
What is A in the given diagram?
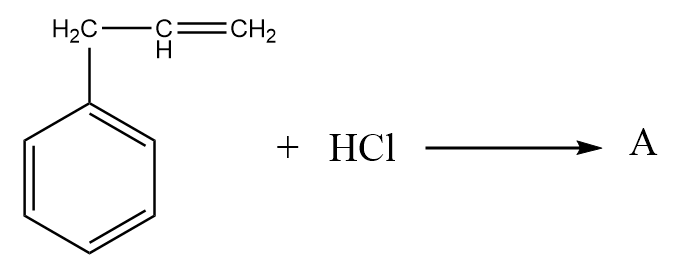

Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Electrophilic addition reaction: It is a chemical reaction in which a reactant is initially attacked by an electrophile and then the final product is the addition of atoms or ions over multiple bonds. These reactions are mainly observed in unsaturated compounds i.e., alkenes and alkynes.
Complete answer:
The given reaction follows the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction which is discussed as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of $HCl$:
The $HCl$ molecule is dissociated into hydrogen ion and chloride ion as follows:
$HCl\rightleftharpoons {{H}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}$
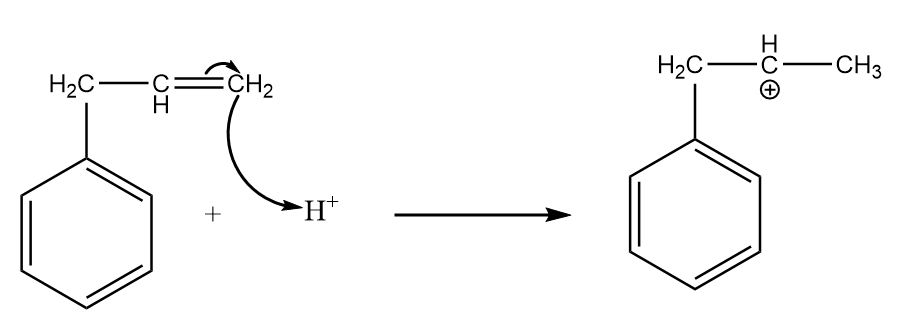
Step-2: Attack of ${{H}^{+}}$ on the given reactant i.e., $3-$phenylpropene:
In the given compound,
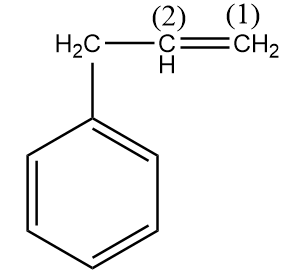
Carbon-(1) is more electronegative than carbon-(2) because a $C{{H}_{2}}$ group is present on carbon-(2) which decreases its electronegativity due to the $+I$ effect. Hence, ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will attack on the carbon-(1) and formation of a carbocation will take place as an intermediate.
The reaction is as follows:
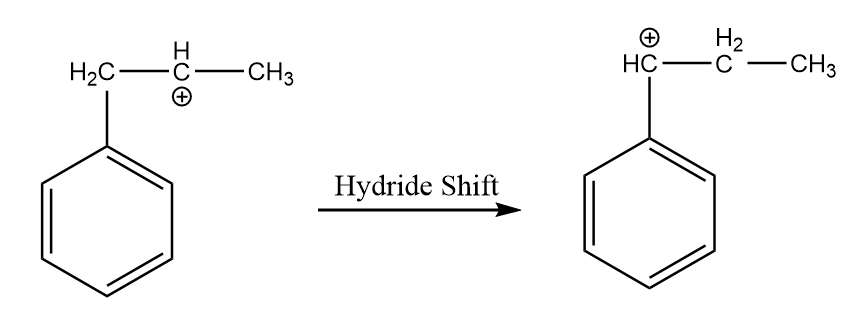
Step-3: Hydride shift of the carbocation:
As the positive ion will be more stable on the carbon atom which is directly attached to the benzene ring because of resonance. So, the hydride shift of the carbocation will take place to form a more stable intermediate. The reaction is as follows:
Step-4: Attack of chlorine ion:
The chlorine ion attacks the most stable carbocation intermediate and the major product is formed after the reaction as follows:
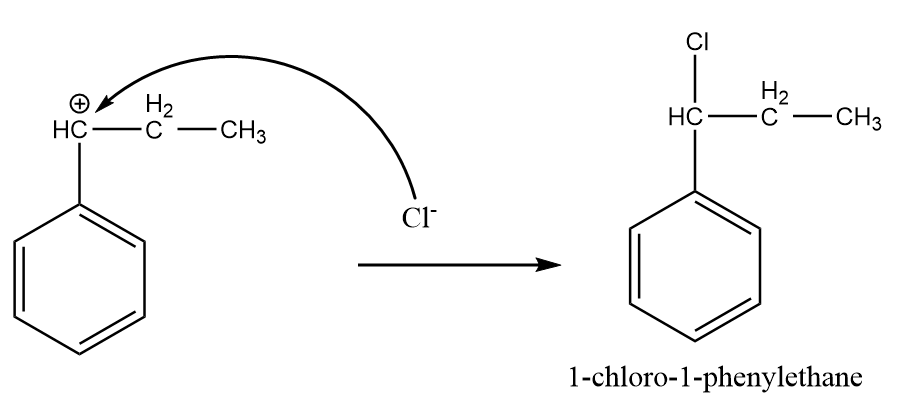
Hence, the major product formed i.e., A is 1-chloro-1-phenylethane.
Note:
It is important to note that, in this case hydride shifts take place because of the presence of a benzene ring which provides extra stability to the carbocation due to resonance. In general cases, the hydride shift takes place to the carbon atom with higher degree.
Complete answer:
The given reaction follows the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction which is discussed as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of $HCl$:
The $HCl$ molecule is dissociated into hydrogen ion and chloride ion as follows:
$HCl\rightleftharpoons {{H}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}}$
Step-2: Attack of ${{H}^{+}}$ on the given reactant i.e., $3-$phenylpropene:
In the given compound,

Carbon-(1) is more electronegative than carbon-(2) because a $C{{H}_{2}}$ group is present on carbon-(2) which decreases its electronegativity due to the $+I$ effect. Hence, ${{H}^{+}}$ ion will attack on the carbon-(1) and formation of a carbocation will take place as an intermediate.
The reaction is as follows:

Step-3: Hydride shift of the carbocation:
As the positive ion will be more stable on the carbon atom which is directly attached to the benzene ring because of resonance. So, the hydride shift of the carbocation will take place to form a more stable intermediate. The reaction is as follows:

Step-4: Attack of chlorine ion:
The chlorine ion attacks the most stable carbocation intermediate and the major product is formed after the reaction as follows:

Hence, the major product formed i.e., A is 1-chloro-1-phenylethane.
Note:
It is important to note that, in this case hydride shifts take place because of the presence of a benzene ring which provides extra stability to the carbocation due to resonance. In general cases, the hydride shift takes place to the carbon atom with higher degree.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




