
What are plasmodesmata? Explain?
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Plasmodesmata are membrane channels that are coaxial that cross walls of plant cells. They link the cytoplasm, plasma membranes, and endoplasmic reticulum of cells. They allow direct communication of cytoplasmic cell-to-cell of both small molecules and macromolecules. Plasmodesmata enables transportation and communication between the cells.
Complete step by step answer:
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels that are evolved in several lineages and have structures that include members of Phaeophyceae, Coleochaetales, etc. The cell is surrounded by a polysaccharide cell wall and neighboring cells are separated by a pair of cell walls. Middle lamella intervenes and forms an extracellular domain known as the apoplast. Plasmodesmata enable direct transport of substances as the cell wall is permeable to small soluble proteins and other solutes. Plasmodesmata are of two forms i.e. primary plasmodesmata which are formed during cell division and I secondary plasmodesmata which are formed between mature cells. They allowed the molecules through the symplastic pathway to travel between the plant cells. The gap junction and membrane nanotubes interconnect animal cells and stromules to form between plastids in plant cells. Plant cell contains 1000 – 100000 plasmodesmata connecting with adjacent cells. They are 50-60 nanometres in India diameter and are constructed of three main layers i.e. cytoplasmic sleeve, plasma membrane, and the desmotubule.
Additional information: The primary plasmodesmata are formed of the endoplasmic reticulum and are trapped across the middle lamella. The new cell wall is synthesized between two newly divided plant cells. They are the cytoplasmic connections between the cell and can also be inserted into existing non-dividing cells and cell walls. The fall of the plasmodesmata is not thick and depresses Earth in areas which are known as pits formed in the walls. It transports proteins, messenger RNA, viroids, viral genomes, and short interfering RNA. They are used by cells in phloem and symplastic transport which is used to regulate sieve tubes by companion cells. Plasmodesmata causes negative effects like the spread of viruses. It contains some cytoskeletal components such as actin microfilaments, myosin proteins, and microtubules. The viral movement proteins to plasmodesmata are transported by actin microfilaments which allow for Cell to cell transport. Myosin directs the viral cargoes to plasmodesmata and the microtubules transport viral RNA.
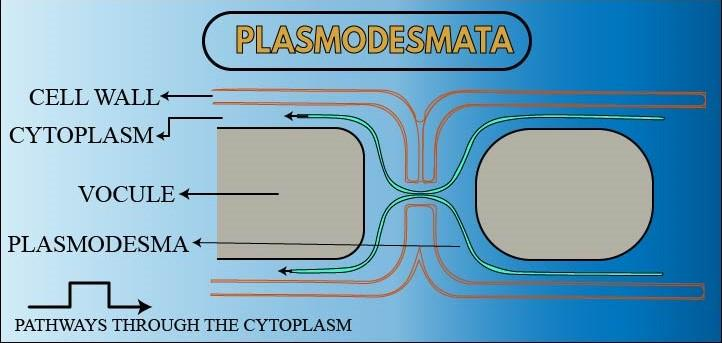
Note: Plasmodesmata impacts on auxin-induced phototropism and lateral root initiation. Plasmodesmata were discovered by Edward Tang in the higher plants in the late 1880s. Later it was found that it is present in all green plants. The origin of plasmodesmata in the endoplasmic reticulum. They are dynamic channels. They are the holes in the cell wall between the cells and allow them to be interconnected.
Complete step by step answer:
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels that are evolved in several lineages and have structures that include members of Phaeophyceae, Coleochaetales, etc. The cell is surrounded by a polysaccharide cell wall and neighboring cells are separated by a pair of cell walls. Middle lamella intervenes and forms an extracellular domain known as the apoplast. Plasmodesmata enable direct transport of substances as the cell wall is permeable to small soluble proteins and other solutes. Plasmodesmata are of two forms i.e. primary plasmodesmata which are formed during cell division and I secondary plasmodesmata which are formed between mature cells. They allowed the molecules through the symplastic pathway to travel between the plant cells. The gap junction and membrane nanotubes interconnect animal cells and stromules to form between plastids in plant cells. Plant cell contains 1000 – 100000 plasmodesmata connecting with adjacent cells. They are 50-60 nanometres in India diameter and are constructed of three main layers i.e. cytoplasmic sleeve, plasma membrane, and the desmotubule.
Additional information: The primary plasmodesmata are formed of the endoplasmic reticulum and are trapped across the middle lamella. The new cell wall is synthesized between two newly divided plant cells. They are the cytoplasmic connections between the cell and can also be inserted into existing non-dividing cells and cell walls. The fall of the plasmodesmata is not thick and depresses Earth in areas which are known as pits formed in the walls. It transports proteins, messenger RNA, viroids, viral genomes, and short interfering RNA. They are used by cells in phloem and symplastic transport which is used to regulate sieve tubes by companion cells. Plasmodesmata causes negative effects like the spread of viruses. It contains some cytoskeletal components such as actin microfilaments, myosin proteins, and microtubules. The viral movement proteins to plasmodesmata are transported by actin microfilaments which allow for Cell to cell transport. Myosin directs the viral cargoes to plasmodesmata and the microtubules transport viral RNA.

Note: Plasmodesmata impacts on auxin-induced phototropism and lateral root initiation. Plasmodesmata were discovered by Edward Tang in the higher plants in the late 1880s. Later it was found that it is present in all green plants. The origin of plasmodesmata in the endoplasmic reticulum. They are dynamic channels. They are the holes in the cell wall between the cells and allow them to be interconnected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




