
What is a reflex arc?
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint: Sensory, motor, and relay neurons are the three main types of neuron.
In a reflex action, these many types of neurons operate together. A reflex action is an automatic (involuntary) and quick reaction to a stimulus that protects the body from potentially dangerous situations like touching something hot. Many species' existence depends on their ability to react quickly. This typical process is followed by a reflex action, which does not involve the conscious section of the brain. This is why there is such a quick response.
Complete answer:
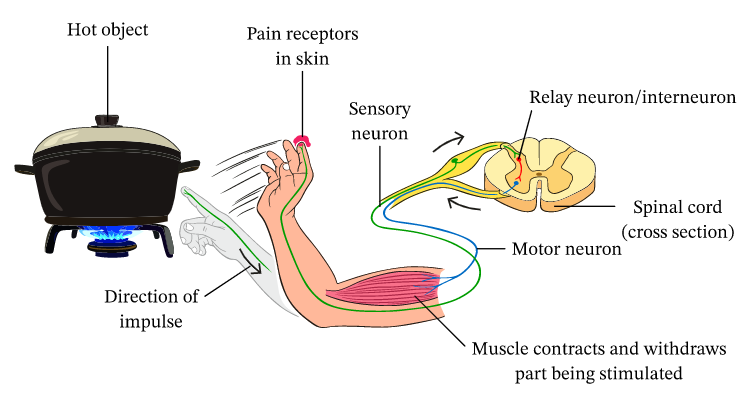
The reflex arc is the neural pathway that reflex activity follows. For example when we inadvertently touch something hot, we experience the reaction arc. The receptor detects the change in temperature first. The electrical impulses are then delivered to the relay neuron in the spinal cord. Sensory neurons bridge the gap between motor neurons and sensory neurons. The motor neuron sends electrical impulses to an effector. The effector generates a response.
The reflex arc is a sort of neural circuit that starts with a sensory neuron at a receptor and finishes with a motor neuron at an effector (for example, a pain receptor in the fingertip) (e.g., a skeletal muscle).
Most sensory neurons in vertebrates synapse in the spinal cord rather than passing directly into the brain. This enables faster reflex actions by engaging spinal motor neurons without having to wait for messages to go to the brain.
Receptors, sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons, and muscles are the five primary components of most reflex arcs. Interneurons are not used by all reflexes. Some do not employ interneurons and connect sensory neurons directly to motor neurons.
Note:
The autonomic reflex arc, which affects inner organs, and the somatic reflex arc, which affects muscles, are the two types of reflex arcs. Monosynaptic reflex arcs are those that have only two neurons, one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron.
The presence of a single chemical synapse is referred to as monosynaptic. Brief stimulation of the muscle spindle causes the agonist or effector muscle to contract in peripheral muscle reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex).
In a reflex action, these many types of neurons operate together. A reflex action is an automatic (involuntary) and quick reaction to a stimulus that protects the body from potentially dangerous situations like touching something hot. Many species' existence depends on their ability to react quickly. This typical process is followed by a reflex action, which does not involve the conscious section of the brain. This is why there is such a quick response.
Complete answer:
The reflex arc is the neural pathway that reflex activity follows. For example when we inadvertently touch something hot, we experience the reaction arc. The receptor detects the change in temperature first. The electrical impulses are then delivered to the relay neuron in the spinal cord. Sensory neurons bridge the gap between motor neurons and sensory neurons. The motor neuron sends electrical impulses to an effector. The effector generates a response.
The reflex arc is a sort of neural circuit that starts with a sensory neuron at a receptor and finishes with a motor neuron at an effector (for example, a pain receptor in the fingertip) (e.g., a skeletal muscle).
Most sensory neurons in vertebrates synapse in the spinal cord rather than passing directly into the brain. This enables faster reflex actions by engaging spinal motor neurons without having to wait for messages to go to the brain.
Receptors, sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons, and muscles are the five primary components of most reflex arcs. Interneurons are not used by all reflexes. Some do not employ interneurons and connect sensory neurons directly to motor neurons.

Note:
The autonomic reflex arc, which affects inner organs, and the somatic reflex arc, which affects muscles, are the two types of reflex arcs. Monosynaptic reflex arcs are those that have only two neurons, one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron.
The presence of a single chemical synapse is referred to as monosynaptic. Brief stimulation of the muscle spindle causes the agonist or effector muscle to contract in peripheral muscle reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




