
What is a parallel circuit?
Answer
503.7k+ views
Hint: A parallel circuit has branches that divide the current so that just a portion of it passes through each branch. In a parallel circuit, the voltage, or potential difference, between each branch is the same, but the currents may differ.
Complete answer:
An electrical circuit is a collection of devices used for energy storage, transmission, and conversion. One or more sources supply energy to a circuit, and one or more sinks remove it. Energy is converted from thermal, chemical, electromagnetic, or mechanical form to electrical form in the sources; the process is reversed in the sinks. Energy is carried in an electrical circuit through the use of electrical charge and the medium of magnetic and electric fields. Parallel and series circuits are two different types of circuits.
We are going to discuss parallel circuits: a parallel circuit is one in which many resistances are connected across one another in such a way that one terminal of each resistance is connected to form a junction point, and the remaining end is also connected to make another point.
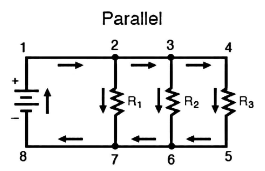
Parallel Circuits Have the Following Characteristics:
1. A similar potential difference is shared by all resistances at the same time.
2. The total current is divided into the number of parallel routes equal to the number of resistances. The sum of all the individual currents is always the aggregate current.
\[{\mathbf{I}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{1}}\;}} + {\text{ }}{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{2}}\;}} + \;{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{3}}\;}} + \; \ldots \ldots + \;{{\mathbf{I}}_{\mathbf{n}}}\]
3. The reciprocal of a parallel circuit's equivalent resistance is equal to the total of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
4. The smallest of all resistances is the comparable resistance.
\[{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{1}}},{\text{ }}{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{2}}},{\text{ }} \ldots ..,{\text{ }}{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{n}}}\]
5. The equivalent conductance is the result of adding the single conductance mathematically.
Note: The parallel circuit is the most common type of electrical circuit used in houses and equipment. It generates a considerably more stable and efficient power system than would otherwise be conceivable since it allows more than one channel for a current to travel through to a device. The parallel circuit has numerous applications.
Complete answer:
An electrical circuit is a collection of devices used for energy storage, transmission, and conversion. One or more sources supply energy to a circuit, and one or more sinks remove it. Energy is converted from thermal, chemical, electromagnetic, or mechanical form to electrical form in the sources; the process is reversed in the sinks. Energy is carried in an electrical circuit through the use of electrical charge and the medium of magnetic and electric fields. Parallel and series circuits are two different types of circuits.
We are going to discuss parallel circuits: a parallel circuit is one in which many resistances are connected across one another in such a way that one terminal of each resistance is connected to form a junction point, and the remaining end is also connected to make another point.

Parallel Circuits Have the Following Characteristics:
1. A similar potential difference is shared by all resistances at the same time.
2. The total current is divided into the number of parallel routes equal to the number of resistances. The sum of all the individual currents is always the aggregate current.
\[{\mathbf{I}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{1}}\;}} + {\text{ }}{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{2}}\;}} + \;{{\mathbf{I}}_{{\mathbf{3}}\;}} + \; \ldots \ldots + \;{{\mathbf{I}}_{\mathbf{n}}}\]
3. The reciprocal of a parallel circuit's equivalent resistance is equal to the total of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
4. The smallest of all resistances is the comparable resistance.
\[{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{1}}},{\text{ }}{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{2}}},{\text{ }} \ldots ..,{\text{ }}{\mathbf{R}}\; < \;{{\mathbf{R}}_{\mathbf{n}}}\]
5. The equivalent conductance is the result of adding the single conductance mathematically.
Note: The parallel circuit is the most common type of electrical circuit used in houses and equipment. It generates a considerably more stable and efficient power system than would otherwise be conceivable since it allows more than one channel for a current to travel through to a device. The parallel circuit has numerous applications.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




