
What is a delocalized bond?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: The word delocalized bond means the bond is not going to get stability. Means the bond will be in continuous motion due to the sharing atoms. Generally the compounds which consist of conjugated double or triple will show the delocalization of the bond.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is about the delocalized bond.
- There are two types of compounds which show the delocalization of the bonds.
- They are metals and the organic compounds which are in conjugation.
- Coming to the concept of metals, metals shows the property of electrical and thermal conductivity due the presence of the delocalized outermost electrons in the atoms.
- Coming to the concept of organic compound.
- Take an example of benzene. It contains three double bonds in its structure and is delocalized between the six carbon atoms and shows the following resonance structure.
- The resonance structures of benzene are as follows.
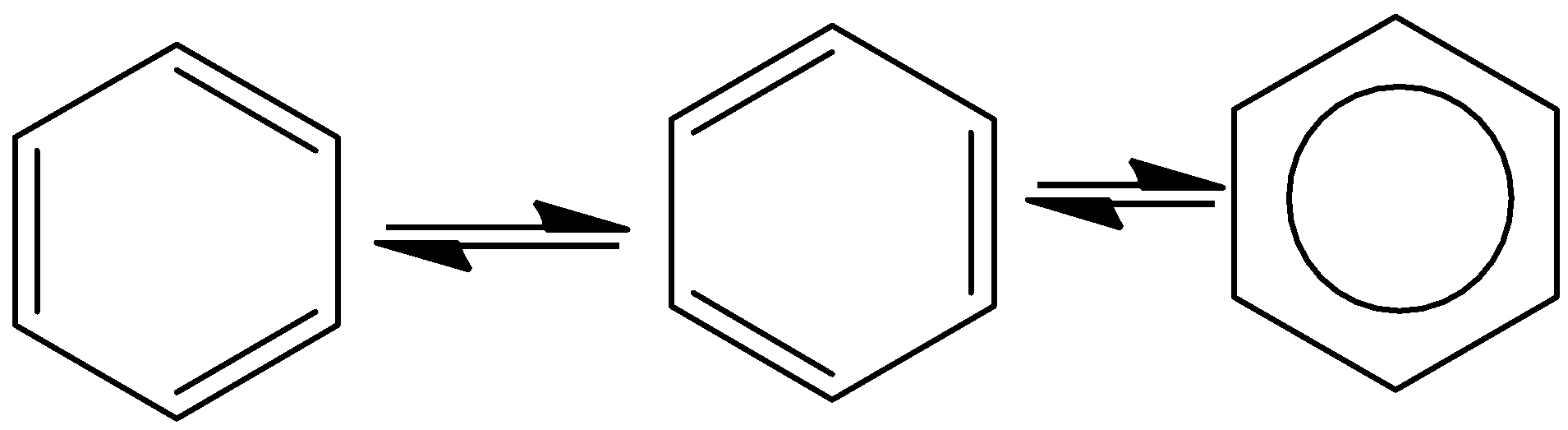
- The presence of the delocalized bonds is reasonable for the formation of the resonance structures in the organic compound especially in the case of benzene.
- Delocalization is not about the bond it is a property of the pi bond.
Note:
Due to the delocalization of the double bonds in the benzene ring the aromatic character of the benzene molecule exists. A lot of different molecules in nature existed in the form of containing delocalization like keto-enol tautomerism etc. The delocalized electrons do not belong to any atom in the molecule.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is about the delocalized bond.
- There are two types of compounds which show the delocalization of the bonds.
- They are metals and the organic compounds which are in conjugation.
- Coming to the concept of metals, metals shows the property of electrical and thermal conductivity due the presence of the delocalized outermost electrons in the atoms.
- Coming to the concept of organic compound.
- Take an example of benzene. It contains three double bonds in its structure and is delocalized between the six carbon atoms and shows the following resonance structure.
- The resonance structures of benzene are as follows.

- The presence of the delocalized bonds is reasonable for the formation of the resonance structures in the organic compound especially in the case of benzene.
- Delocalization is not about the bond it is a property of the pi bond.
Note:
Due to the delocalization of the double bonds in the benzene ring the aromatic character of the benzene molecule exists. A lot of different molecules in nature existed in the form of containing delocalization like keto-enol tautomerism etc. The delocalized electrons do not belong to any atom in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




