
What is \[|| < 4,9, - 8 > ||\] ?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, first we will understand the concept of vector and the magnitude of a vector. Then we will understand the meaning of the double vertical lines on both sides and finally we will be able to find the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
A vector quantity is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. The length of the vector represents the magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. We are well aware of the fact that a vector is an object which has magnitudes as well as it has a direction. So, if we have to find the magnitude of a vector then we have to calculate the length of any given vector. The various quantities such as velocity, displacement and force are examples of vector quantities.
The vector given in this question can be represented as,
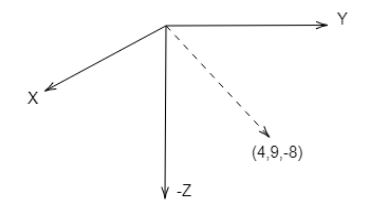
In this particular question, the double vertical lines represent that in this question, we have to find the magnitude of this vector. We know that the magnitude of a vector is the square root of the sum of the squares of all the three components of a vector. So, the magnitude of this vector is,
$l = \sqrt {{{(4)}^2} + {{(9)}^2} + {{( - 8)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {16 + 81 + 64} $
On further solving this, we get,
$l = \sqrt {161} $
On finding the approximate value of the above root, we get,
$\therefore l = 12.7\,units$
Therefore, the magnitude or the length of this vector is $l = 12.7\,units$.
Note: It is important to note that in this question, although the vector is present in three dimensions, we have taken the square root, and not the cube root. When the vector is in two dimensions then also we take the square root. So, it does not matter whether the vector is in two dimensions or in three dimensions, we always take square roots.
Complete step by step answer:
A vector quantity is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. The length of the vector represents the magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction. We are well aware of the fact that a vector is an object which has magnitudes as well as it has a direction. So, if we have to find the magnitude of a vector then we have to calculate the length of any given vector. The various quantities such as velocity, displacement and force are examples of vector quantities.
The vector given in this question can be represented as,

In this particular question, the double vertical lines represent that in this question, we have to find the magnitude of this vector. We know that the magnitude of a vector is the square root of the sum of the squares of all the three components of a vector. So, the magnitude of this vector is,
$l = \sqrt {{{(4)}^2} + {{(9)}^2} + {{( - 8)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {16 + 81 + 64} $
On further solving this, we get,
$l = \sqrt {161} $
On finding the approximate value of the above root, we get,
$\therefore l = 12.7\,units$
Therefore, the magnitude or the length of this vector is $l = 12.7\,units$.
Note: It is important to note that in this question, although the vector is present in three dimensions, we have taken the square root, and not the cube root. When the vector is in two dimensions then also we take the square root. So, it does not matter whether the vector is in two dimensions or in three dimensions, we always take square roots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




