational change and the change in the structure of the proteins. Those effectors that increase the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric activators, while those effectors that decrease the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric inhibitors. An example of allosteric regulation is the ability of the cell to adjust the active site. The example of allosteric enzymes are glycogen phosphorylase, aspartate transcarbamylase, phosphofructokinase, etc are used during the various metabolic pathways.
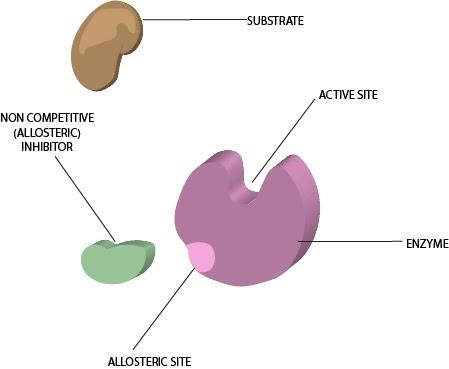
Allosteric Enzyme
Note:
The term allostery is derived from the Greek word allos, meaning ‘other’ and stereos, meaning ‘object’. This indicates that the active site and the regulatory site of an allosteric protein are different from each other. The first crystal structure of the allosteric enzyme was introduced by Max Perutz.
Complete answer:
An allosteric enzyme is an enzyme that binds to the allosteric modulator that changes the conformational structure and when binds to the ligands then it results in the change in the structure of the ligand. This concept is called the allosteric concept which affects the binding of the ligand at one point and also affects the binding of the ligand at another point. This process helps in the functioning of the various metabolism regulation, cell signaling along with various other biological processes. In biochemistry, allostery is found to be the binding of the protein to an effector molecule instead of the active site of the enzyme.
The point at which the effector molecule binds is called the allosteric site. At this site, the protein binds to the effector molecule and may result in the conformational change and the change in the structure of the proteins. Those effectors that increase the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric activators, while those effectors that decrease the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric inhibitors. An example of allosteric regulation is the ability of the cell to adjust the active site. The example of allosteric enzymes are glycogen phosphorylase, aspartate transcarbamylase, phosphofructokinase, etc are used during the various metabolic pathways.

Allosteric Enzyme
Note:
The term allostery is derived from the Greek word allos, meaning ‘other’ and stereos, meaning ‘object’. This indicates that the active site and the regulatory site of an allosteric protein are different from each other. The first crystal structure of the allosteric enzyme was introduced by Max Perutz.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




