
What is a chelating agent?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Chelation is a type of bonding in which chemical substances (ions or molecules) are bonded to a central metal ion by two or more coordinate bonds. Coordinate bonds are the type of covalent bonds in which both electrons are given by one atom and shared by both atoms. During the chelation process, a complex ring type structure is formed between the central metal ion and donor molecules.
Complete answer:
Chelating ligands are generally Lewis bases which have available lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. These cheating agents should have at least two or more pairs of available electrons for coordinate bonding in order to make complex ring-like structures. This illustrated in the following diagram
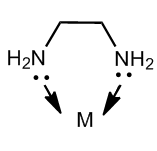
The above diagram shows ethylene diamine as a chelating agent which has two donor sites i.e. nitrogen. Therefore, this ligand is capable of forming two coordinate bonds with a central metal atom and forming a five membered ring complex.
Additional information: Coordination bonds are also called dative bonds. Chelating agents have several practical applications including reducing the blood level of injurious heavy metals.
Note:
It is important to note that chelates are generally lewis bases which have available lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. These cheating agents should have at least two or more pairs of available electrons for coordinate bonding in order to make complex ring-like structures. Ethylene diamine is one example of a chelating agent.
Complete answer:
Chelating ligands are generally Lewis bases which have available lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. These cheating agents should have at least two or more pairs of available electrons for coordinate bonding in order to make complex ring-like structures. This illustrated in the following diagram

The above diagram shows ethylene diamine as a chelating agent which has two donor sites i.e. nitrogen. Therefore, this ligand is capable of forming two coordinate bonds with a central metal atom and forming a five membered ring complex.
Additional information: Coordination bonds are also called dative bonds. Chelating agents have several practical applications including reducing the blood level of injurious heavy metals.
Note:
It is important to note that chelates are generally lewis bases which have available lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. These cheating agents should have at least two or more pairs of available electrons for coordinate bonding in order to make complex ring-like structures. Ethylene diamine is one example of a chelating agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




